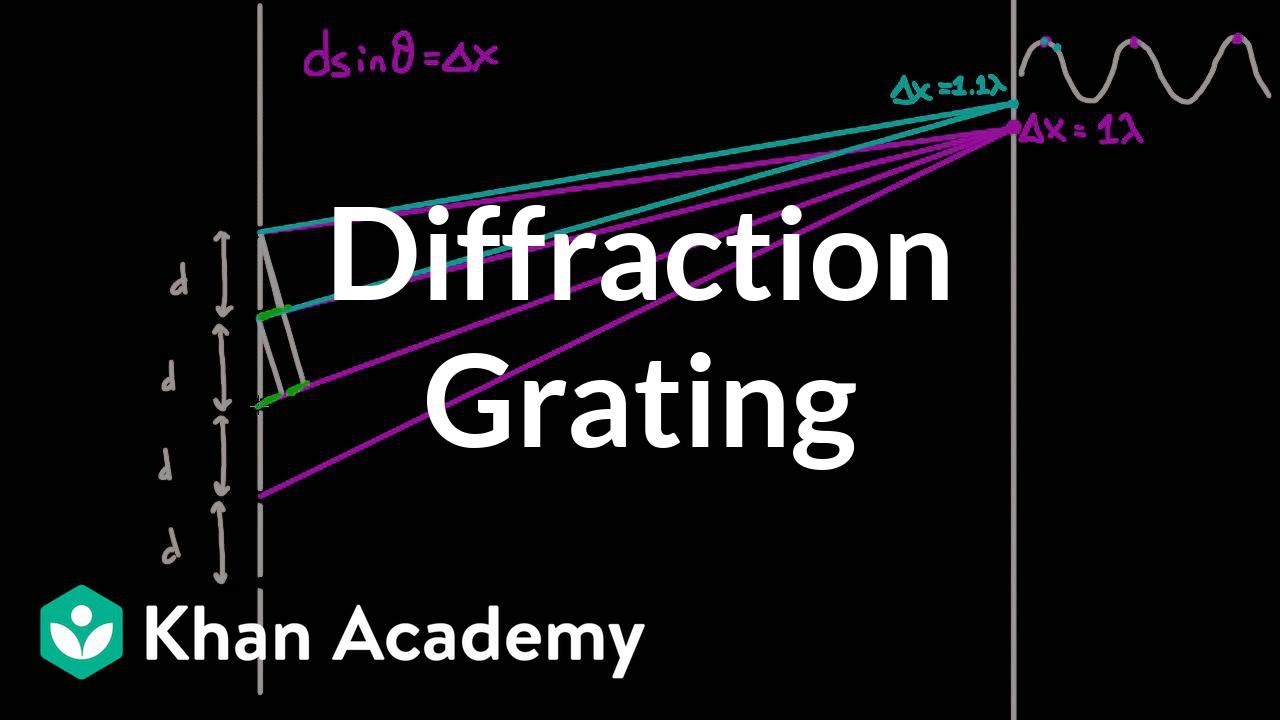
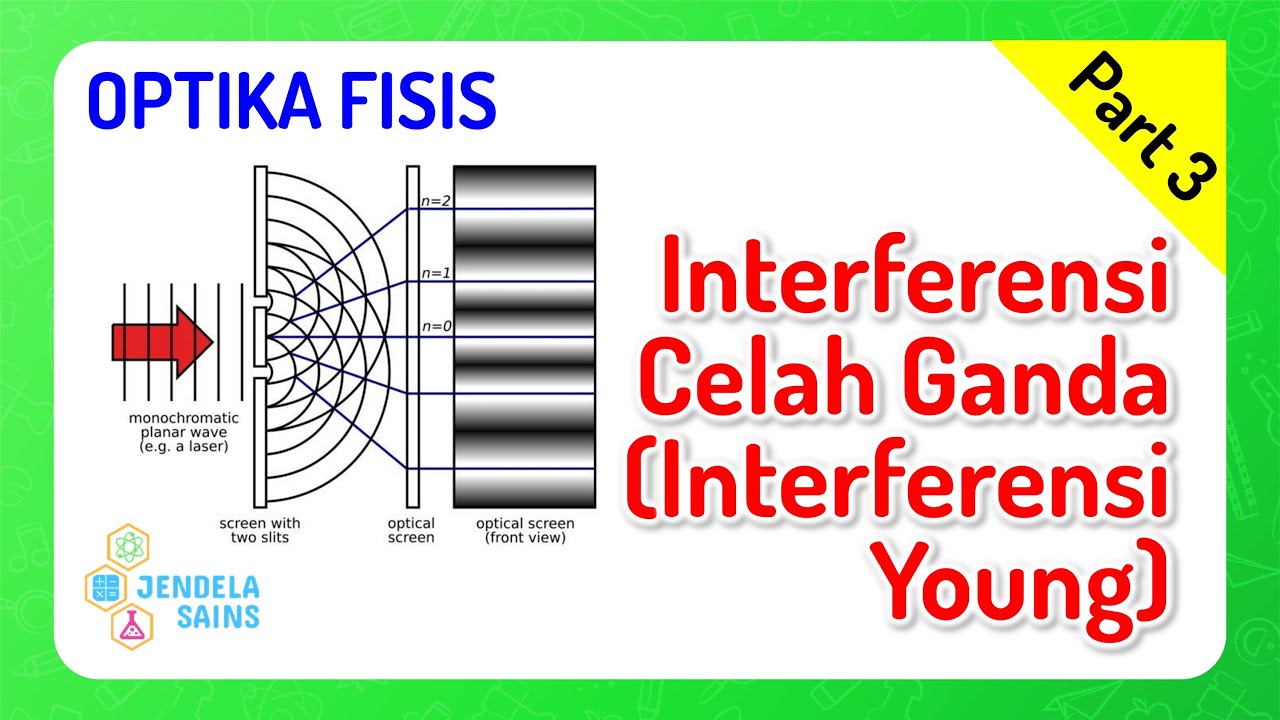
DEMO:To determine the wavelength of spectral line of mercury light using Plane Transmission Grating.
Summary
TLDRIn this educational experiment, students explore the diffraction of light using a plane transmission grating. The process involves measuring diffraction angles for various colors of light—red, green, and violet—using a spectrometer. By applying a grating equation, the wavelengths of these colors are calculated. The experiment emphasizes key concepts like diffraction, the bending of light, and the use of precise measurement tools like Vernier and main scales. The findings reveal the diffraction patterns of light, with wavelengths close to theoretical values, providing insights into the wave nature of light and its interaction with materials.
Takeaways
- 😀 The experiment demonstrates the spectral lines of mercury using a plane transmission grating and spectrometer.
- 😀 Diffraction is the key principle of the experiment, which involves the bending of light around sharp corners.
- 😀 The formula used for the experiment relates the wavelength of light to the diffraction angle: nλ = (a + b) sin θ.
- 😀 The spectrometer is used to measure diffraction angles for different colors of light (red, green, violet).
- 😀 The experiment measures the wavelength of light by calculating the diffraction angles for each color in the visible spectrum.
- 😀 The diffraction pattern of mercury light consists of seven colors, each corresponding to different wavelengths.
- 😀 Red light has the longest wavelength, followed by green and violet, which have progressively shorter wavelengths.
- 😀 Vernier and main scales are used to measure the angles accurately, with readings taken for each color of light.
- 😀 The calculated wavelengths for red, green, and violet light are 3529 Å, 4900 Å, and 3730 Å, respectively.
- 😀 The experiment demonstrates how diffraction depends on the wavelength of light, with shorter wavelengths diffracting at larger angles.
- 😀 A percentage error is calculated for each wavelength by comparing the experimental value with the expected value, providing insight into the accuracy of measurements.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the experiment described in the script?
-The main objective of the experiment is to determine the wavelengths of different colors in the visible spectrum of mercury light using a spectrometer with a plane transmission grating.
What phenomenon does the experiment primarily demonstrate?
-The experiment primarily demonstrates the diffraction phenomenon, which is the bending of light as it passes through narrow slits or around obstacles.
How is the diffraction angle related to the wavelength of light?
-The diffraction angle is directly related to the wavelength of light, with shorter wavelengths producing smaller diffraction angles and longer wavelengths producing larger diffraction angles.
What is the formula used to calculate the wavelength of light in the experiment?
-The formula used is: n λ = d (sin θ + b), where n is the diffraction order, λ is the wavelength, d is the slit separation, and θ is the diffraction angle.
What is the role of the plane transmission grating in the experiment?
-The plane transmission grating splits the incoming light into its component colors by diffracting the light into different angles based on its wavelength. This allows the experimenter to measure the angles for each color.
Why are three colors (red, green, violet) chosen for this experiment?
-Three colors are chosen to demonstrate the varying diffraction angles for different wavelengths. These colors represent different parts of the visible spectrum and help in measuring the accuracy of the diffraction and wavelength calculations.
How is the angle for diffraction measured in the experiment?
-The angle for diffraction is measured using a spectrometer with Vernier and main scales. The crosswires are set to align with the diffracted light peaks, and the angle is then recorded and used for calculations.
What are the measured wavelengths for red, green, and violet light in the experiment?
-The measured wavelengths are: 5232 Å for red light, 4900 Å for green light, and 3529 Å for violet light.
How is the percentage error calculated in this experiment?
-The percentage error is calculated by comparing the experimentally measured wavelengths with the known theoretical wavelengths for the colors used in the experiment.
What is the significance of the plane transmission grating having 15,000 lines per inch?
-The plane transmission grating with 15,000 lines per inch provides a high resolution for diffraction, allowing for accurate measurement of the diffraction angles and thereby precise determination of the wavelengths of the light.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)