Siklus sel
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the cell cycle, detailing its four main phases: G1 (growth), S (DNA synthesis), G2 (preparation for mitosis), and M (mitosis). It discusses the roles of key vitamins like B9 and B12 in DNA synthesis, the importance of telomeres in aging, and the implications of genetic disorders like polyploidy and nondisjunction. The video highlights the significance of cell division in growth, regeneration, and maintaining organismal health, as well as the potential consequences of errors during the cycle, including conditions like Down syndrome and cancer.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cell cycle is a crucial process involving the growth, DNA replication, and cell division to produce new cells, essential for organism survival and regeneration.
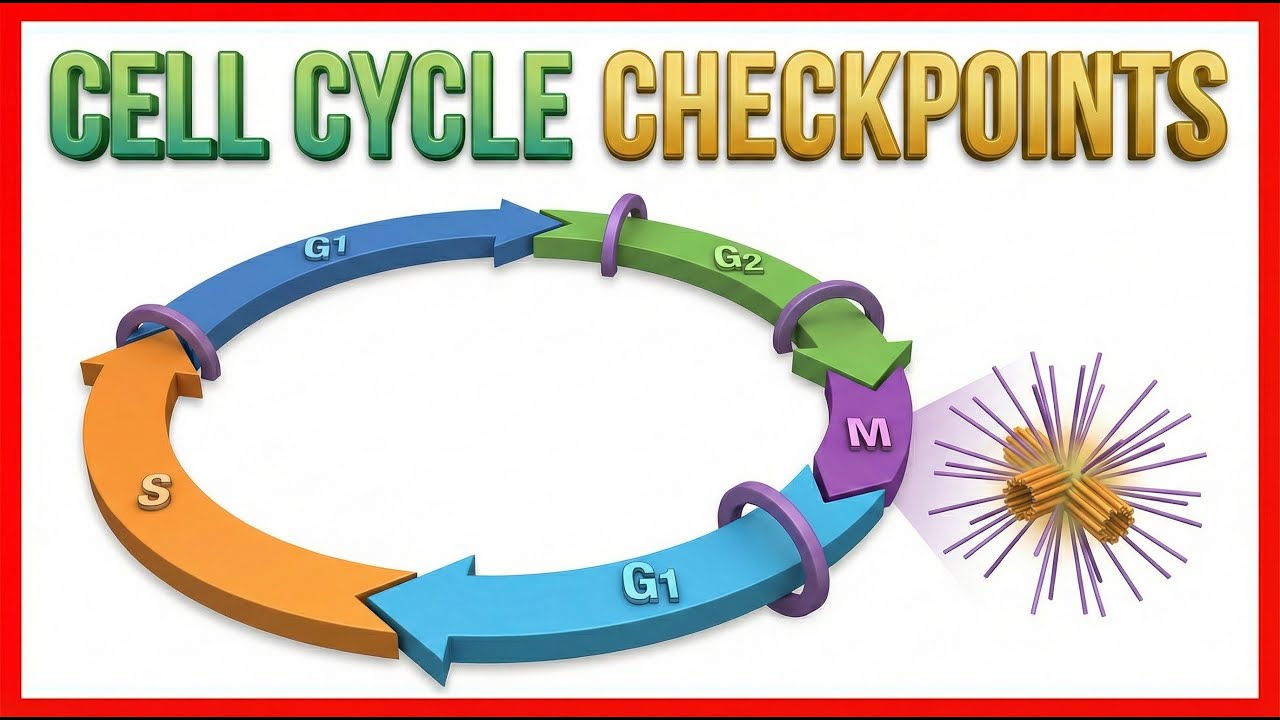
- 😀 The cell cycle consists of four main phases: G1, S, G2, and M, with G1, S, and G2 together known as interphase.
- 😀 The G0 phase is a resting state where cells exit the normal cycle, with some cells in this phase permanently (e.g., neurons) and others temporarily (e.g., some stem cells).
- 😀 Vitamin B9 (folic acid) and B12 (cobalamin) are essential for DNA synthesis; deficiencies can lead to diseases like megaloblastic anemia and developmental issues such as spina bifida.
- 😀 DNA replication occurs during the S phase, where chromosomes duplicate to form sister chromatids connected at the centromere.
- 😀 Telomeres shorten with each cell division, and this shortening is associated with aging, cancer, and diseases like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- 😀 The G2 phase involves the final preparation for mitosis, including DNA damage repair and further organelle duplication.
- 😀 Mitosis, the M phase, consists of several stages—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis, where the cell physically divides into two daughter cells.
- 😀 In mitosis, spindle fibers play a crucial role in separating chromatids, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
- 😀 Abnormalities like nondisjunction during mitosis can lead to chromosomal abnormalities, such as trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), which often results in developmental syndromes or even miscarriage.
Q & A
What is the significance of the cell cycle in organism development?
-The cell cycle is crucial for the growth, repair, and regeneration of cells. It ensures that damaged, old, or dead cells are replaced and that new cells are produced to support organism survival.
What are the four main phases of the cell cycle?
-The four main phases of the cell cycle are G1 (Gap 1), S (Synthesis), G2 (Gap 2), and M (Mitosis). G1, S, and G2 are collectively known as interphase, while M represents the phase of cell division.
What is the role of the G0 phase in the cell cycle?
-The G0 phase is a resting phase where cells exit the cycle either temporarily or permanently. Some cells, like neurons, remain in G0 indefinitely, while others can re-enter the cycle if triggered by certain signals.
How does vitamin B9 (folate) and B12 contribute to DNA synthesis?
-Vitamin B9 (folate) and vitamin B12 are essential for the synthesis of DNA. They play key roles in the production of nucleotides and in preventing DNA replication errors that could lead to diseases like anemia and birth defects.
What are the consequences of a deficiency in vitamin B9 and B12?
-A deficiency in these vitamins can lead to megaloblastic anemia, premature birth, low birth weight, congenital heart defects, and neural tube defects like spina bifida and anencephaly.
What happens to telomeres during cell division?
-Telomeres, which are repetitive DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes, shorten each time a cell divides. This shortening is linked to aging and conditions like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, bone marrow failure, and cancer.
What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
-During the S phase, DNA replication occurs, where chromosomes are duplicated. By the end of this phase, each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere.
What is the role of the mitotic spindle in mitosis?
-The mitotic spindle, composed of microtubules, helps organize and separate chromosomes during mitosis. It ensures that sister chromatids are evenly distributed between the two daughter cells.
What is the significance of the metaphase plate during mitosis?
-The metaphase plate is the alignment of chromosomes at the center of the cell during metaphase. This alignment is crucial for the proper segregation of chromosomes to the two daughter cells.
What are the potential consequences of nondisjunction during mitosis?
-Nondisjunction leads to the improper segregation of chromosomes, resulting in daughter cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes. This can cause conditions like Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Klinefelter syndrome.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)