Pharmacokinetics 4 - Metabolism
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial on pharmacokinetics explores drug metabolism, highlighting its primary occurrence in the liver and the significance of first-pass metabolism, which can drastically reduce drug efficacy when taken orally. It introduces cytochrome P450 enzymes, crucial for metabolizing various drugs through processes like oxidation and hydrolysis. The tutorial delineates two metabolic phases: Phase 1, where drugs are chemically modified, and Phase 2, which enhances their water solubility for easier excretion. The example of aspirin as a prodrug is used to illustrate these concepts, setting the stage for future discussions on drug excretion.
Takeaways
- 😀 Drug metabolism primarily occurs in the liver but can also take place in the lungs and gut.
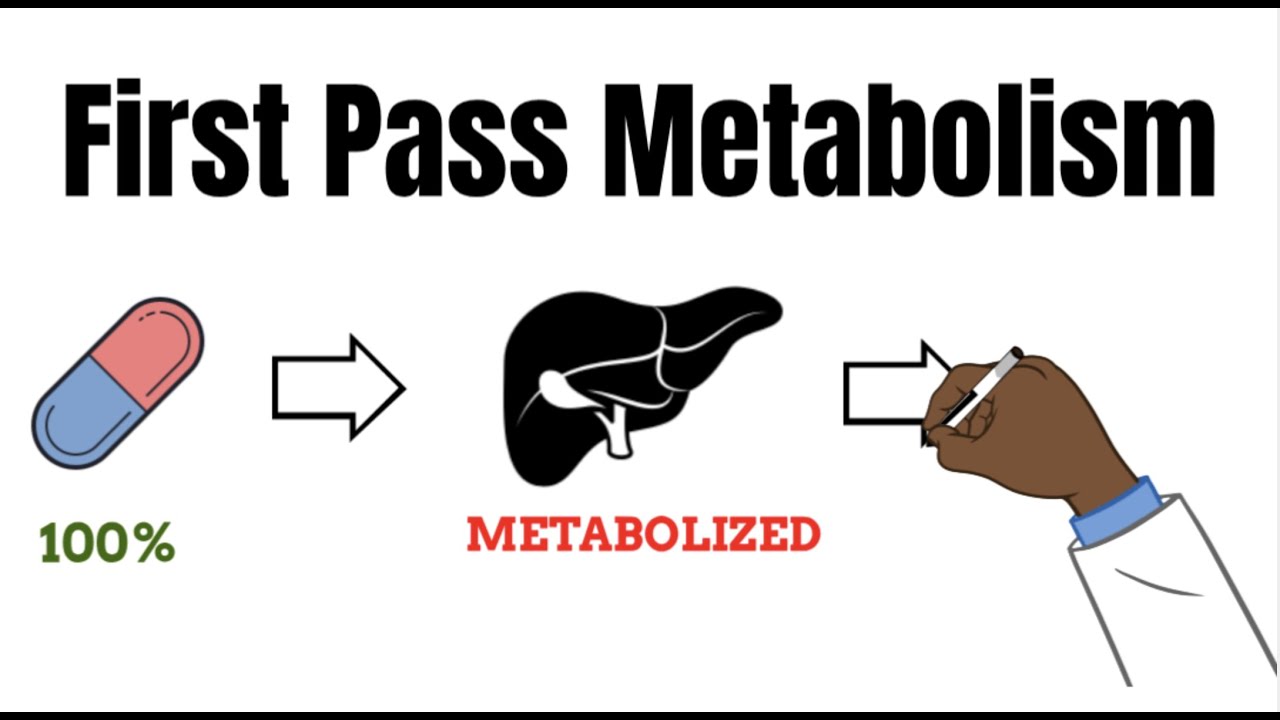
- 🤔 First-pass metabolism can significantly reduce the amount of active drug reaching systemic circulation after oral administration.
- 💉 Intravenous administration may be necessary for some drugs, like morphine, to bypass first-pass metabolism.
- 🔬 Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP) play a crucial role in drug metabolism, with different types metabolizing specific drugs.
- ☕ CYP1A2 metabolizes caffeine, while CYP2E1 is responsible for metabolizing alcohol.
- ⚗️ Phase 1 metabolism involves chemical modifications of drugs, such as oxidation, hydrolysis, and hydroxylation.
- 💧 Hydroxylation introduces a hydroxyl group, which becomes a target for larger molecules in subsequent metabolism.
- 🔗 Phase 2 metabolism involves conjugating the drug with larger molecules, like glucuronic acid, to enhance water solubility.
- 💊 Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a prodrug that must be metabolized to salicylic acid to become active.
- 🏃♂️ The process of drug metabolism prepares drugs for excretion by increasing their hydrophilicity, facilitating elimination through the kidneys.
Q & A
What is drug metabolism, and where does it primarily occur?
-Drug metabolism is the process by which the body chemically alters drugs. It primarily occurs in the liver, although it can also take place in other organs like the lungs and gut.
What is first pass metabolism, and why is it significant?
-First pass metabolism refers to the initial metabolism of a drug by the liver before it enters systemic circulation. It is significant because it can dramatically reduce the amount of active drug available in the bloodstream, sometimes necessitating intravenous administration.
What are cytochrome P450 enzymes, and what role do they play in drug metabolism?
-Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP) are a family of enzymes found abundantly in the liver that metabolize various drugs through processes such as oxidation, hydrolysis, and hydroxylation.
Can you give an example of a drug metabolized by a specific cytochrome P450 enzyme?
-CYP1A2 metabolizes caffeine, while CYP2E1 metabolizes alcohol, showcasing the specificity of different cytochrome P450 enzymes for various substances.
What happens during Phase 1 metabolism?
-In Phase 1 metabolism, a cytochrome P450 enzyme modifies the drug molecule, often converting a hydrogen atom into a hydroxyl group, which prepares the drug for further modification.
What is the significance of hydroxylation in drug metabolism?
-Hydroxylation adds a hydroxyl group to the drug, making it more polar and creating a target for larger molecules to attach in Phase 2 metabolism, facilitating easier excretion.
How does Phase 2 metabolism differ from Phase 1 metabolism?
-Phase 1 metabolism focuses on modifying the drug molecule itself, while Phase 2 metabolism involves conjugating the modified drug with larger molecules, such as glucuronic acid, to enhance water solubility for excretion.
What is an example of a prodrug, and how does it work?
-Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is an example of a prodrug. It is metabolized in the body to its active form, salicylic acid, which is responsible for its therapeutic effects.
Why is water solubility important in drug metabolism?
-Increased water solubility is important because it allows the drug to be easily filtered and excreted by the kidneys, facilitating the elimination of drugs and their metabolites from the body.
What can be concluded about the importance of understanding drug metabolism?
-Understanding drug metabolism is crucial for predicting drug behavior in the body, optimizing therapeutic efficacy, and minimizing potential side effects or drug interactions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)