Wujud Zat dan Partikelnya
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces the three states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—using water as an example. It explains how the arrangement and behavior of particles differ in each state, with a simple experiment to test the compressibility of solids, liquids, and gases. The concept of diffusion is also explored, demonstrating how particles move from high to low concentration. The video emphasizes the importance of learning and understanding basic scientific principles, encouraging viewers to keep exploring the world of natural science.
Takeaways
- 😀 Water can exist in all three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (steam), making it a useful example for understanding matter.
- 😀 Matter generally exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Each state has different properties and behaviors.
- 😀 In solids, particles are tightly packed, organized, and strongly bonded, making them incompressible.
- 😀 In liquids, particles are less tightly packed, move randomly, and are weakly bonded, making liquids slightly compressible.
- 😀 In gases, particles are far apart, move freely, and have very weak bonds, allowing gases to expand and be highly compressible.
- 😀 A simple test of compressibility can demonstrate how solids, liquids, and gases react under pressure.
- 😀 Diffusion is the process where particles move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration, leading to equilibrium.
- 😀 Diffusion occurs in both liquids and gases. In liquids, diffusion can be seen when a dye spreads evenly in water.
- 😀 The process of diffusion also explains how we smell: gas particles (such as scents) enter our nostrils and travel to the brain via sensory nerves.
- 😀 Understanding the properties of different states of matter, including their particle behavior and diffusion, is essential for grasping basic science concepts.
Q & A
What are the three states of matter mentioned in the video?
-The three states of matter mentioned in the video are solid, liquid, and gas.
How does the arrangement of particles differ in solids, liquids, and gases?
-In solids, particles are closely packed and have a regular pattern. In liquids, particles are less tightly packed and can move around. In gases, particles are far apart and move freely.
What is the concept of compressibility and how does it apply to gases?
-Compressibility is the ability of a substance to be squeezed into a smaller space. Gases are compressible because their particles are far apart and can be pushed closer together, unlike solids and liquids where particles are already close.
What is diffusion, and how does it occur in gases and liquids?
-Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. In gases, particles spread out freely, and in liquids, particles move to mix evenly, as shown by the example of a dye spreading in water.
How does water demonstrate all three states of matter?
-Water can exist in three states: as a solid (ice), as a liquid (water), and as a gas (steam or vapor). This makes it a great example for understanding the behavior of matter in different states.
What role does the concept of compressibility play in understanding the behavior of gases?
-The concept of compressibility highlights that gases can be compressed into smaller volumes due to the wide spacing between their particles, unlike solids and liquids which are less compressible.
How do scent particles reach our nose, as explained in the video?
-Scent particles, which are gas molecules, travel through the air and enter the nostrils. These particles then move through fine hairs (cilia) in the nasal cavity and reach the olfactory nerves, which send signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive the scent.
Why is the movement of particles in a gas described as 'free'?
-The movement of particles in a gas is described as 'free' because they are far apart and not strongly bound together. This allows them to move independently in all directions, spreading out to fill any available space.
What does it mean for the particles in a solid to be 'strongly bound'?
-When particles in a solid are 'strongly bound', it means they are closely packed and held together by strong forces, preventing them from moving freely. This gives solids a fixed shape and volume.
How does the video suggest we can observe the properties of matter in everyday life?
-The video suggests that we can observe the properties of matter in everyday life by experimenting with simple tests, such as testing the compressibility of solids, liquids, and gases, or by observing how substances like water change state depending on temperature.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

3 States of Matter - Solid, Liquid, Gas
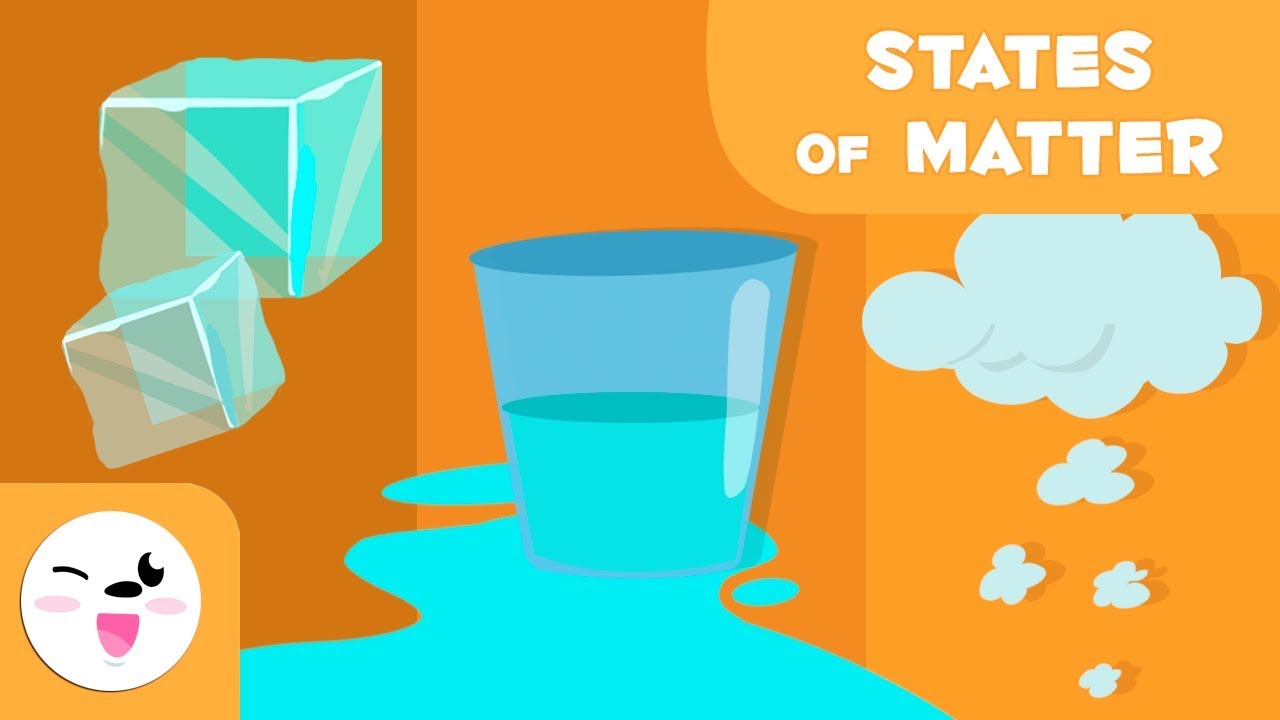
States of matter for kids - What are the states of matter? Solid, liquid and gas

CHANGES IN STATES OF MATTER || FREEZING, MELTING, CONDENSATION, EVAPORATION, SUBLIMATION, DEPOSITION

Bill Nye: Phases of Matter

S1.1.2 States of matter, changes of state and state symbols

Bill Nye the Science guy: Phases of Matter
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
