The Future of Houseplants: Tissue Culture (TC)
Summary
TLDRTissue culture, or micropropagation, is a revolutionary biotechnology technique that allows rapid, sterile plant production from small tissue samples. By cultivating plant cells in a lab setting, it accelerates growth compared to traditional propagation methods. The process involves sterilizing plant tissue, placing it in nutrient-rich media with growth hormones, and inducing multiplication, rooting, and acclimation. This technique enables the production of genetically identical plants, enhances plant traits, and plays a crucial role in conservation efforts by preserving endangered species. Tissue culture is vital for large-scale propagation, new plant varieties, and advancing agricultural research.
Takeaways
- 😀 Tissue culture is a biotechnology technique that cultivates plant cells in a controlled lab environment, allowing for the rapid propagation of plants from small plant tissue samples.
- 🌱 The process is often called 'micropropagation' as it follows similar principles to asexual propagation methods like cutting and seed-based propagation.
- 🔬 The tissue culture process begins with selecting a small plant tissue (e.g., stem or leaf), sterilizing it to eliminate microorganisms, and then growing it on nutrient-rich media.
- 🧪 The most common nutrient medium used in tissue culture is MS (Murashige and Skoog) media, which contains essential plant nutrients, sugars, agar, and growth hormones like BAP (Cytokinin) and NAA (Auxin).
- 💡 The cytokinin BAP helps cells multiply, while the auxin NAA is used to induce rooting in the plant tissue during the propagation process.
- 🧼 Sterility is critical at every stage of tissue culture to prevent contamination. Tools, plant tissue, and the air in the lab are kept sterile using devices like laminar flow hoods, alcohol torches, and HEPA filters.
- 🔪 The plant tissue is sterilized by submerging it in a bleach solution, followed by rinsing with distilled water and ethanol before placing it in the nutrient media.
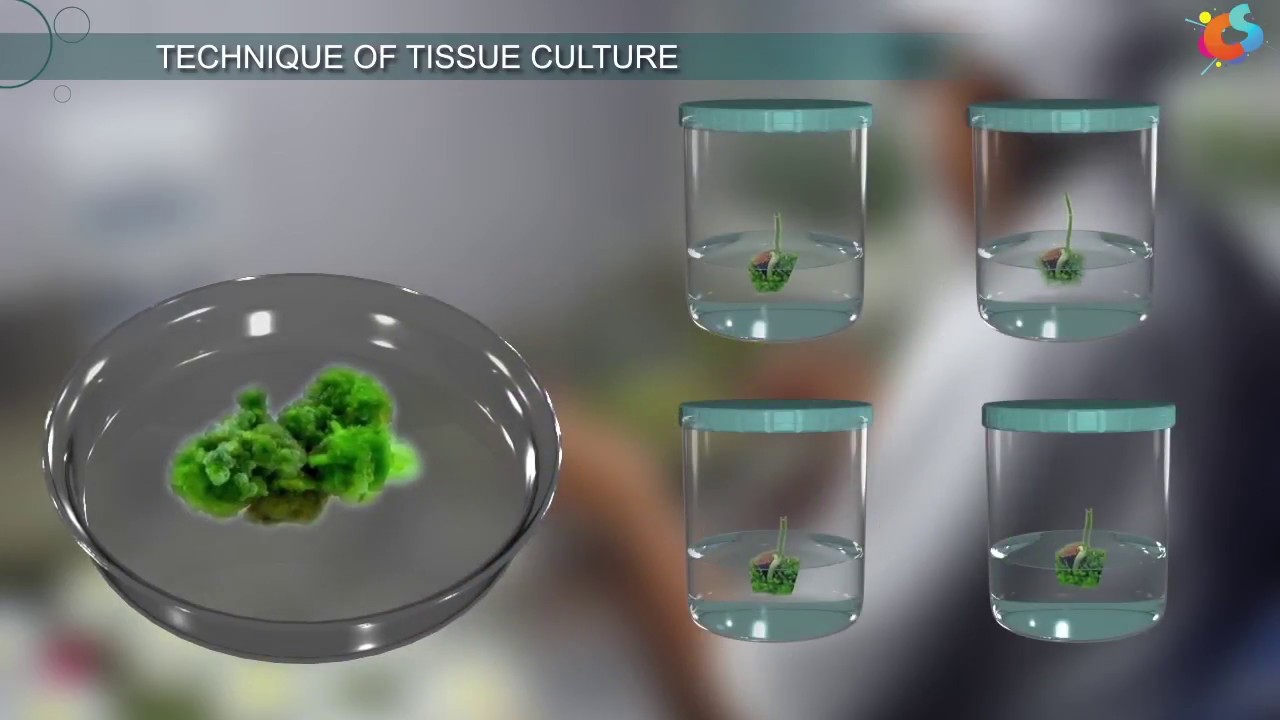
- 🌿 The plant tissue begins to grow and multiply, producing multiple shoots from a single explant, demonstrating the power of tissue culture to rapidly propagate plants.
- ⚙️ Once the plantlets have multiplied, they are subcultured to a fresh batch of multiplication media to continue growth and multiplication before being transitioned to rooting media.
- 🌳 After rooting, plants undergo an acclimation process in a controlled environment with high humidity and warmth before being transferred to a greenhouse for further growth.
- 💥 Tissue culture has the ability to create uniform, genetically identical plants, and it is especially useful for producing plants with desirable traits such as disease resistance and tolerance to environmental stress.
Q & A
What is tissue culture, and how does it differ from traditional plant propagation methods?
-Tissue culture is a biotechnology technique that cultivates plant cells in a controlled, sterile lab environment to rapidly grow plants from small pieces of plant tissue. Unlike traditional methods like seed and cutting propagation, tissue culture can expedite plant production, creating genetically identical plants from just a small section of plant tissue.
What is the most commonly used nutrient medium for tissue culture, and what does it contain?
-The most commonly used nutrient medium in tissue culture is called MS (Murashige and Skoog medium). It contains essential plant nutrients, sugars, agar (a solidifying agent), and growth hormones like BAP (a cytokinin) to stimulate cell division and NAA (an auxin) for rooting.
What role do growth hormones like BAP and NAA play in tissue culture?
-BAP (a cytokinin) promotes cell division and the multiplication of plant cells, while NAA (an auxin) is used to induce rooting, allowing plantlets to develop a root system in the culture medium.
What is the purpose of a laminar flow hood in a tissue culture lab?
-A laminar flow hood provides a sterile working environment by pushing air through a HEPA filter, which filters out contaminants and ensures that the workspace remains free of microorganisms, thus preventing contamination of plant tissue cultures.
How is sterilization achieved in tissue culture, and why is it important?
-Sterilization is crucial in tissue culture to prevent contamination by bacteria, fungi, or pathogens. Plant tissues are sterilized using bleach solutions and alcohol, and tools like forceps and razor blades are also sterilized using alcohol torches. Maintaining sterility is critical to the success of tissue culture.
What is the process of acclimating tissue-cultured plants, and why is it necessary?
-Acclimation involves transferring tissue-cultured plants into a controlled environment with high humidity, warm temperatures, and limited exposure to biological contaminants. This process helps the plants adapt to normal greenhouse conditions before being transferred to outdoor environments. It is essential to prevent shock and ensure successful growth.
What types of plants are most commonly grown through tissue culture?
-Common plants grown through tissue culture include houseplants like peace lilies, alocasias, philodendrons, calatheas, anthuriums, and Ficus. These plants are often propagated in tissue culture to ensure uniformity, disease resistance, and the production of stable variegation.
What are the potential downsides or challenges associated with tissue culture?
-One challenge is that newer generations of plants, like the Monstera deliciosa 'Thai Constellation', produced through tissue culture may be more susceptible to diseases like Pythium and other root and stem infections. Additionally, the process requires high levels of precision and control, which can be labor-intensive.
How does tissue culture contribute to plant conservation efforts?
-Tissue culture plays a vital role in plant conservation by preserving endangered species. It allows for the storage of genetic material in culture banks, which can be used to regenerate and restore populations of threatened plants, ensuring their survival.
How does tissue culture support advancements in plant biotechnology?
-Tissue culture is a powerful tool in plant biotechnology as it enables the rapid propagation of plants, genetic modification for desirable traits (e.g., disease resistance, drought tolerance), and the development of new plant varieties. It also helps improve crop yields and supports research in agriculture and plant science.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

#bioteknologi #kulturjaringantumbuhan #biologisma BIOTEKNOLOGI MODERN | KULTUR JARINGAN TUMBUHAN
Tissue Culture

Kultur Jaringan, Apa Faedahnya?

Jaringan Pada Tumbuhan Kelas 11 | Sifat Totipotensi Pada Tumbuhan Dan Kultur Jaringan

Mengenal Teknik Kultur Jaringan Tanaman

Bioteknologi Konvensional di bidang lainnya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
