[1] Comment fonctionne un scanner-CT (TDM) / Bases Physiques du scanner en Imagerie Médicale
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth look at conventional medical imaging, highlighting the limitations of X-ray and gamma ray techniques, such as poor contrast and anatomical localization challenges. It contrasts these methods with tomography (CT scanning), which offers clearer, more accurate images through multi-angle projections and better differentiation of structures based on their radiological density. The video also covers the components of a CT scanner, including the X-ray tube, detectors, filters, and console. With technological advancements in CT, such as multi-barrett detectors and reduced radiation doses, this video explores how scanners have evolved to improve diagnostic capabilities.
Takeaways
- 😀 Conventional medical imaging using X-rays and gamma rays faces limitations due to projection techniques that do not allow for accurate anatomical localization and suffer from poor contrast.
- 😀 Superposition of structures in conventional imaging leads to issues where objects at different depths are projected onto the same plane, making it difficult to distinguish them based on density and size.
- 😀 In conventional imaging, the density of an object can lead to misinterpretation, where an object of different width and lower density can have the same attenuation as a smaller, denser object.
- 😀 The size of objects in conventional imaging changes based on their distance from the X-ray source and the detectors, causing distortion in measurements, such as magnification or reduction.
- 😀 Tomography, particularly CT scans, overcomes these issues by creating multiple projections from different angles, helping differentiate structures based on their radiologic density.
- 😀 The first CT scan was performed in 1972 by Godfrey Hounsfield, who, along with Alan Cormack, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1979 for their work on its development.
- 😀 Technological improvements in CT scans since 1972 have included faster acquisition times, reduced radiation doses, and enhanced image quality.
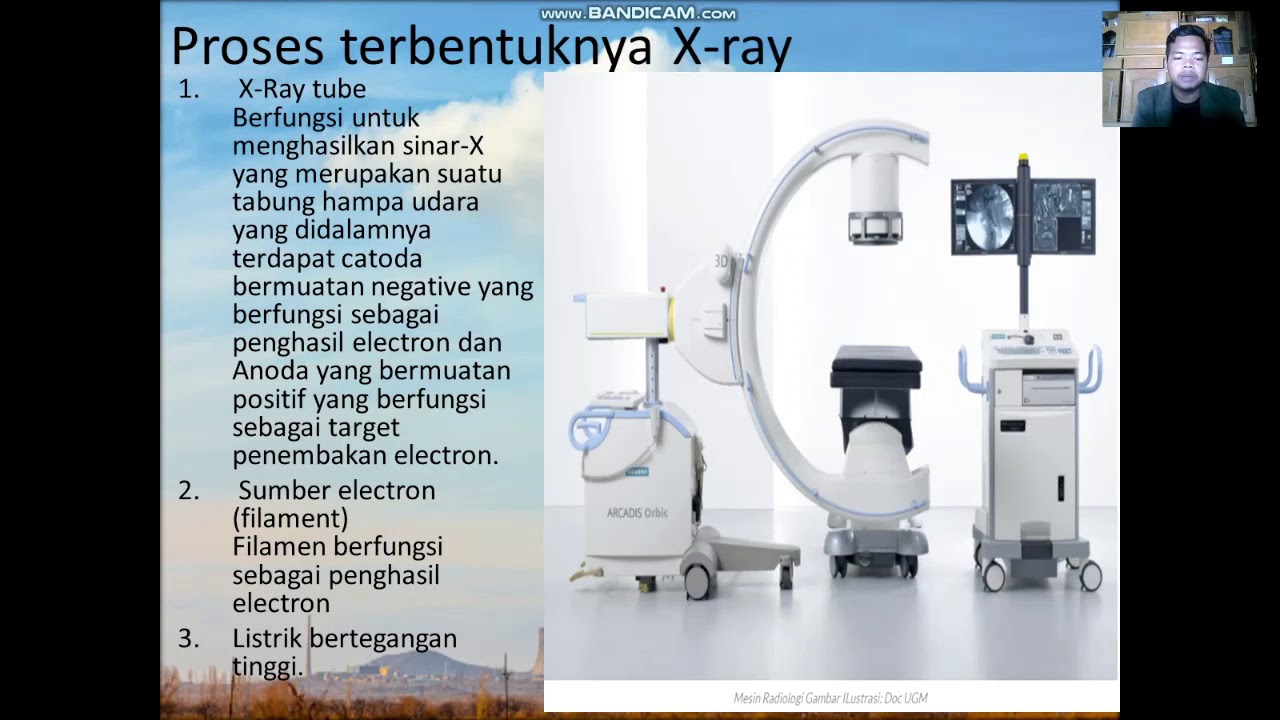
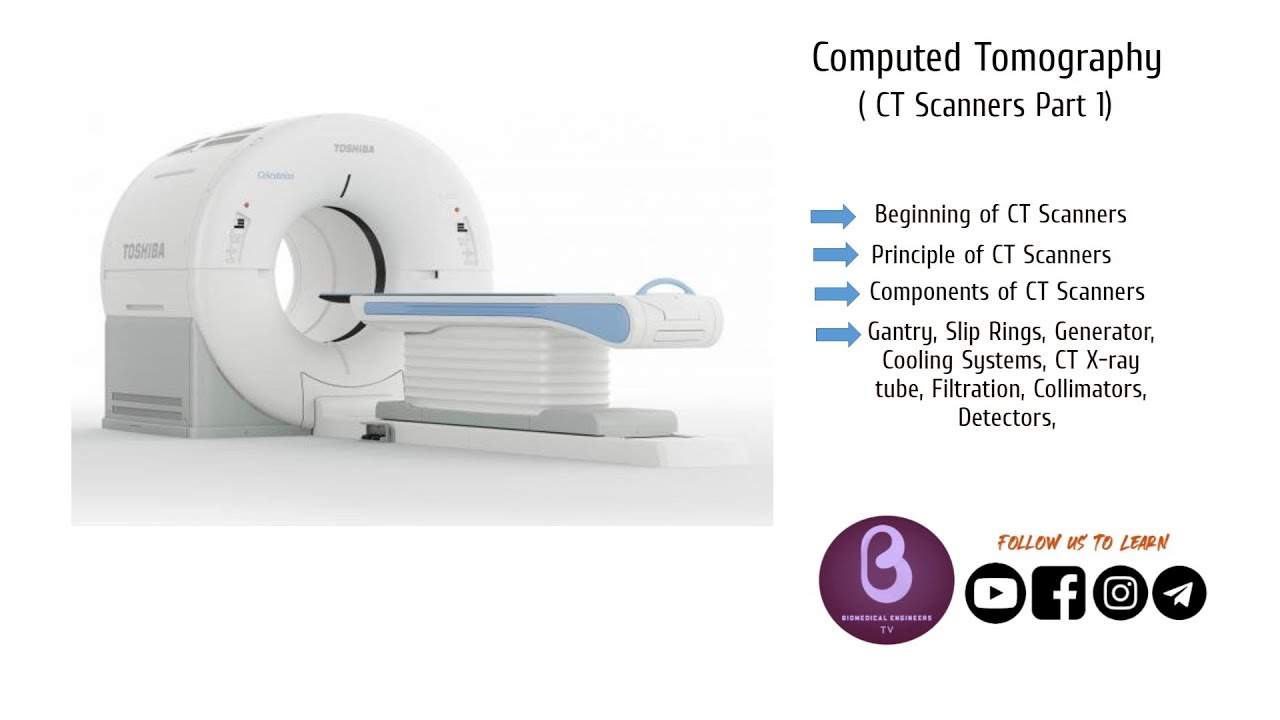
- 😀 A CT scanner consists of several components, including a console, a rotating gantry, a table, and X-ray tube detectors arranged in a fixed and rotating system.
- 😀 The X-ray tube in CT scanners is designed for high performance, with a rotating anode that can handle higher power and dissipate heat efficiently, unlike conventional radiology tubes.
- 😀 The detector system in CT scans uses photoluminescent ceramic crystals to convert X-rays into visible light photons, which are then turned into electrical signals for image reconstruction.
Q & A
What is a major limitation of conventional medical imaging techniques such as X-rays and gamma rays?
-A major limitation is the superposition of structures in the 2D projection, which makes it difficult to localize anatomical details and results in poor contrast, obscuring the information in the image.
Why is superimposition a problem in conventional imaging?
-Superimposition occurs because multiple structures at different depths are projected onto the same 2D plane, which results in a summation of objects that makes it impossible to distinguish them based on density or size.
What are some challenges related to the density in conventional imaging?
-In conventional imaging, objects of different densities and sizes can have the same attenuation, which makes it hard to differentiate them based on their physical properties.
How does the size of an object impact its representation in conventional imaging?
-The size of an object in the image can change depending on the distance from the X-ray source and detectors, leading to distortion through enlargement or reduction of the object's dimensions.
How does tomography address the limitations of conventional imaging?
-Tomography overcomes these limitations by performing multiple projections from different angles, allowing structures to be differentiated based on their radiological density, improving image clarity and anatomical localization.
What year did Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack contribute to the development of CT scanning?
-Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack contributed to the development of CT scanning in 1972, and they jointly received the Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology in 1979 for their work.
What are the key components of a CT scanner?
-A CT scanner consists of an acquisition console, a table, and a rotating gantry that houses the X-ray tube and detector arrays. The gantry rotates around the patient to capture multiple images from different angles.
What role does the X-ray tube play in a CT scanner?
-The X-ray tube in a CT scanner generates X-rays and directs them through the patient's body to the detector. It has enhanced performance compared to conventional radiology tubes, including longer rotation times and higher heat dissipation capabilities.
How do filters and collimators function in a CT scanner?
-Filters remove low-energy X-rays that would not contribute useful information, reducing unnecessary radiation. Collimators modify the X-ray beam geometry to match the desired scan area and thickness of slices.
What is the purpose of the detection system in a CT scanner?
-The detection system in a CT scanner converts X-ray photons that pass through the patient into electrical signals. Most modern scanners use photoluminescent ceramic crystals, which emit visible light when struck by X-rays, and the light is then converted into electrical current by photodiodes.
What is the significance of multi-detector arrays in modern CT scanners?
-Multi-detector arrays, such as 16, 32, or even up to 320 rows of detectors, allow for simultaneous acquisition of multiple slices, improving the speed and resolution of scans while reducing the radiation dose required for high-quality images.
What is the role of the CT scanner table in the imaging process?
-The CT scanner table supports the patient during the scan and is motorized for precise positioning. It is made from radio-transparent materials like carbon fiber to minimize attenuation of X-rays while allowing for accurate imaging.
Why is the acquisition console important in a CT scanner?
-The acquisition console is responsible for controlling the scanner and processing the acquired data. It requires significant computational power to reconstruct and visualize the images quickly, which is crucial for timely diagnosis.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)