Perbedaan X-Ray Konvensional & X-Ray Mobile
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the differences between conventional X-ray and mobile X-ray (X-ray Mobile) machines, detailing their functions and operating principles. The presenters, students from Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, outline the components and workings of both X-ray systems, including the high-voltage transformers, filaments, and the role of capacitors. Conventional X-rays are stationary and require external power sources, while mobile X-ray machines are portable and can operate on battery power. The video serves as an educational overview of these technologies, emphasizing their diagnostic capabilities and distinct operational features.
Takeaways
- 😀 X-ray machines are essential diagnostic tools used for radiography and fluoroscopy, capable of producing X-rays to examine internal body structures.
- 😀 Conventional X-ray machines are fixed in specific rooms and require a stable power supply, usually from PLN (electrical grid).
- 😀 Mobile X-ray machines offer flexibility as they can be moved between rooms and operate on battery power or standard electrical outlets.
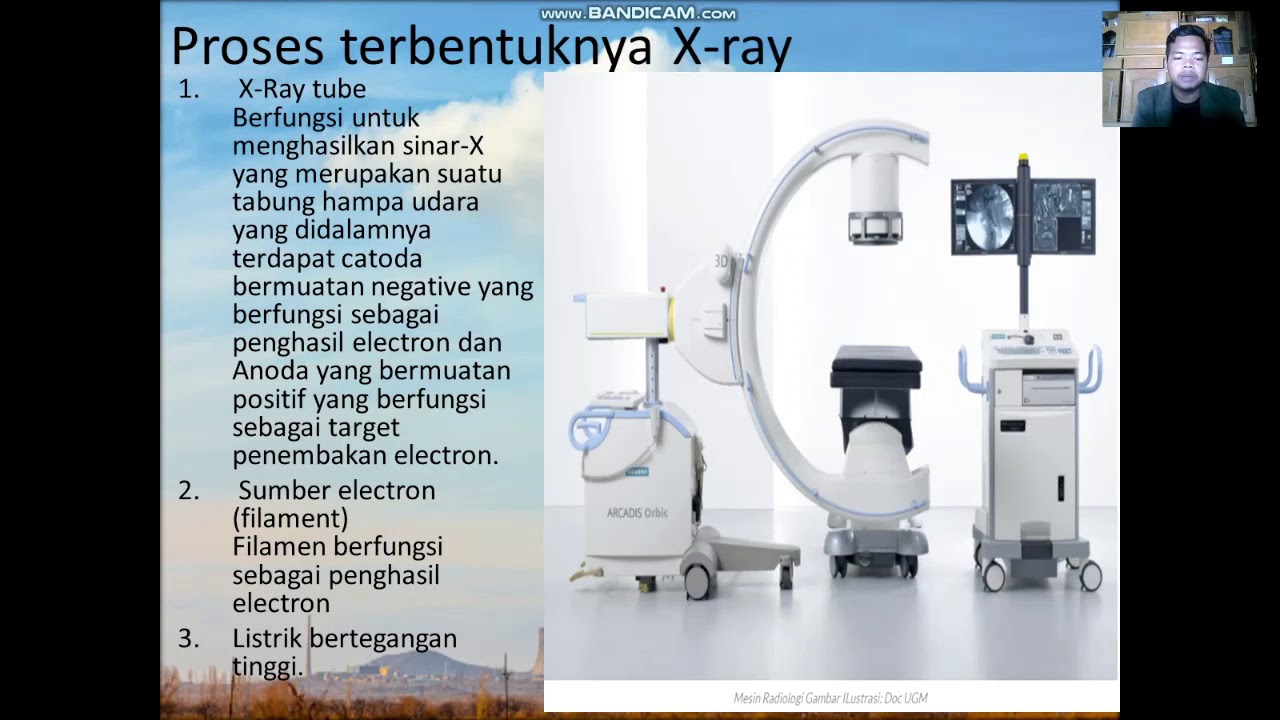
- 😀 The X-ray process begins with a heated cathode that releases electrons, which are then accelerated towards the anode, generating X-rays.
- 😀 High voltage systems, including transformers, are crucial in both conventional and mobile X-ray machines for creating the necessary energy to produce X-rays.
- 😀 Conventional X-ray systems have a fixed setup with components like transformers, filaments, and capacitors to manage electrical power and radiation output.
- 😀 Mobile X-ray systems use rechargeable batteries and capacitors to generate X-rays, offering more portability compared to conventional systems.
- 😀 The main difference between conventional and mobile X-ray systems lies in mobility; mobile X-rays can be used in various locations, whereas conventional ones are stationary.
- 😀 Mobile X-ray machines can be powered by either AC (220V) from the power grid or DC from batteries, making them adaptable for various settings.
- 😀 Both types of X-ray machines use similar technology, such as transformers, filaments, and capacitors, but mobile X-rays are designed for more flexible and portable use.
Q & A
What is the purpose of this video presentation?
-The purpose of the video is to explain the working principles of conventional X-ray systems and mobile X-ray machines as part of an academic assignment for a course on advanced radiology equipment at Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
What are the key components of a conventional X-ray machine?
-The key components of a conventional X-ray machine include the X-ray tube (with cathode and anode), transformers, a power supply system, compensators, and a high-voltage generator. Additionally, the system includes a radiator and protective shielding.
How does an X-ray tube generate X-rays?
-An X-ray tube generates X-rays by heating the cathode filament, which releases electrons. These electrons are then accelerated towards the anode. When they strike the anode target, they suddenly stop, releasing energy in the form of X-rays.
What role does the diaphragm or collimator serve in the X-ray system?
-The diaphragm or collimator regulates the radiation beam, ensuring that it is directed precisely and safely, preventing unnecessary radiation exposure. It also limits the leakage of radiation, keeping it below allowable limits.
What is the difference between conventional X-ray and mobile X-ray systems?
-The main difference between conventional X-ray and mobile X-ray systems is mobility. Conventional X-ray machines are fixed in one location, typically in a dedicated room, while mobile X-ray systems are portable and can be moved between different rooms or environments.
What power sources can a mobile X-ray system use?
-A mobile X-ray system can operate using either AC power from a standard electrical source (220V AC) or DC power from an internal battery, providing flexibility in various clinical settings.
What is the purpose of the inverter in a mobile X-ray system?
-The inverter in a mobile X-ray system converts AC power from the electrical grid into DC power to charge the capacitors, which store energy for the X-ray generation process.
How does the capacitor in a mobile X-ray system work?
-The capacitor in a mobile X-ray system stores electrical energy, which is then discharged to power the X-ray tube, generating the X-rays. Once the capacitor is fully charged, it releases the stored energy to initiate the X-ray generation process.
What is the function of the high-voltage transformer in both X-ray systems?
-The high-voltage transformer in both conventional and mobile X-ray systems increases the voltage between the cathode and anode to the necessary levels for generating X-rays. It is crucial for achieving the required energy to accelerate electrons in the X-ray tube.
How do the two X-ray systems differ in terms of energy generation?
-Conventional X-ray systems rely on AC power from the electrical grid, while mobile X-ray systems can use either AC power or battery-powered energy, making mobile systems more flexible and adaptable for use in different locations.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)