(Macro) Episode 33: Exchange Rates
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the dynamics of the foreign exchange market, where currencies are bought and sold based on demand for travel, trade, and investment. It details how fluctuations in demand for a currency, such as the New Zealand dollar, can cause its value to appreciate or depreciate against others, like the US dollar. The script also explores how governments manipulate currency supply to impact trade balances. A weaker currency boosts exports but makes imports more expensive, influencing global trade strategies, as seen in US-China relations. The video offers key insights into exchange rates and their broader economic implications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Foreign exchange refers to foreign currency, which is essentially another commodity bought and sold in the market.
- 😀 There are three primary reasons people purchase foreign exchange: for travel, trade, and investment purposes.
- 😀 Changes in demand for foreign currency occur due to factors like tourism, trade, and investment decisions.
- 😀 A surge in tourists or investments in a country increases the demand for its currency, leading to currency appreciation.
- 😀 An increase in demand for a currency causes its value to rise, while the value of the other currency depreciates.
- 😀 Governments control the supply of foreign currency and can manipulate its value by adjusting supply, which influences the exchange rate.
- 😀 A country may manipulate its currency to drive up or down its value in order to benefit trade and its economy.
- 😀 Exchange rates impact the cost of foreign goods and services, with a weaker currency making imports more expensive and exports cheaper.
- 😀 A stronger currency benefits consumers by making foreign goods cheaper but hurts exports, while a weaker currency boosts exports.
- 😀 China has been known to keep its currency value low to maintain a favorable trade balance, which has been a point of contention with the US.
Q & A
What are the three main reasons people want to purchase foreign exchange?
-The three main reasons people want to purchase foreign exchange are for travel and tourism, for trade to buy foreign goods and services, and for investment purposes, such as purchasing foreign-denominated financial assets or making real investments like building factories overseas.
How does an increase in demand for a foreign currency affect its value?
-When the demand for a foreign currency increases, its value rises. This is called an appreciation of the currency. For example, if more tourists visit New Zealand or if companies invest in the country, the demand for the New Zealand dollar increases, causing it to appreciate relative to other currencies like the US dollar.
What happens to the value of the other currency when one currency appreciates?
-When one currency appreciates, the value of the other currency depreciates. In the example of the New Zealand dollar appreciating, the US dollar weakens relative to it, meaning the US dollar depreciates.
Who controls the supply of foreign currency and how can it be manipulated?
-The supply of foreign currency is controlled by the foreign government. A country can manipulate its currency value by decreasing or increasing the supply of its currency. For example, if the US wanted to raise the value of the dollar, it could decrease the supply of US dollars.
Why might a country manipulate its currency value?
-A country might manipulate its currency value to influence its trade balance. By keeping its currency cheap, it can make its exports more competitive abroad, while making foreign goods more expensive domestically, which can improve the trade balance.
How does the exchange rate affect the cost of foreign imports?
-The exchange rate determines how much foreign currency is needed to purchase foreign goods. If the foreign currency is cheaper, the cost of imports decreases. Conversely, if the foreign currency is stronger, the cost of imports increases.
What is an example of a situation where a country’s currency value is manipulated?
-An example of currency manipulation is China keeping its currency value artificially low to maintain a favorable trade balance. By doing so, Chinese exports remain cheaper and more attractive in global markets.
What is the relationship between a weak currency and a country's trade balance?
-A weak currency benefits a country's trade balance by making its exports cheaper for foreign buyers, leading to an increase in exports. At the same time, the cost of imports rises, which can reduce the volume of imports.
How does the appreciation of a currency affect a country's imports and exports?
-When a currency appreciates, it makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive. This typically leads to an increase in imports and a decrease in exports, potentially harming the country’s trade balance.
What is the significance of the exchange rate in international trade?
-The exchange rate is crucial in international trade because it determines how much of one currency is needed to purchase another currency, affecting the cost of foreign goods and services. A favorable exchange rate can boost a country's exports and improve its trade balance.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
VALUTA ASING DAN DEVISA - EKONOMI - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI
The Foreign Exchange Market- Macro 6.3

What is Forex trading basic lecture no#1 and how can we generate money in Forex Bright TrustAcademy

Mengapa Rupiah Bisa Menguat atau Melemah?
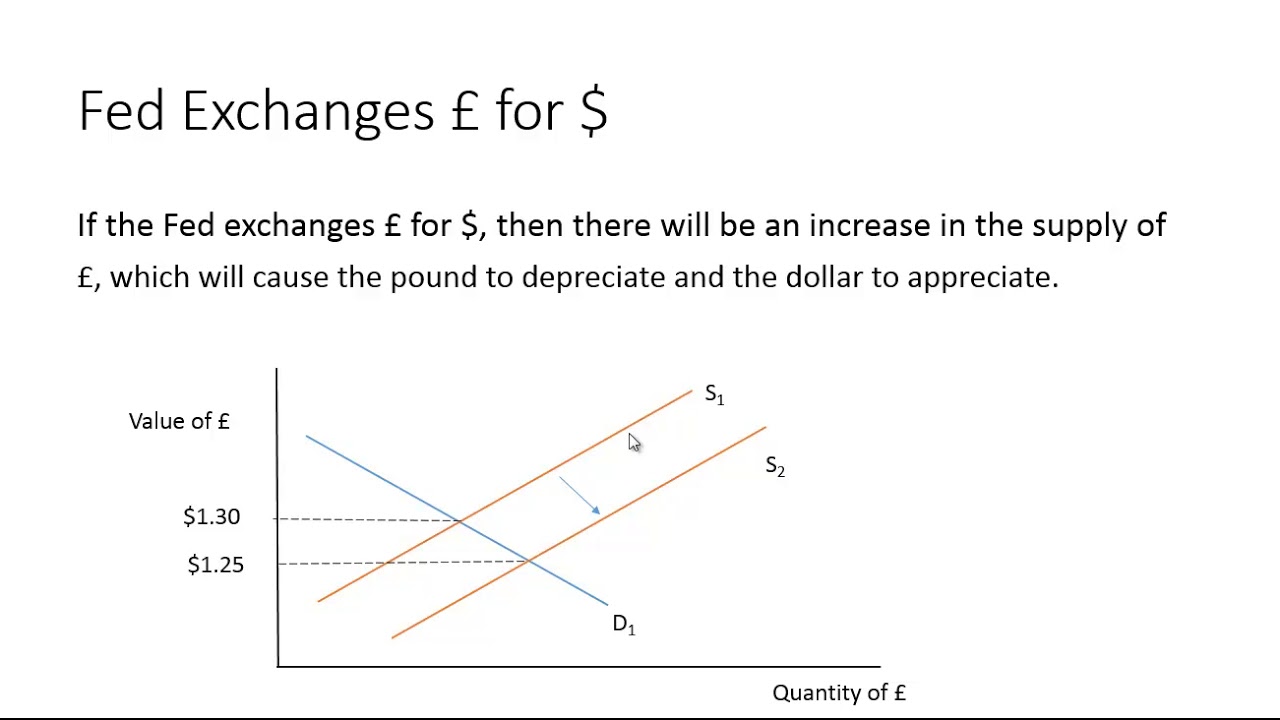
Foreign Exchange Government Intervention

What is Forex Market | How Forex Market Works | Foreign Exchange Market (हिंदी में )
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
