EMS Part 2: Sensor-sensor Mobil I Engine Management System #ems #enginemanagementsystem #sensor
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a detailed exploration of various sensors within the Engine Management System (EMS) of modern vehicles. It covers sensors such as the Intake Air Temperature (IAT), Throttle Position Sensor (TPS), Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF), and more, explaining their functions in regulating engine performance. The video clarifies how these sensors monitor key aspects such as air pressure, temperature, and speed, and how they work together to ensure optimal fuel efficiency and engine operation. A valuable resource for anyone interested in automotive technology or looking to understand vehicle sensor systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sensors in vehicles detect various physical quantities like temperature, pressure, and airflow, similar to human senses like sight, touch, and hearing.
- 😀 The intake air temperature sensor (IAT) measures the temperature of the air entering the intake manifold to ensure optimal engine performance.
- 😀 The throttle position sensor (TPS) detects the angle of the throttle valve to regulate the amount of fuel entering the engine based on throttle input.
- 😀 The mass airflow sensor (MAF) measures the mass of air entering the intake manifold, ensuring the correct air-fuel mixture for combustion.
- 😀 The manifold air pressure sensor (MAP) measures the pressure in the intake manifold, replacing the vacuum advancer in older carburetor engines for ignition timing.
- 😀 The crankshaft position sensor (CKP) tracks the engine's RPM (revolutions per minute) to monitor the speed of the engine.
- 😀 The camshaft position sensor (CMP) identifies the top position of each cylinder, assisting in fuel injection and ignition timing.
- 😀 The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) measures the vehicle's speed by tracking rotation from the transmission, providing data for the ECU.
- 😀 The oxygen sensor detects the level of oxygen in exhaust gases, helping to optimize the air-fuel mixture and reduce harmful emissions.
- 😀 The oil pressure sensor monitors oil pressure within the engine, alerting the driver via a dashboard light if the oil pressure is too low or high.
Q & A
What is the role of sensors in automotive engine management systems?
-Sensors in automotive engine management systems monitor various engine parameters, such as temperature, pressure, airflow, and vehicle speed, to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions. These sensors provide real-time data that is processed by the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) to adjust fuel injection, ignition timing, and other parameters.
What does the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor measure?
-The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the intake manifold. This information is used by the ECU to adjust the air-fuel mixture based on the temperature, ensuring efficient combustion.
How does the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) affect the engine?
-The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) measures the angle of the throttle valve. This data helps determine how much air and fuel is required by the engine. It influences fuel injection, throttle response, and engine performance based on the throttle's position.
What is the function of the Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor?
-The Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor measures the mass of the air entering the engine. This information helps the ECU calculate the correct air-fuel ratio for combustion, ensuring that the engine receives the optimal amount of air for efficient performance.
What does the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measure?
-The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures the air pressure in the intake manifold. It provides data to the ECU to help control fuel injection, ignition timing, and other engine functions based on the engine load.
What is the difference between the Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) and the Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)?
-The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) monitors the position and speed of the crankshaft, which helps calculate engine RPM and synchronize ignition and fuel injection. The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) monitors the position of the camshaft to determine the top dead center of each cylinder for accurate timing of fuel injection and ignition.
What is the purpose of the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)?
-The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) measures the speed of the vehicle. It provides data to the ECU for features like cruise control, transmission shifting, and optimizing engine performance based on the vehicle's speed.
How does the Oxygen Sensor affect engine emissions?
-The Oxygen Sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This data is used by the ECU to adjust the air-fuel ratio, helping to ensure complete combustion and reduce harmful emissions in the vehicle's exhaust.
What does the Oil Pressure Sensor detect?
-The Oil Pressure Sensor monitors the pressure of the oil within the engine. It alerts the driver if the oil pressure is too low or too high, which could indicate potential issues like insufficient lubrication or a malfunctioning oil pump.
How does the Knock Sensor protect the engine?
-The Knock Sensor detects abnormal vibrations or knocking in the engine. It alerts the ECU to adjust the ignition timing to prevent engine damage caused by detonation, which can result from knocking or pinging during combustion.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

EMS Part 1: Engine Management System I Bahasa Indonesia #ems #enginemanagementsystem

Pengenalan Dasar Engine Management System (EMS) di Kendaraan EFI - Sensor, ECM, dan Aktuator ‼️

Sistem EFI Cara Kerja dan Komponennya
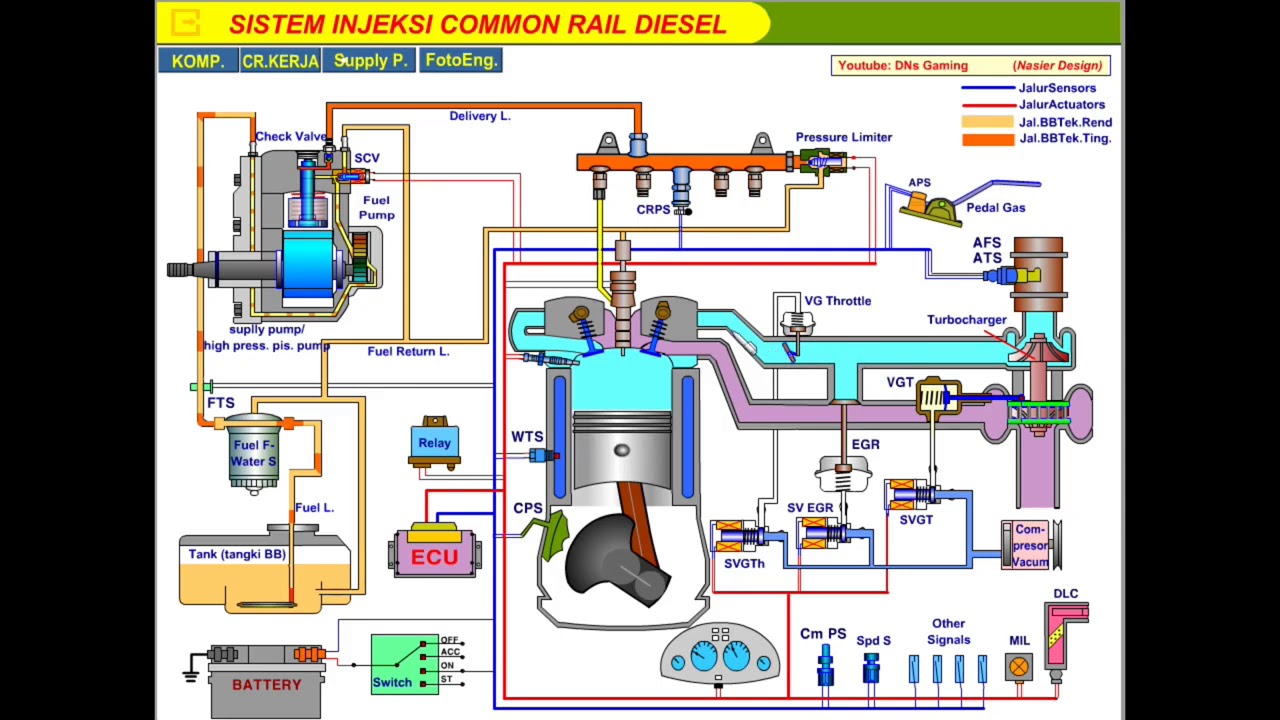
cara kerja bahan bakar diesel (Tipe common rail)

Motor Drivers In Engine Control Units (ECUs)

EMS Part 3, Macam macam Aktuator Engine Management system #ems #enginemanagementsystem
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
