Lesson 4: The Feedback Mechanism in Menstrual Cycle
Summary
TLDRThis lesson provides an in-depth explanation of the female menstrual cycle, focusing on its phases—menstrual, follicular, ovulatory, and luteal—and the hormonal feedback mechanisms that regulate it. The process begins with menstruation, followed by follicular maturation and ovulation. The lesson explains how hormones like FSH, estrogen, LH, and progesterone interact to control the cycle, ensuring the body is prepared for a potential pregnancy. The script serves as an informative guide to understanding the biological processes that govern female reproductive health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormones, with one egg being released every 28 days on average.
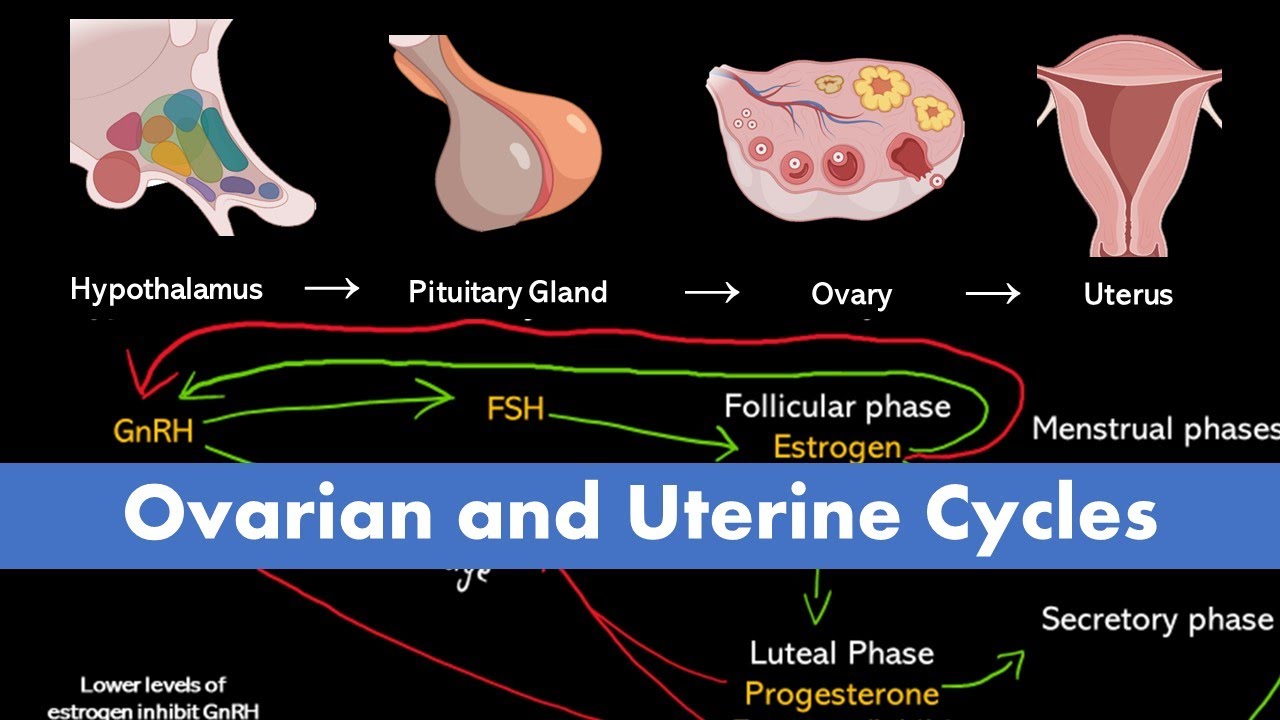
- 😀 The menstrual cycle consists of two interconnected cycles: the ovarian cycle and the uterine cycle.
- 😀 Menstruation is the process of shedding blood and tissues from the uterus, which lasts 1-5 days.
- 😀 The follicular phase follows menstruation, where the uterine lining rebuilds and follicles in the ovaries mature.
- 😀 Only one follicle fully matures in the follicular phase, while others deteriorate.
- 😀 Ovulation occurs around day 14, when the mature follicle releases the egg from the ovary.
- 😀 The luteal phase follows ovulation, where the endometrium thickens in preparation for pregnancy.
- 😀 If fertilization does not occur, the endometrium breaks down, leading to menstruation, restarting the cycle.
- 😀 Hormonal feedback mechanisms control the menstrual cycle, ensuring proper regulation of hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone.
- 😀 High estrogen levels inhibit further production of FSH, while estrogen also stimulates the release of LH from the pituitary gland.
- 😀 Progesterone production is regulated by LH, and high levels of progesterone inhibit the further release of LH during the luteal phase.
Q & A
What is the menstrual cycle, and how long does it typically last?
-The menstrual cycle is a monthly process in females that involves hormonal changes and the release of an egg from the ovary, followed by the shedding of the uterine lining if pregnancy does not occur. It typically lasts about 28 days, although this can vary.
What are the two main cycles of the menstrual cycle, and what do they involve?
-The menstrual cycle is divided into two main cycles: the ovarian cycle, which involves the events in the ovary like ovulation, and the uterine cycle, which refers to the events in the uterus, such as menstruation.
What happens during the menstrual phase of the cycle?
-During the menstrual phase, which typically lasts 1-5 days, the endometrial lining of the uterus sheds, and blood and tissues are expelled from the body. This phase is also when many females experience menstrual cramps.
What occurs during the follicular phase?
-In the follicular phase, after menstruation, the endometrium of the uterus begins to rebuild. Simultaneously, several ovarian follicles start maturing, and one will eventually release a matured egg during ovulation.
What is ovulation, and when does it usually occur?
-Ovulation is the release of a mature egg (oocyte) from the ovary. It typically occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle, in the middle of the cycle.
What happens after ovulation in the luteal phase?
-During the luteal phase, the uterine lining continues to thicken, and blood vessels increase in preparation for a possible fertilized egg. The ovulated follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone.
What is the role of progesterone in the luteal phase?
-Progesterone, produced by the corpus luteum after ovulation, helps to maintain the thickened uterine lining in case a fertilized egg implants. If no fertilization occurs, progesterone levels drop, leading to menstruation.
What is the feedback mechanism in the menstrual cycle, and how does it work?
-The feedback mechanism involves hormones influencing each other to regulate the menstrual cycle. For example, high estrogen levels inhibit the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), while estrogen also stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), which in turn regulates progesterone production.
What is the role of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) in the menstrual cycle?
-FSH stimulates the ovaries to release estrogen, which in turn affects other hormonal levels and helps regulate the ovarian cycle.
What happens if the egg is not fertilized during the menstrual cycle?
-If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a decrease in progesterone and estrogen levels. This causes the uterine lining to break down and be shed, resulting in menstruation, which marks the beginning of a new cycle.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 3 Module 2 | Feedback Mechanism of the Female Reproductive System

GRADE 10 SCIENCE QUARTER 3 WEEK 2 | MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Ovarian and Uterine Cycle (Menstrual Cycle)

Female Reproductive System - Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Regulation

Menstrual Cycle Walkthrough: Phases & Hormonal Regulation

Nutrition for the 4 Phases of the Menstrual cycle
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
