¿Qué es el electromagnetismo? | 101 Videos
Summary
TLDRThe video explores electromagnetism, one of the four fundamental forces of nature, detailing its role in generating light and energy while holding atoms together. It explains how electric charges interact, creating electric fields and currents that form magnetic fields. The electromagnetic spectrum is introduced, highlighting visible light and various invisible waves, including radio and gamma radiation. Furthermore, the video discusses the geodynamo effect, where liquid metals beneath the Earth's surface generate electric currents and magnetic fields, making Earth a giant electromagnet that protects us from harmful space radiation.
Takeaways
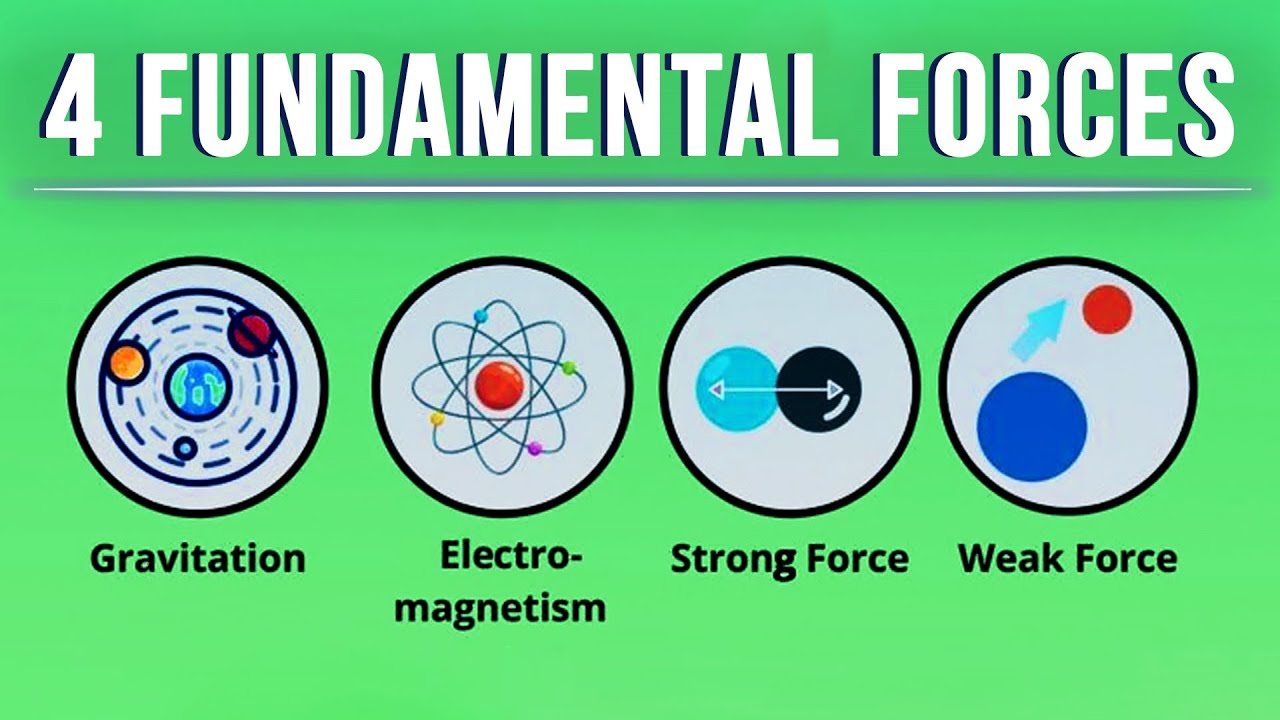
- ⚡ Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
- 🌌 It generates light, energy, and holds atoms and matter together.
- 🔌 Electromagnetism studies the interactions between electric and magnetic fields.
- 🔋 All matter has an electric charge: positive, negative, or zero.
- 🧲 Opposite charges attract, while like charges repel each other.
- 🌊 Moving electrically charged particles create an electric current and a magnetic field.
- 🌈 The electromagnetic spectrum includes various frequencies, with visible light in the middle.
- 📡 Low-frequency waves include radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves.
- 🔭 High-frequency waves like ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation can penetrate the human body, useful in medical applications.
- 🌍 Earth's geodynamo generates electric currents and magnetic fields, making the planet a giant electromagnet and providing a protective layer against harmful radiation.
Q & A
What is electromagnetism?
-Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature that studies the interactions between electric and magnetic fields, generating light and energy, and holding atoms together.
What are the types of electric charges?
-There are three types of electric charges: positive, negative, and neutral (zero). Opposite charges attract, while like charges repel each other.
How is an electric field formed?
-An electric field is formed when atoms gain a positive or negative charge through the transfer of electrons.
What happens when electrically charged particles move?
-When electrically charged particles start to move, they create a flowing electric current, which in turn generates a magnetic field around it.
What is the electromagnetic field?
-An electromagnetic field is generated when interacting electric and magnetic fields continuously produce and sustain one another, transmitting waves of electromagnetic energy or radiation into space.
What determines the intensity of electromagnetic radiation?
-The intensity of electromagnetic radiation is determined by its frequency.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
-The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all the frequencies of electromagnetic waves, including visible light, radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma radiation.
How do high-frequency waves interact with the human body?
-High-frequency waves, such as ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma radiation, can pass through the human body, making them useful for medical applications.
What is the geodynamo?
-The geodynamo is a process occurring thousands of miles below the Earth's surface where liquid metals churn and flow, generating electric currents that produce magnetic fields encompassing the planet.
What protective function does Earth's magnetic field serve?
-Earth's magnetic field acts as a protective layer that shields us from harmful radiation in space, allowing us to enjoy a stable environment.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)