Understanding Motorcycle Transmission System
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the intricate workings of a motorcycle's transmission system, focusing on the gear mechanism. It explores the role of gears, shafts, and shifting forks, demonstrating how splined and freewheeling gears interact to transfer power. The gearshift lever, linked to a star shift detent mechanism, is used to engage different gears smoothly, avoiding undesirable neutral positions. The process of shifting through gears is illustrated with a 6-speed transmission system, showing how the gears lock and slide to shift effectively. The video also highlights the role of the star wheel in preventing neutral between gear shifts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Motorcycles are complex machines with mechanical and electrical components working together.
- 😀 The transmission system consists of a series of gears mounted on two shafts.
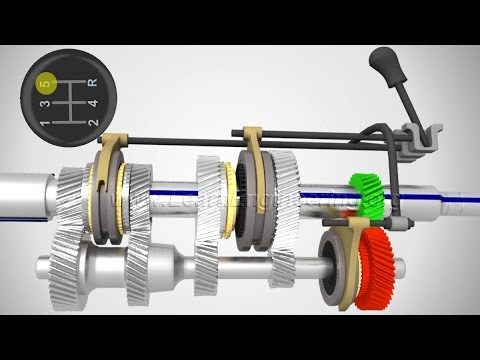
- 😀 Riders control the gearshift mechanism using a gear lever linked to a star shift detent mechanism.
- 😀 The star wheel, attached to the shift drum, has grooves that accommodate shifting forks synchronized with the rotating drum.
- 😀 Gears are mounted on input and output shafts, with splined and smooth sections to accommodate different gears.
- 😀 Splined gears can slide laterally and rotate with the shaft, while freewheeling gears can spin independently but cannot slide.
- 😀 Dog teeth on some gears lock into the freewheeling gear slots, enabling power transfer.
- 😀 A simplified demonstration shows how splined gears mesh with freewheeling gears to transfer power when locked.
- 😀 In a 6-speed transmission system, each gear shift involves sliding and locking gears, with a neutral position between shifts.
- 😀 The star shift detent mechanism prevents neutral positions during gear shifts by using a spring-biased roller and notches on the star wheel.
- 😀 A neutral position is achieved by cutting off a peak of the star wheel to create a neutral notch, allowing the roller to rest there when needed.
Q & A
What are the main components of a motorcycle's transmission system?
-The main components of a motorcycle's transmission system include the gearshift lever, star shift detent mechanism, shift drum, shifting forks, gear dogs, and the gears mounted on the input and output shafts.
How does the gearshift lever control the motorcycle's transmission?
-The gearshift lever is connected to the star shift detent mechanism, which controls the shifting process by moving the shift drum and engaging the shifting forks and gear dogs to select the desired gear.
What role does the star shift detent mechanism play in the gear shifting process?
-The star shift detent mechanism prevents the system from resting in a neutral position between gears, ensuring smooth and consistent gear engagement by using a spring-loaded roller that moves between notches and peaks on the star wheel.
What is the function of the gears mounted on the input and output shafts?
-The gears mounted on the input and output shafts transfer power from the engine to the wheels. The input shaft's gears mesh with the output shaft's gears to control the speed and torque delivered to the motorcycle.
What is the difference between splined gears and freewheeling gears?
-Splined gears can slide laterally and rotate with the shaft, while freewheeling gears can spin independently but cannot slide laterally. Freewheeling gears are used in conjunction with splined gears to transfer power when locked.
How do the dog teeth function in the gear shifting system?
-The dog teeth slide into the slots of the freewheeling gears, temporarily locking them into place to transfer power between the gears. This mechanism ensures the correct gear engagement during shifting.
Why is there a neutral position between each gear shift, and how is it prevented?
-The neutral position occurs when the previously locked teeth slide back before locking into the next gear. This is prevented by the star shift detent mechanism, which ensures that the roller moves past the neutral position to engage a gear.
How does the system ensure that the neutral position is only used when required?
-The system uses a modified star wheel with a neutral notch that allows the roller to rest in the neutral position only when necessary. This ensures that the neutral position can be engaged when required by the rider.
What happens when the input shaft rotates in the simplified gear setup?
-When the input shaft rotates in the simplified setup, it spins the freewheeling gear without rotating the output shaft, demonstrating the need for the splined gear to lock with the freewheeling gear to transfer power.
What is the process for shifting through the gears in a 6-speed transmission system?
-In a 6-speed transmission system, the rider engages each gear by sliding the appropriate splined gear into place, with the gear dogs locking the gears in sequence. The system progresses from neutral to first gear, then to second, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth, with the dog teeth sliding back to neutral before locking into the next gear.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)