Makrosporogenesis dan Mikrosporogenesis (Reproduksi pada Tumbuhan)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the process of plant reproduction is explained, focusing on macrosporogenesis and microsporogenesis. Macrosporogenesis involves the formation of female gametes (megaspore) through meiosis and subsequent mitosis, leading to the development of the embryo sac. Microsporogenesis details the formation of male gametes (microspores or pollen) via meiosis, with differentiation into vegetative and generative nuclei. The video also covers the concept of double fertilization in angiosperms, where two fertilization events occur to form the zygote and endosperm. This clear and engaging explanation is designed for students learning about plant reproduction.
Takeaways
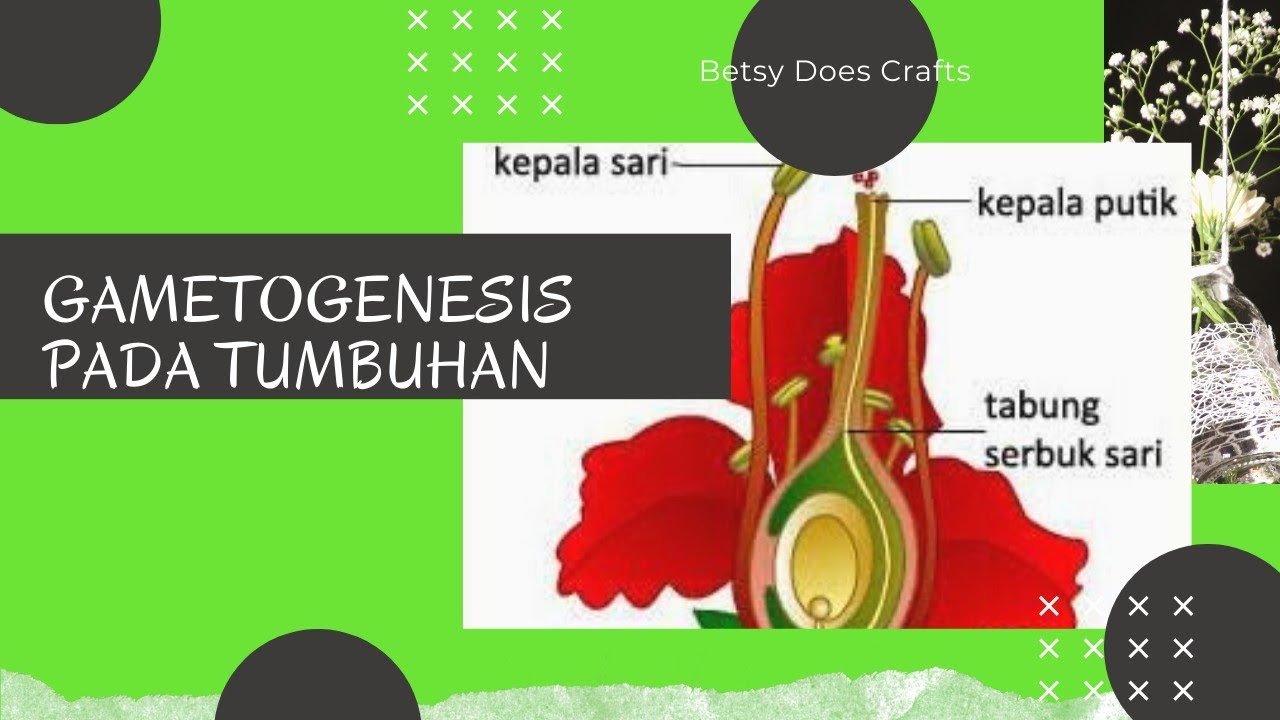
- 😀 Makrosporogenesis is the process of forming and developing macrospores (female spores) in the pistil of a plant.
- 😀 The diploid macrospore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form a haploid megaspore, which then undergoes three mitotic divisions without cytokinesis.
- 😀 In makrosporogenesis, the final 8 nuclei consist of 1 haploid ovum, 2 haploid synergids, 1 diploid secondary nucleus, and 3 haploid antipodal cells.
- 😀 Mikrosporogenesis is the formation of microspores (pollen or male gametes) in the anther of a plant.
- 😀 The diploid microspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form four haploid microspores.
- 😀 Each microspore differentiates into a vegetative nucleus and two generative nuclei, which are essential for fertilization.
- 😀 The vegetative nucleus guides the growth of the pollen tube, while the generative nuclei participate in fertilization processes.
- 😀 Double fertilization occurs in angiosperms, where two fertilization events happen: one to form a diploid zygote and the other to form a triploid endosperm.
- 😀 In double fertilization, the egg cell (haploid) fuses with generative nucleus 1 (haploid) to form a diploid zygote.
- 😀 The second fertilization event involves generative nucleus 2 (haploid) fusing with the secondary nucleus (diploid) to form the triploid endosperm, which serves as food storage for the embryo.
- 😀 Both macrospores and microspores undergo meiosis and mitosis, but their processes differ in terms of the number of divisions and the final products involved in plant reproduction.
Q & A
What is makrosporogenesis?
-Makrosporogenesis is the process of formation and development of megaspores (macrospores) in the ovule, which is the female reproductive organ in plants. It involves meiosis followed by mitosis to produce eight haploid nuclei.
Where does makrosporogenesis occur in plants?
-Makrosporogenesis occurs in the ovule, which is part of the pistil (female reproductive organ) of a flower.
What are the stages involved in makrosporogenesis?
-The stages of makrosporogenesis include: 1) Meiosis in the diploid megaspore mother cell to produce haploid megaspores, 2) Three rounds of mitosis (without cytokinesis) leading to the formation of eight nuclei, including the ovum and synergids.
What are the key components produced by makrosporogenesis?
-Makrosporogenesis produces eight haploid nuclei, which include one ovum (egg cell), two synergids, one diploid secondary nucleus, and three haploid antipodal cells.
What is mikrosporogenesis?
-Mikrosporogenesis is the process by which microspores (pollen) are formed in the anther (male reproductive organ) of plants. It involves meiosis followed by the differentiation of microspores into pollen grains.
Where does mikrosporogenesis take place in plants?
-Mikrosporogenesis occurs in the anther, which is part of the stamen (male reproductive organ) in flowering plants.
What are the stages of mikrosporogenesis?
-The stages of mikrosporogenesis involve: 1) Meiosis of the diploid microspore mother cell to produce four haploid microspores, 2) The differentiation of these microspores into pollen grains consisting of a vegetative nucleus and two generative nuclei.
What is the role of the generative nuclei in pollen?
-The generative nuclei in pollen play key roles in fertilization. Generative nucleus 1 fertilizes the egg cell, while generative nucleus 2 fertilizes the secondary central cell, forming the endosperm.
What is double fertilization in angiosperms?
-Double fertilization in angiosperms involves two fertilization events: 1) The fertilization of the egg cell by generative nucleus 1, forming a diploid zygote, and 2) The fertilization of the secondary central cell by generative nucleus 2, forming a triploid endosperm.
Why is double fertilization important for plant reproduction?
-Double fertilization is crucial because it ensures the formation of both the zygote, which will develop into the embryo, and the endosperm, which provides nutrition for the developing seed.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

FTB UAJY | Bu Dewi | SPT | Anatomi Bunga

GAMETOGENESIS- Biologi Kelas 12, BAB PEMBELAHAN SEL

Pembelahan sel - Biologi kelas 12 SMA
GAMETOGENESIS PADA TUMBUHAN || MIKROSPOROGENESIS & MEGASPOROGENESIS #biologikelas12 #pembelahansel

IPA Kelas 9 : Sistem Perkembangbiakan Tumbuhan (Part 3 : Pembuahan Ganda pada Tumbuhan Angiospermae)

IPA Kelas 9 : Sistem Perkembangbiakan Tumbuhan (Part 1 : Perkembangbiakan Vegetatif)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
