ACCA F2 Cost Classification
Summary
TLDRThis video explains essential concepts in cost classification for F2 students, covering cost objects, units, and centers. It defines direct and indirect costs, and delves into the various cost elements such as material, labor, and expenses. The video further explores cost behavior—fixed, variable, semi-variable, and stepped costs—and the significance of understanding these concepts in budgeting and decision-making. Managers need to classify costs by their nature, function, controllability, and behavior to optimize cost management and accountability within organizations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cost objects are items or activities for which costs are measured, like products, services, or departments.
- 😀 Cost units represent the cost incurred by a company to produce, store, and sell one unit of a product or service, calculated as an average cost.
- 😀 Cost centers refer to parts of an organization, such as departments or locations, where costs can be controlled and ascertained.
- 😀 Costs can be classified by elements like materials, labor, or expenses; by function (e.g., production or non-production); and by controlability (controllable vs. uncontrollable).
- 😀 Direct costs, including direct materials, labor, and expenses, are directly attributable to a specific cost object and are known as prime costs.
- 😀 Indirect costs, such as indirect materials, labor, and expenses, benefit multiple cost objects and cannot be directly traced to one item.
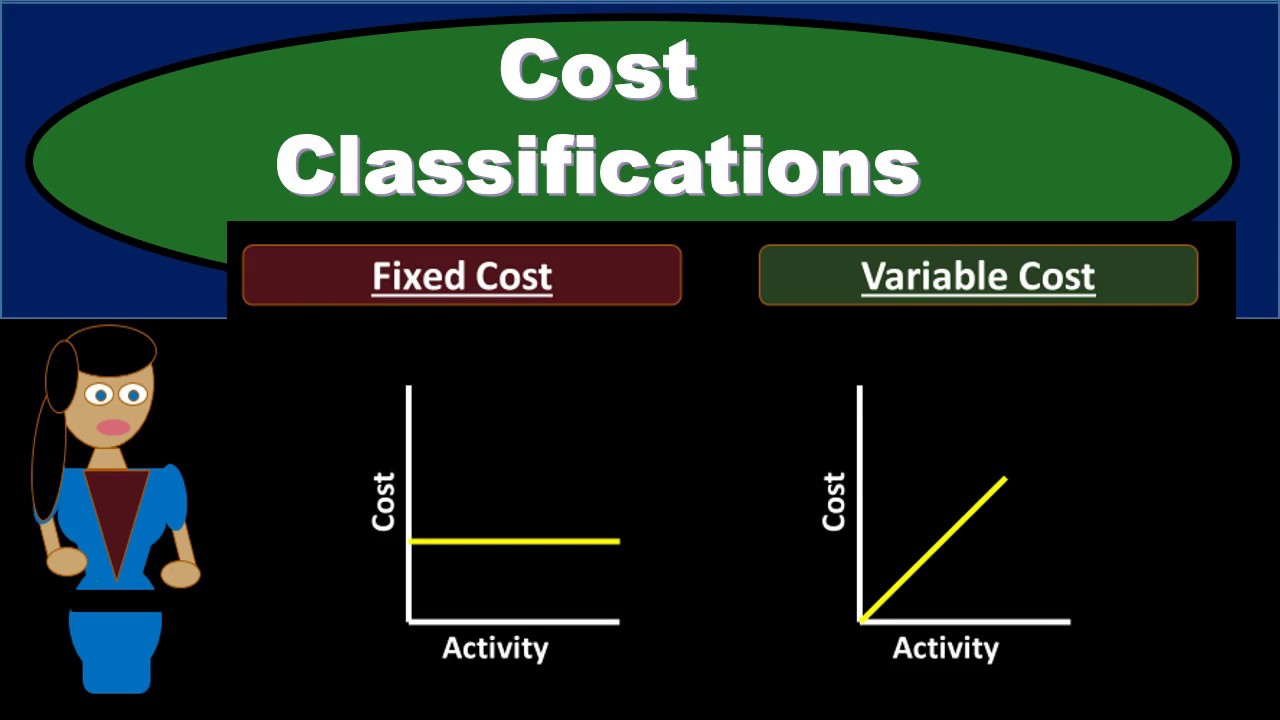
- 😀 Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production activity levels, whereas variable costs change in direct proportion to output changes.
- 😀 Semi-variable costs include both fixed and variable elements, such as telephone bills, where there's a fixed charge plus a variable usage cost.
- 😀 Stepped costs increase when certain thresholds of activity are reached, such as requiring an additional supervisor when a workforce exceeds a specific size.
- 😀 Understanding cost behavior—fixed, variable, semi-variable, and stepped—is essential for budgeting, planning, and decision-making processes in management.
Q & A
What is a cost object?
-A cost object is any item or activity for which costs are separately measured, such as a product, service, department, or process.
How is a cost unit defined?
-A cost unit is the unit of product or service in relation to which costs are ascertained, typically calculated as the average cost of producing one unit of a product.
What are cost centers and give examples?
-Cost centers are parts of an organization where costs can be determined and used for cost control. Examples include departments like research and development, marketing, and customer service.
How can costs be classified by function?
-Costs can be classified by function into production costs and non-production costs. Production costs include direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses, while non-production costs include administration, selling, distribution, and finance costs.
What is the difference between direct and indirect costs?
-Direct costs can be directly attributed to a specific cost object, such as direct materials, labor, and expenses. Indirect costs, or overheads, benefit multiple cost objects and cannot be directly traced to a single one.
What are prime costs?
-Prime costs are the total direct costs associated with production, calculated as the sum of direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses.
What is meant by controllable and uncontrollable costs?
-Controllable costs are those that a manager or department has authority over and can influence, while uncontrollable costs are beyond their control and cannot be changed.
How are costs classified by responsibility?
-Costs can be grouped by responsibility, where an organization is divided into responsibility centers, each managed by a person accountable for its costs and performance.
What is the distinction between product costs and period costs?
-Product costs are costs incurred in the production of goods and are included in inventory until sold. Period costs are costs not related to production and are expensed in the period incurred.
What is cost behavior and why is it important for management?
-Cost behavior refers to how costs change in relation to changes in activity levels. Understanding cost behavior is crucial for budgeting, costing, and decision-making, as it helps predict how costs will fluctuate with different levels of output.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)