Prinsip Kerja Generator AC
Summary
TLDRThis lecture provides an in-depth exploration of synchronous generators, focusing on their principles of operation based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. It discusses the essential components, including the rotor and stator, and illustrates how mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through induced electromotive force (EMF). The lecture also covers the right-hand rule for determining the direction of induced current, the generation of alternating current (AC), and the differences between single-phase and three-phase systems, highlighting the efficiency and stability of three-phase generation in electrical applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Synchronous generators, also known as alternators, convert mechanical energy into electrical energy using a prime mover like a diesel engine.
- 😀 The generation of electromotive force (EMF) is explained by Faraday's law, which states that a change in magnetic flux induces voltage in a coil.
- 😀 Two types of EMF generation exist: transformer EMF, used in transformers, and rotational EMF, used in generators.
- 😀 Key components of a synchronous generator include the coil (armature), the magnetic field, and the relative motion between them.
- 😀 Fleming's Right-Hand Rule helps determine the direction of induced current: the thumb indicates motion, the index finger shows magnetic field direction, and the middle finger points to the induced current.
- 😀 The rotation of the coil within the magnetic field produces alternating current (AC), with the current direction changing as the coil moves through different positions.
- 😀 Single-phase generation requires one coil, while three-phase generation needs three coils spaced 120 degrees apart to produce three simultaneous waveforms.
- 😀 The frequency of the generated current is related to the speed of the rotor and the number of poles in the generator, governed by the formula f = (P × n) / 120.
- 😀 For every complete rotation of the rotor, two AC waveforms are produced, showing the relationship between physical rotation and electrical output.
- 😀 Understanding these principles is essential for effectively designing and operating synchronous generators in power generation.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a synchronous generator?
-The primary function of a synchronous generator is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
What law explains the generation of electromotive force (emf) in generators?
-The generation of electromotive force in generators is explained by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
What are the three essential components required for generating emf in a synchronous generator?
-The three essential components required are a coil, a magnetic field, and relative motion between the coil and the magnetic field.
How can the direction of induced current in a generator be determined?
-The direction of induced current can be determined using Fleming's right-hand rule, which correlates the motion of the conductor, the magnetic field, and the direction of current.
What roles do the stator and rotor play in a synchronous generator?
-In a synchronous generator, the stator is the stationary part that contains the armature winding, while the rotor is the rotating part that houses the magnetic poles.
How does the rotation of the armature lead to the generation of alternating current (AC)?
-As the armature rotates, the direction of the induced current changes periodically, resulting in the generation of alternating current (AC).
What is the relationship between the speed of the rotor and the frequency of the generated AC?
-The frequency of the generated AC is directly related to the speed of the rotor and the number of poles in the generator.
What is the formula to calculate the frequency of a synchronous generator?
-The frequency can be calculated using the formula: f = (P × n) / 120, where P is the number of poles and n is the rotor speed in RPM.
What distinguishes a single-phase generator from a three-phase generator?
-A single-phase generator produces one full wave per cycle using one armature winding, while a three-phase generator produces three simultaneous waves using three armature windings spaced 120 degrees apart.
Why is understanding synchronous generators important in electrical engineering?
-Understanding synchronous generators is crucial because they are widely used in power generation systems, including renewable energy applications like wind and hydroelectric power.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

MK Elektrodinamika - Persamaan Maxwell

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 9 Bab 4 Magnet

INDUKSI ELEKTROMAGNETIK || KEMAGNETAN || DINAMO || TRANSFORMATOR || IPA || KELAS 9

All of MAGNETIC FIELDS in 15 mins - A-level Physics

Electromagnetic Induction Revision in 20 minute || Chapter 6 class 12 Physics oneshot || CBSE/MP/UP
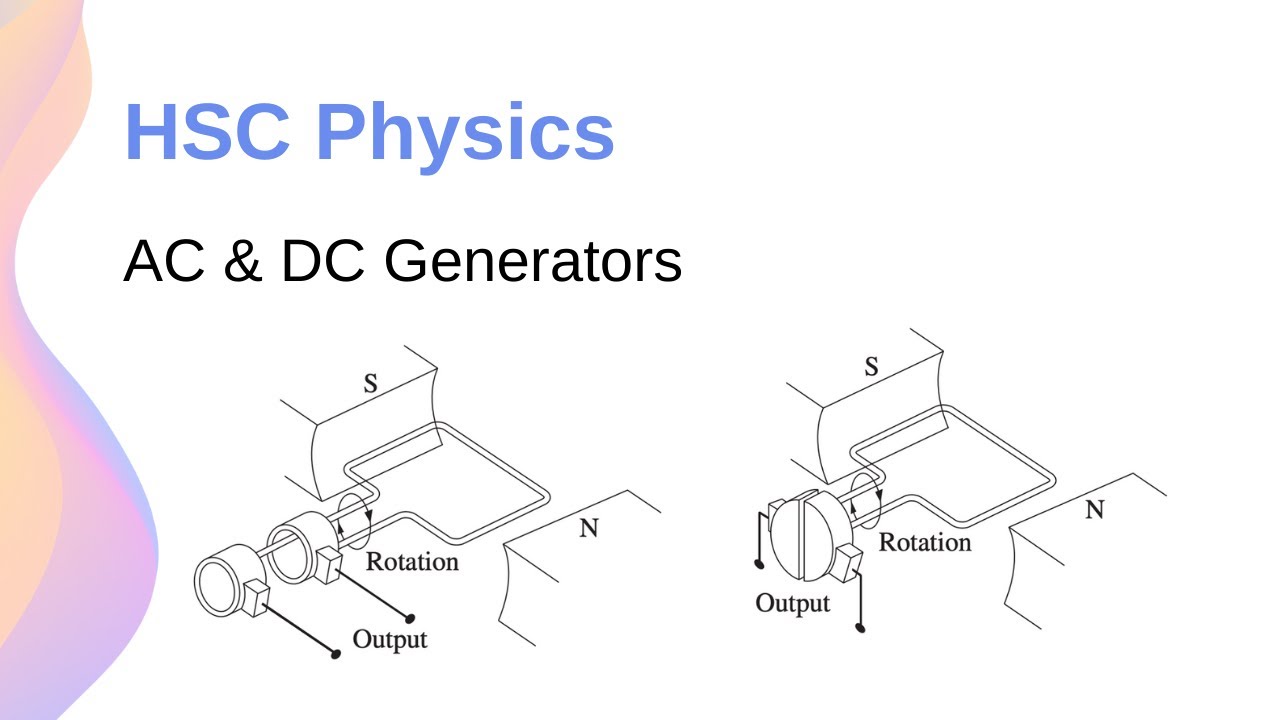
How Do AC and DC Generators Work? // HSC Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
