❌ STOP using the 'future tenses' in English - THIS is how we REALLY do it! (Full Grammar Lesson)
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the speaker challenges the conventional belief of a 'future tense' in English, explaining that technically there is no specific future tense. Instead, English uses various structures like 'will,' 'to be going to,' present continuous, and present simple to talk about future events. The speaker provides clear examples of the future simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous tenses, highlighting their uses for predictions, plans, and completed actions. The video also offers a free PDF guide and a quiz to help learners test their understanding of these future forms.
Takeaways
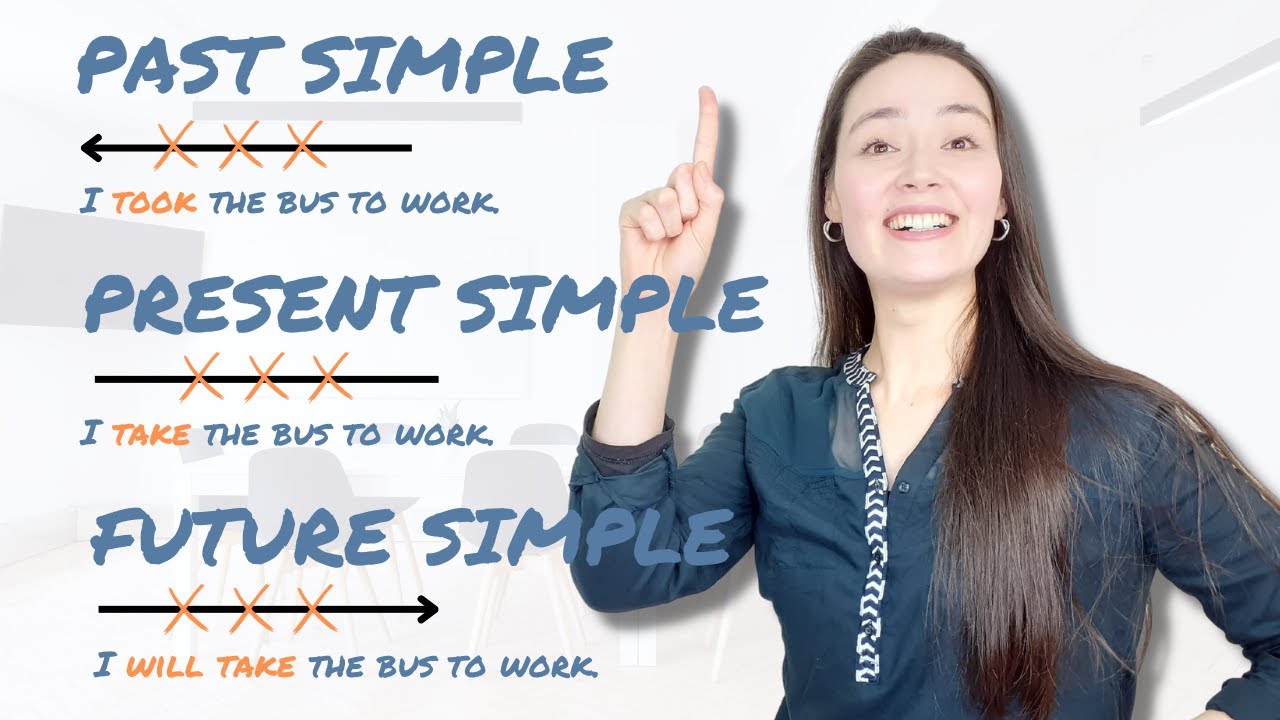
- 😀 There's no specific 'future tense' in English, as English doesn't use verb inflections to indicate the future.
- 😀 English has two main tenses: the present and the past, which are further divided into aspects like continuous and perfect.
- 😀 The future is expressed through modal verbs like 'will,' 'going to,' and structures such as present continuous and present simple.
- 😀 'Will' is the most common way to express the future, used in future simple, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous.
- 😀 Future simple (will + base verb) is used for predictions, spontaneous decisions, offers, and promises.
- 😀 Future continuous (will + be + -ing verb) is used for actions in progress at a future time, such as plans or events happening in the future.
- 😀 Future perfect (will + have + past participle) expresses actions that will be completed by a certain time in the future.
- 😀 Future perfect continuous (will + have been + -ing verb) emphasizes the duration of an action that will be ongoing at a future time.
- 😀 Some verbs like 'work,' 'live,' and 'play' can be used interchangeably in the future perfect simple and continuous, with minimal difference in meaning.
- 😀 Alternatives to 'will' include 'to be going to' (for predictions and plans) and present continuous (for arrangements), with the present continuous often indicating more certainty about plans.
Q & A
Why does the speaker claim there is no future tense in English?
-The speaker claims there is no future tense in English because there is no specific verb inflection for the future. Instead, future actions are expressed using other grammatical structures like modal verbs and auxiliary verbs.
What are the two main tenses in English according to the video?
-According to the video, the two main tenses in English are the present and the past. All other tenses, such as continuous or perfect, are variations of these two.
What role does the verb 'will' play in expressing future actions?
-'Will' is a modal verb used to form different future tenses, such as future simple, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous. It helps to indicate actions that will happen in the future.
Can 'will' be used for both predictions and decisions made at the moment of speaking?
-Yes, 'will' is used to make predictions about the future, as well as to describe decisions made spontaneously while speaking. For example, 'I will walk him' shows a decision made in the moment.
How is the future continuous tense formed, and what is its purpose?
-The future continuous tense is formed using 'will + be + -ing verb' and is used to describe actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. For example, 'I will be walking to work tomorrow.'
What is the difference between the future perfect simple and the future perfect continuous?
-The future perfect simple ('will have + past participle') talks about actions that will be completed by a certain future time, while the future perfect continuous ('will have been + -ing verb') emphasizes the duration of an action that will be ongoing until that time.
Why is the verb 'work' used in both the future perfect simple and continuous with similar meaning?
-The verb 'work' can be used in both the future perfect simple and continuous tenses without a significant change in meaning. Both tenses suggest the completion of the action by a future point, but the continuous form emphasizes the duration of the action.
How does the structure 'to be going to' differ from the present continuous when expressing future intentions?
-'To be going to' is used to talk about future plans or predictions based on current evidence, while the present continuous indicates a more definite plan or arrangement, often involving prior decisions and specific details.
What types of events do we use the present simple tense for in relation to the future?
-The present simple tense is used for scheduled or timetabled events in the future, such as public transport times or events that are fixed and not influenced by personal intention. For example, 'The train leaves at 9 AM tomorrow.'
What distinction does the speaker make between the present continuous and 'to be going to' in expressing future events?
-The distinction is that the present continuous is used for firm arrangements where the details are already decided, whereas 'to be going to' is used for plans that may be less fixed or based on current intentions or predictions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Perbedaan Present Perfect, Past Perfect, dan Future Perfect - Materi Bhs. Inggris Kelas XI Peminatan

The Usages of Present Simple Tense

Simple Future Tense: Fungsi, Rumus dan Contoh - Kampung Inggris LC

PEMBAHASAN LENGKAP LONGMAN TOEFL EXERCISE SKILLS 33-36 || PROBLEMS WITH THE USE OF THE VERB
ALL SIMPLE TENSES in English - present simple | past simple | future simple

Simple Future Tense/Pengertian dan contoh kalimatnya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
