Genetic Principles
Summary
TLDRThis lecture explores the molecular basis of inheritance, focusing on DNA as the genetic material, its replication, and gene expression. It discusses the central dogma of molecular biology (DNA → RNA → Protein) and highlights key experiments that confirmed DNA's role in heredity. The script also explains the processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, comparing mechanisms in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The lecture delves into the importance of DNA in protein synthesis and genetic diversity, underscoring its role in shaping physical traits and metabolic functions across organisms.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA is the genetic material that carries inherited information and is essential for gene expression.
- 😀 DNA replication is a semiconservative process where each strand of the original DNA serves as a template for a new strand.
- 😀 The central dogma of molecular biology explains how DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins.
- 😀 Gene expression in prokaryotes occurs in the cytoplasm, as they lack a nucleus, while in eukaryotes, it happens in both the nucleus (transcription) and the cytoplasm (translation).
- 😀 Classic experiments, such as those using radioactive isotopes, confirmed that DNA, not proteins, is the genetic material that is inherited by organisms.
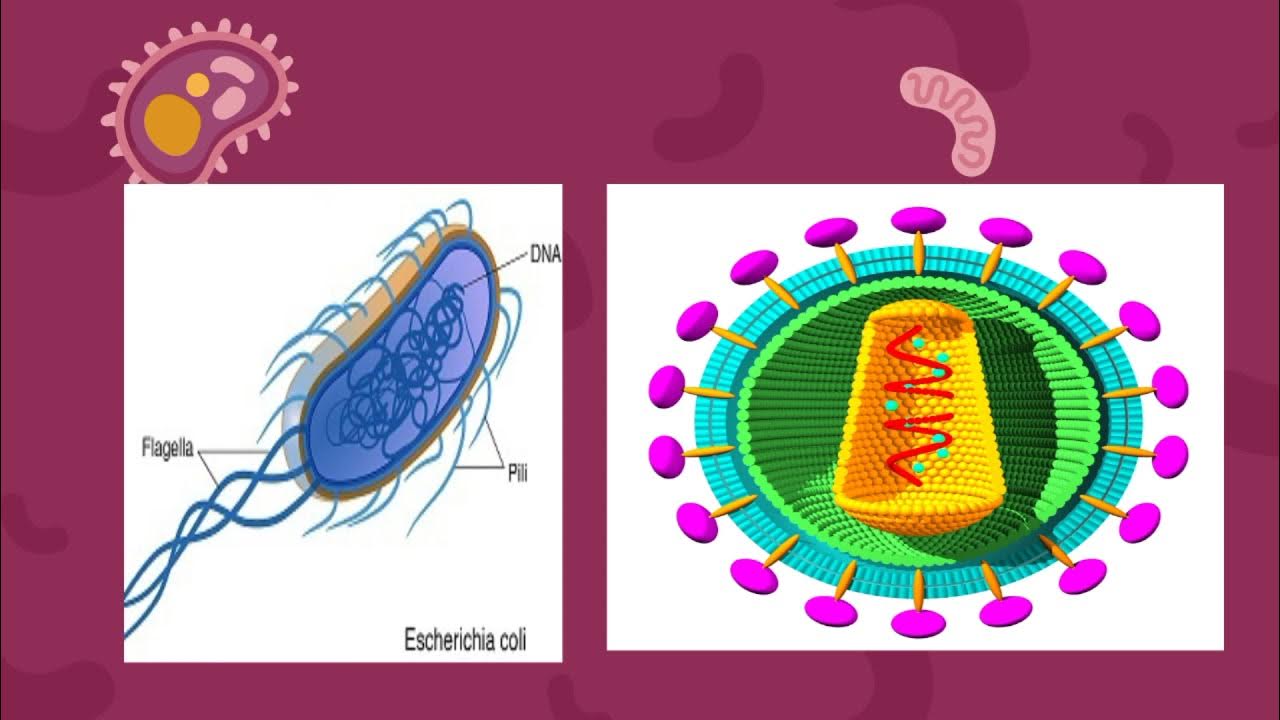
- 😀 DNA strands are held together by hydrogen bonds, with guanine-cytosine pairs forming three hydrogen bonds and adenine-thymine pairs forming two hydrogen bonds.
- 😀 Enzymes like helicase, DNA polymerase, and ligase play crucial roles in DNA replication by unwinding DNA, adding new nucleotides, and sealing the gaps between fragments.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic cells have multiple origins due to their complexity and larger size.
- 😀 In eukaryotes, after transcription in the nucleus, mRNA undergoes splicing to remove introns before it is exported to the cytoplasm for translation.
- 😀 The process of gene expression involves the synthesis of proteins based on the instructions encoded in DNA, which control an organism's structure, function, and development.
Q & A
What is the molecular basis of inheritance discussed in the video?
-The molecular basis of inheritance involves the study of DNA as the genetic material, how DNA replicates, and how genes are expressed through the process of transcription and translation to form proteins.
How is DNA structured and how do its components interact?
-DNA is structured as a double helix, where bases pair specifically: adenine (A) with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) with guanine (G). These base pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds, with A-T having two hydrogen bonds and C-G having three hydrogen bonds.
What experiment demonstrated that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material?
-The experiment conducted in the 1950s used radioactive sulfur to label protein and radioactive phosphorus to label DNA. It was found that DNA, not protein, entered bacterial cells and was passed on, confirming DNA as the genetic material.
What is the significance of the 'central dogma' in molecular biology?
-The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. It explains how genetic information in DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) and then translated into a protein that carries out specific functions.
What are the three main theories of DNA replication and which one is correct?
-The three main theories of DNA replication are the semiconservative, conservative, and dispersive models. The semiconservative model is the correct one, where each new DNA molecule consists of one strand from the original molecule and one newly synthesized strand.
How does DNA replication differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
-In prokaryotes, DNA replication occurs at a single origin of replication, whereas in eukaryotes, multiple origins of replication exist due to the larger size of their genomes.
What role do enzymes like DNA polymerase and ligase play in DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication, while DNA ligase connects the fragments of DNA (like Okazaki fragments) to complete the strand.
What is the difference between gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-In prokaryotes, transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm since there is no nucleus. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and the mRNA is processed and then transported to the cytoplasm for translation.
What is the significance of splicing in eukaryotic gene expression?
-Splicing in eukaryotic cells removes non-coding regions (introns) from the mRNA, leaving only the coding regions (exons) to form mature mRNA, which is then translated into protein.
How do mutations in DNA impact protein synthesis and function?
-Mutations in DNA can lead to changes in the mRNA sequence, which may result in the production of a malfunctioning or nonfunctional protein. This can affect various cellular processes and may lead to diseases or abnormalities.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation | Khan Academy Hebrew

DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation | Khan Academy

GENETIKA MIKROORGANISME. OH JADI INI BEDA ANTARA DNA DAN RNA YA?

PROSES REPLIKASI DNA | TRANSKRIPSI | TRANSLASI
Mikrobiologi | Genetika Mikroorganisme

#5 Bahan Genetik DNA dan RNA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
