Ikatan Kimia (3) | Ikatan Kovalen |Kimia Kelas 10
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of covalent bonding, focusing on how atoms share electrons to achieve stable electron configurations. It compares covalent bonds with ionic bonds, highlighting that covalent bonds occur between nonmetals. The presenter uses examples like CH₄, PCl₃, and SO₂ to illustrate how atoms share electrons, creating single, double, and triple bonds. The video also introduces the idea of coordinate covalent bonds, where shared electrons originate from only one atom. Overall, the video provides a clear explanation of covalent bonds and their different types.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Covalent bonds form between non-metal atoms to achieve stable electron configurations, either a duet (two electrons) or an octet (eight electrons).
- ⚛️ Covalent bonds involve sharing electron pairs between atoms rather than transferring them, as in ionic bonds.
- 🧪 Example: Carbon (C) with atomic number 6 forms covalent bonds with Hydrogen (H) with atomic number 1, creating the compound CH4.
- 💡 Each hydrogen atom shares one electron with carbon, which shares four electrons to satisfy its octet requirement.
- 📐 Lewis structures depict how atoms share electron pairs, showing stable electron configurations in covalent bonding.
- 🧬 In a covalent bond, atoms contribute the same number of electrons they need to achieve stability.
- 🔗 Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple, depending on the number of electron pairs shared between atoms.
- 📚 Example: PCl3 (phosphorus trichloride) forms a covalent bond where phosphorus shares three electrons with three chlorine atoms.
- 🌀 Some covalent bonds, like in SO2, involve a special form called coordinate covalent bonds, where one atom provides both electrons for the shared pair.
- 🔍 To distinguish between ionic and covalent bonds, remember that covalent bonds occur between non-metals sharing electrons, while ionic bonds form between positive and negative ions.
Q & A
What is a covalent bond?
-A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed between two non-metal atoms when they share a pair of electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
How does a covalent bond differ from an ionic bond?
-A covalent bond involves the sharing of electron pairs between non-metal atoms, while an ionic bond occurs when electrons are transferred from a metal to a non-metal, creating positive and negative ions that attract each other.
What is the significance of electron valence in covalent bonding?
-Electron valence determines how many electrons an atom needs to achieve a stable configuration. In covalent bonding, atoms share electrons to fill their outermost shells, achieving stability, such as the octet (8 electrons) or duplet (2 electrons) rule.
Can you provide an example of a covalent bond involving carbon and hydrogen?
-Yes, methane (CH4) is an example where carbon (C) with 4 valence electrons shares one electron with each of four hydrogen atoms (H), which have one valence electron each, resulting in a stable molecule where carbon has 8 electrons and hydrogen has 2.
How is a covalent bond represented in a Lewis structure?
-In a Lewis structure, a covalent bond is represented by lines or dots showing shared electron pairs between atoms. For example, in CH4, the central carbon atom is surrounded by four hydrogen atoms, each connected with a line representing a shared pair of electrons.
What are single, double, and triple covalent bonds?
-Single covalent bonds involve one pair of shared electrons (e.g., HCl), double bonds involve two pairs of shared electrons (e.g., O2), and triple bonds involve three pairs of shared electrons (e.g., N2).
What is a covalent coordinate bond?
-A covalent coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond where both shared electrons come from one atom. This happens when one atom provides both electrons for the bond, such as in the bonding of sulfur and oxygen in SO2.
How does the octet rule apply to covalent bonding?
-The octet rule states that atoms tend to bond in a way that gives them eight electrons in their valence shell, mimicking the electron configuration of noble gases. In covalent bonding, atoms share electrons to achieve this stable configuration.
Why do atoms form covalent bonds instead of ionic bonds?
-Atoms form covalent bonds when both atoms need to gain electrons to achieve a stable configuration. In such cases, rather than transferring electrons (as in ionic bonding), they share them because both atoms have similar electronegativity and cannot easily donate or accept electrons.
What role do lone pairs play in covalent bonding?
-Lone pairs are pairs of valence electrons that are not shared between atoms but remain on an individual atom. These pairs affect the shape and reactivity of molecules. For example, in PCl3, phosphorus has one lone pair of electrons, which affects the molecule's geometry.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

IKATAN ANTAR ATOM - Bagaimana Atom Dapat Saling Berikatan?
Chemical Bonding: Covalent Bonding Lewis Dot Diagrams
Types Of Chemical Bonds - What Are Chemical Bonds - Covalent Bonds And Ionic Bonds - What Are Ions
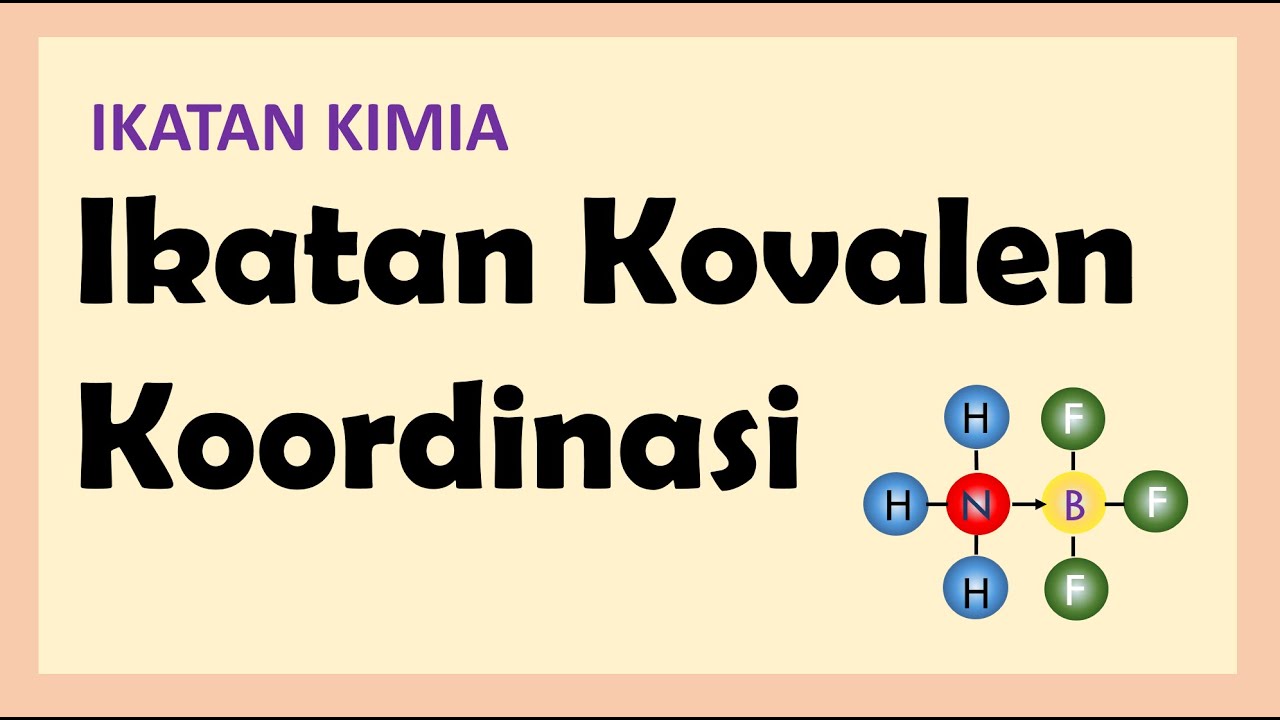
IKATAN KIMIA : IKATAN KOVALEN KOORDINASI | KIMIA SMA KELAS 10

KOVALEN TUNGGAL, RANGKAP 2 DAN 3

Chem Done Easy - Chemical Bonding (Ionic Vs Covalent)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
