Konsep Otonomi Daerah : Yang Perlu Anda Tahu!
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the evolution of Indonesia's regional autonomy, tracing its development from the early days after independence to the reform-era laws of 1999, 2004, and 2014. The speaker explains key principles of regional autonomy, such as broad, real, and responsible autonomy, and emphasizes how these principles empower local governments to foster welfare and development. The video highlights both the benefits, like increased local resources and improved social-cultural development, and the challenges, such as disparities, lack of coordination, and reduced central oversight. Ultimately, the speaker advocates for a balanced approach to regional autonomy for the prosperity and welfare of the people.
Takeaways
- 😀 Regional autonomy (otonomi daerah) in Indonesia has evolved through multiple laws, starting from the 1945 Constitution and continuing with laws passed post-reformasi (reformation).
- 😀 The concept of regional autonomy provides regions with the authority to manage their own governance, with the goal of increasing local welfare and development.
- 😀 Three key principles of regional autonomy are: broad autonomy (otonomi luas), real autonomy (otonomi nyata), and responsible autonomy (otonomi bertanggung jawab).
- 😀 Broad autonomy (otonomi luas) grants regions the authority to govern and manage local issues independently, focusing on the region’s specific needs.
- 😀 Real autonomy (otonomi nyata) ensures that autonomy is aligned with the specific conditions and situations of each region, promoting local relevance and effectiveness.
- 😀 Responsible autonomy (otonomi bertanggung jawab) emphasizes that regional governments must use their authority to empower and improve the welfare of their citizens.
- 😀 The three core principles of regional autonomy are grounded in the legal concepts of decentralization, deconcentration, and delegated tasks.
- 😀 Decentralization (desentralisasi) transfers power from the central government to regional governments, allowing them to handle local affairs directly.
- 😀 Deconcentration (dekonsentrasi) involves delegating authority to regional representatives who act on behalf of the central government at the local level.
- 😀 Delegated tasks (tugas pembantuan) allow the central government or provinces to assign specific tasks to local governments to ensure effective implementation of national priorities.
- 😀 Regional autonomy, when implemented effectively, can lead to increased local prosperity, better resource utilization, and the development of social and cultural aspects of the community.
- 😀 However, if not managed well, regional autonomy can result in negative outcomes such as uneven development, social inequality, and a lack of coordination between regions.
Q & A
What is the concept of regional autonomy (Otonomi Daerah) in Indonesia?
-Regional autonomy refers to the decentralization of power from the central government to local governments, allowing them to manage and govern their own affairs according to their specific needs and conditions.
How did regional autonomy evolve in Indonesia?
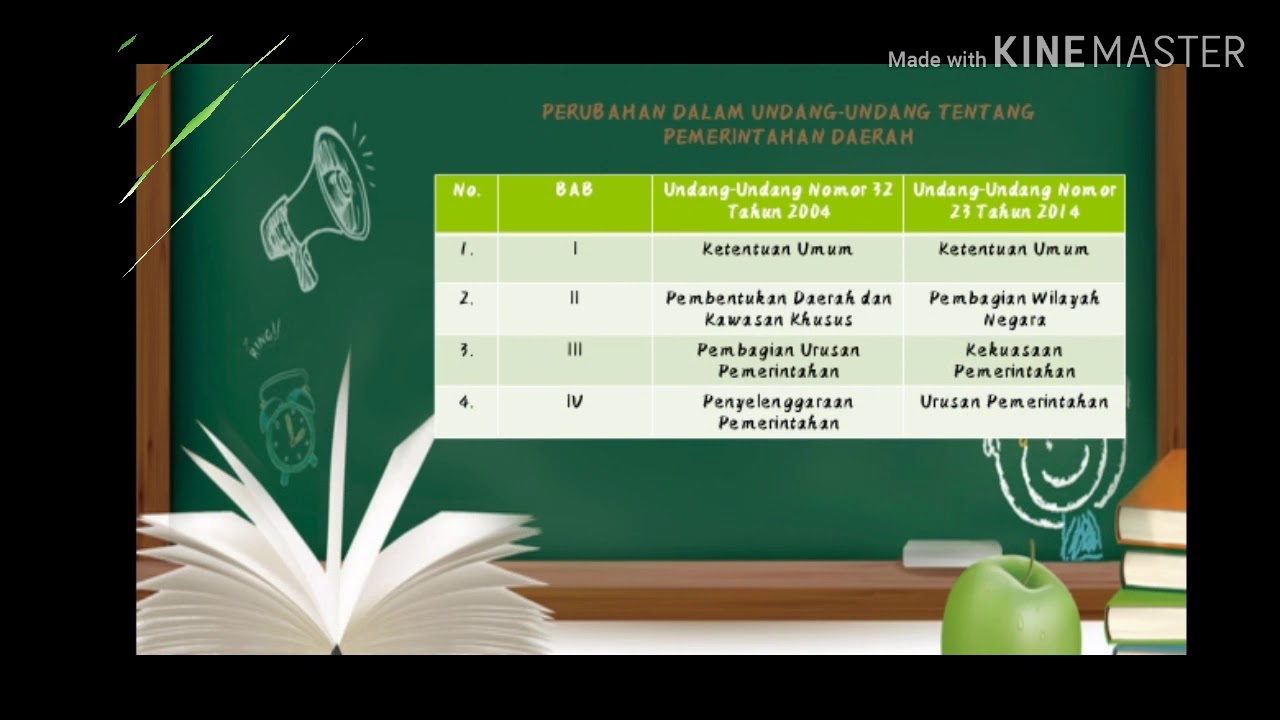
-The concept evolved through various laws starting from Law No. 1 of 1945, followed by Law No. 5 of 1974, Law No. 22 of 1999, Law No. 32 of 2004, and the most recent, Law No. 23 of 2014, reflecting the shift from centralization to decentralization after the 1998 reform movement.
What are the three main principles of regional autonomy?
-The three main principles are: Otonomi Luas (Wide Autonomy), Otonomi Nyata (Real Autonomy), and Otonomi Bertanggung Jawab (Responsible Autonomy). These principles ensure that local governments have the power, are tailored to local conditions, and are accountable for the welfare of their communities.
What is the significance of the 1945 Constitution in the context of regional autonomy?
-The 1945 Constitution laid the foundation for regional autonomy by establishing the relationship between the central government and local governments. It has undergone amendments to support the evolution of regional autonomy.
What is the difference between decentralization, deconcentration, and task delegation in regional governance?
-Decentralization involves giving local governments the authority to manage local affairs. Deconcentration gives regional offices of central government the authority to manage certain affairs. Task delegation refers to the central government or regional governments assigning certain tasks to local authorities.
Why is coordination between central and regional governments crucial in implementing regional autonomy?
-Coordination ensures that policies and resources are effectively distributed and that regional governments work harmoniously with central authorities to achieve national development goals and prevent regional disparities.
How does regional autonomy benefit the welfare of local communities?
-It allows local governments to use their knowledge of local conditions to better manage resources, develop tailored solutions, and promote social, cultural, and economic development, ultimately improving the welfare of the local population.
What are the potential negative impacts of regional autonomy if not managed properly?
-The negative impacts include slower development in poorer regions, social inequality, lack of coordination between regions, and weaker oversight, leading to mismanagement or corruption.
What is the role of local governments in maximizing regional potential?
-Local governments are responsible for identifying and maximizing regional resources, which can increase local income, accelerate development, and ensure the sustainability of regional growth.
How does regional autonomy contribute to equitable development across Indonesia?
-By granting more power to local governments, regional autonomy helps address specific local needs, promotes equitable distribution of resources, and ensures that each region's development is aligned with its potential and challenges.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)