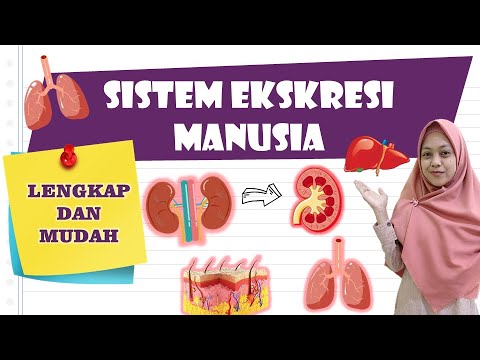
Struktur dan Fungsi Organ Ginjal Pada Sistem Ekskresi Manusia Serta Proses Pembentukan Urine
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of the human excretory system, focusing particularly on the kidneys. It describes the process of waste elimination, explaining how the kidneys filter blood and form urine in three stages: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. The video also covers the structure of the kidneys, their functional units (nephrons), and the different regions of the kidney involved in urine production. Additionally, the journey of urine from the kidneys to the bladder is discussed, highlighting the role of the ureter and bladder in urine storage and excretion.
Takeaways
- 😀 The excretory system in humans helps eliminate waste products from the body to prevent toxicity and potential organ damage.
- 😀 Key excretory organs in humans include the kidneys, skin, lungs, and liver.
- 😀 The kidneys filter blood to remove metabolic waste products and regulate fluid balance.
- 😀 The kidneys are located on both sides of the spine and are shaped like kidney beans.
- 😀 Blood enters the kidneys through large arteries and exits through veins. The kidneys have three distinct layers: the cortex, medulla, and renal pelvis.
- 😀 Each kidney contains about a million nephrons, which are the functional units responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
- 😀 The nephron consists of the Malpighian body (glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule) and tubules that filter and reabsorb essential substances.
- 😀 Filtration begins when blood flows through the glomerulus, where pressure forces small substances like water, urea, glucose, amino acids, and ions out of the blood into the Bowman’s capsule.
- 😀 Reabsorption occurs in the proximal tubule, where substances like glucose, amino acids, and ions are reabsorbed back into the blood, while urea remains mostly in the filtrate.
- 😀 The secondary urine, formed after reabsorption, contains water, salts, urea, and urobilin, which gives urine its yellow color and characteristic odor.
- 😀 Urine travels through the Loop of Henle and distal tubule, where additional reabsorption of water and salts takes place. Finally, excess waste is secreted into the urine.
- 😀 The final urine is collected in the renal pelvis, travels through the ureters to the bladder, and is expelled through the urethra when the bladder is full, prompted by muscle contractions.
Q & A
What is excretion and why is it necessary for the human body?
-Excretion is the process of eliminating waste materials produced by the body’s metabolism. It is necessary to prevent these waste products from accumulating and potentially poisoning the body, which could damage organs and lead to death.
Which organs are involved in the human excretory system?
-The human excretory system involves several organs: the kidneys, skin, lungs, and liver.
What is the function of the kidneys in the excretory system?
-The kidneys filter the blood, removing metabolic waste products from cells throughout the body. This filtration process is crucial for maintaining proper bodily function.
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
-The kidneys are located on either side of the spine, at the level of the lower back, within the abdominal cavity. The left kidney is positioned slightly higher than the right.
How is the kidney structured internally?
-The kidney consists of three main layers: the outer layer called the renal cortex, the middle layer known as the renal medulla, and the inner space called the renal pelvis.
What is a nephron and why is it important?
-A nephron is the functional and structural unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering the blood. It plays a vital role in the process of waste removal and urine formation.
What happens in the glomerulus during the filtration stage?
-In the glomerulus, blood pressure forces water and small molecules, such as urea, glucose, amino acids, and ions, through the capillary pores, beginning the filtration process. Larger substances like proteins and blood cells remain in the bloodstream.
What occurs during the reabsorption stage in the kidneys?
-During reabsorption, essential substances such as glucose, amino acids, and ions are reabsorbed from the filtrate back into the bloodstream, ensuring that the body retains valuable resources. Some water is also reabsorbed.
What is urine composed of after the reabsorption process?
-After reabsorption, the urine contains water, urea, salts, and urochrome (which gives urine its yellow color), along with any waste that the body no longer needs.
How is urine formed in the kidneys and how does it reach the bladder?
-Urine is formed through filtration, reabsorption, and secretion processes within the nephron. Once formed, it flows into the renal pelvis, then through the ureters, and is stored in the bladder until it is expelled through the urethra.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)