Что происходит в Сирии | Syria Latest (English subtitles)
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the ongoing Syrian conflict, focusing on the recent offensive launched by Tahrir al-Sham and the Free Syrian Army against Aleppo. The script delves into the history of Syria's civil war, starting from the 1994 car crash that set Bashar al-Assad on the path to power, to the rise of radical Islamist groups, and international intervention. It also examines Turkey’s role in supporting militant groups and its neo-Ottoman ambitions. With the fall of Aleppo, the video highlights the dire consequences for civilians, including ethnic and religious cleansing, and the potential for wider instability in the region.
Takeaways
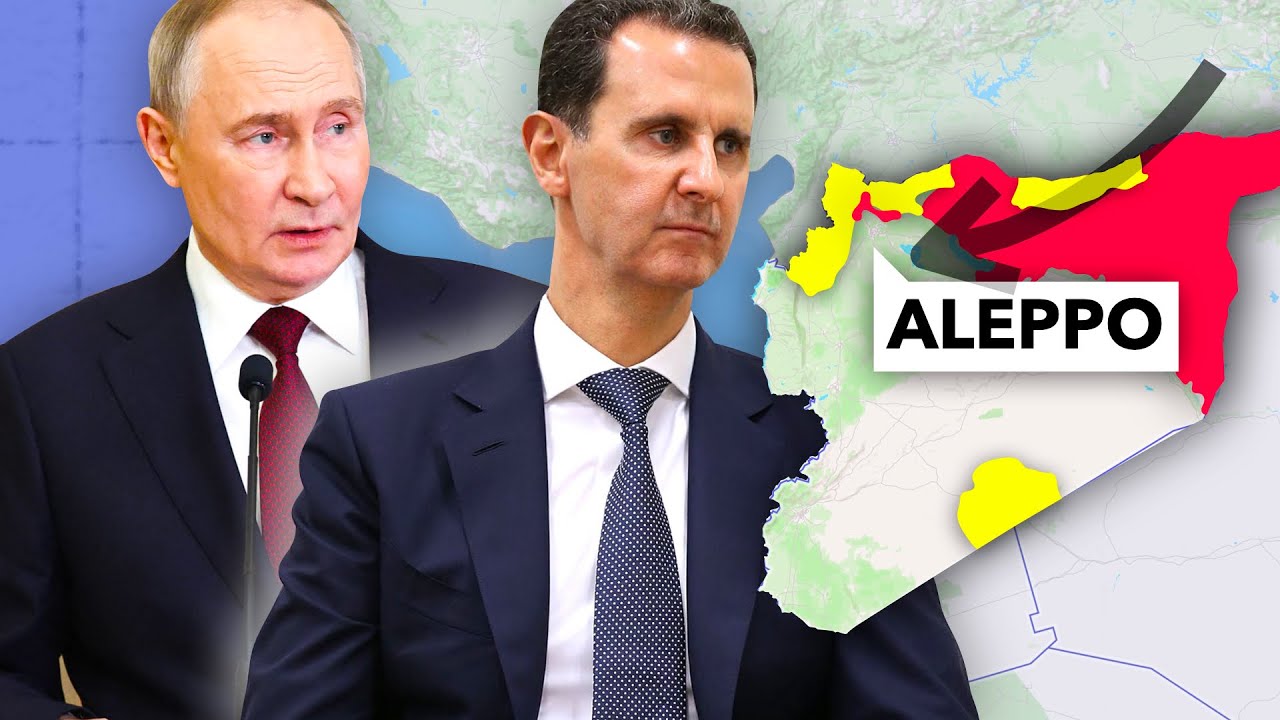
- 😀 Since 2019, the Syrian civil war has been largely overshadowed in international media, but a significant offensive began on November 27, 2024, as Tahrir al-Sham and the Free Syrian Army launched an attack on Aleppo.
- 😀 The Syrian government forces quickly retreated from Aleppo, allowing the militants to seize most of the city, as well as military hardware, towns, and airbases along the way.
- 😀 The conflict in Syria has deep historical roots, starting with the 1994 car accident that led to Bashar al-Assad taking over the presidency after the death of his brother, Bassel al-Assad.
- 😀 Initially viewed as a reformer, Bashar al-Assad's regime became increasingly corrupt and authoritarian, ultimately leading to the outbreak of the Syrian Civil War in 2011 after brutal repression of protests.
- 😀 The Free Syrian Army, initially seen as moderate, quickly became associated with Islamist groups, particularly after the involvement of international players like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and Turkey, who supported radical factions to weaken al-Assad's regime.
- 😀 Major Islamist groups like ISIS and al-Qaeda, along with their splinter groups, gained significant territory in Syria by 2015, and their brutal tactics resulted in widespread atrocities, including the genocide of Yazidis.
- 😀 The Syrian civil war became a proxy conflict, with Russia and Iran backing al-Assad's regime, while Turkey, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia supported various opposition groups, often including radical Islamists.
- 😀 By 2016, Bashar al-Assad's government began reclaiming territory, notably Aleppo, marking a turning point in the civil war, although the situation remained highly unstable.
- 😀 In 2024, Turkey's involvement intensified with Recep Erdogan supporting Turkish-backed militants, including Tahrir al-Sham and the Free Syrian Army, to control parts of Syria, especially in Idlib and Aleppo.
- 😀 Erdogan's motivations include both territorial ambitions, as he seeks to annex parts of northern Syria, and efforts to suppress the Kurdish population, whom he views as a threat to Turkey's stability.
- 😀 The Syrian Kurds, despite facing persecution from both al-Assad's regime and Turkish-backed militants, have been among the most resilient fighters, with Kurdish female soldiers gaining international recognition for their bravery.
- 😀 Russia's diminished military presence in Syria, due to its focus on Ukraine, has allowed Turkey to pursue more aggressive actions in Syria, undermining al-Assad's efforts and further complicating the already volatile situation.
Q & A
What triggered the large-scale offensive in Aleppo in November 2023?
-The offensive was initiated by Tahrir al-Sham and the Free Syrian Army from the Idlib Governorate, with their primary target being Aleppo, Syria's largest city. It escalated quickly as government troops fled, and by November 29, the militants had seized most of the city.
What are the implications of the offensive for the residents of Aleppo and the surrounding areas?
-The ongoing offensive is expected to lead to widespread atrocities, including executions, torture, and abductions, particularly targeting various ethnic and religious groups such as Alawites, Yazidis, Shia Muslims, and others. Civilians are facing grave danger, and the situation is deteriorating rapidly.
How did Bashar al-Assad come to power in Syria?
-Bashar al-Assad became president of Syria after his older brother Bassel died in a car accident in 1994. Initially, Bashar was an ophthalmologist studying in London, but his family's political pull brought him back to Syria. Following the death of his father Hafez al-Assad in 2000, Bashar was chosen as the sole candidate in the presidential election.
How did the Free Syrian Army evolve during the civil war?
-Initially viewed as moderate opposition forces, the Free Syrian Army's factions became increasingly radicalized over time. With external support from countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and Turkey, many of its groups eventually aligned with Islamist militants, and the term 'moderate' was used ironically as these forces engaged in brutal tactics against civilians and rival factions.
Why did Saudi Arabia and Qatar shift their stance on Bashar al-Assad's regime by 2023?
-By 2023, both Saudi Arabia and Qatar had reconsidered their opposition to Bashar al-Assad. Their earlier push to topple him had failed, and they had become less radicalized in their foreign policies, with Saudi Arabia even recognizing Assad as Syria's legitimate leader.
What role has Turkey played in the Syrian conflict?
-Turkey, led by Recep Erdogan, has been heavily involved in the Syrian conflict, particularly since 2019. Erdogan’s forces invaded northern Syria to support pro-Turkish militant groups and have clashed with Kurdish forces. Turkey has also supported radical Islamist groups, such as Tahrir al-Sham, and has pursued both strategic and ideological goals in the region, including annexing parts of northern Syria.
What is Tahrir al-Sham's background, and why is it significant in the ongoing conflict?
-Tahrir al-Sham, initially part of al-Qaeda under the name Nusra Front, has transformed into a pro-Turkish militant group. It is now a major player in the offensive against Aleppo and has become notorious for its radical Islamist ideology. Despite its claims of moderation, its actions include severe repression and violence against civilians and minority groups.
What is Erdogan's long-term vision for Syria and its region?
-Erdogan's long-term goal is to restore parts of Syria to Turkey, viewing northern Syria as integral to Turkey's territorial claims. He also seeks to weaken Kurdish autonomy and influence, both within Turkey and Syria. Erdogan's foreign policy has been driven by a neo-Ottoman ideology, seeking to restore Turkey's influence over former Ottoman territories.
How has the Russian involvement in Syria been affected by the war in Ukraine?
-Russia's military involvement in Syria has significantly weakened due to its ongoing conflict in Ukraine. As a result, Russia’s military presence in Syria is now limited to a small police force and a few fighter jets, which has allowed Turkey to assert more control over northern Syria and led to the failure of Russia's earlier efforts to contain Erdogan's ambitions.
What is the significance of the Kurds in the Syrian conflict, and how have they resisted the offensive?
-The Kurds, who form a significant ethnic minority in Syria, have been crucial in resisting ISIS and other militant groups during the civil war. Despite being marginalized by Assad, they have maintained autonomous control over parts of northern Syria. They are facing increasing threats from Turkey and its allies, but have shown fierce resistance in places like Tell Rifaat against Turkish-backed militants.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

الأسد ينهار... المعارضة تدخل قلب حلب وروسيا تتبرأ من القتال سوريا تشتعل من جديد
Why Syria’s Civil War Has Restarted

Memahami Perang Suriah: Apa yang Terjadi, Siapa yang Terlibat?

Pepe Escobar : Russia’s Next Move.

Toppling Assad: Hayat Tahrir al-Sham’s Fragile Grip on a Divided Syria

Hundreds of Iran-backed fighters to confront Syrian rebels | REUTERS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
