What Is the Judicial Branch of the U.S. Government? | History
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the structure and power of the U.S. judicial branch, primarily the Supreme Court, which has evolved since its establishment in 1789. The Supreme Court consists of nine justices, appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate, serving without term limits. The court's significant power to interpret the constitutionality of laws was established in the landmark case Marbury v. Madison in 1803. The video highlights the Supreme Court's role in shaping American law, including pivotal decisions like Brown v. Board of Education, emphasizing its influence on daily life and the importance of judicial review.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ There are three branches of government in the United States: legislative, executive, and judicial.
- ⚖️ The judicial branch includes the Supreme Court and federal courts, responsible for ruling on legal matters and the Constitution.
- 📜 The Supreme Court has evolved since its establishment in 1789, originally starting with six justices and growing to nine in 1869.
- 🗳️ Supreme Court justices are nominated by the president and confirmed by the Senate, and they do not face term limits.
- 👨⚖️ Federal law does not require justices to be attorneys, though most have legal backgrounds.
- 📖 The Constitution provides limited details on the Supreme Court's powers, primarily identifying it as a third branch of government.
- 🔍 The power of judicial review was established by the 1803 case Marbury v. Madison, allowing the Court to interpret the constitutionality of laws.
- 🏆 Supreme Court decisions are final unless overturned by a future ruling from the Court itself.
- 📚 A notable case, Brown v. Board of Education (1954), overturned the precedent set by Plessy v. Ferguson (1896), declaring racial segregation unconstitutional.
- 🔒 The judicial branch operates independently of elections and public opinion, significantly impacting daily life by ensuring laws adhere to the Constitution.
Q & A
What are the three branches of government in the United States?
-The three branches are the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
What is the main function of the judicial branch?
-The judicial branch rules on all matters related to the law and the Constitution.
How many justices were on the Supreme Court when it was first established?
-The first version of the Supreme Court had six justices.
How did the number of justices on the Supreme Court change over time?
-The number of justices grew to nine in 1869 and has remained that way ever since.
How are Supreme Court justices appointed?
-The president nominates Supreme Court members, and the Senate votes to confirm or reject the appointment.
Do Supreme Court justices have term limits?
-No, justices can serve until they die, retire, or are removed through impeachment.
What was established by the case of Marbury versus Madison?
-Marbury versus Madison established the principle of judicial review, allowing the Supreme Court to interpret the constitutionality of laws.
What was the significance of the Supreme Court ruling in Brown versus Board of Education?
-The ruling declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional, overturning the previous decision in Plessy versus Ferguson.
What is the effect of Supreme Court decisions on other courts?
-All other courts must follow the precedent set by the Supreme Court's rulings.
How does the judicial branch operate in relation to elections?
-The judicial branch operates outside of elections and voter input, making its decisions based on cases brought before it.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

How would you go about solving this? Limit of x/sqrt(x^2+1) as x goes to infinity. Reddit inf/inf

Unit Step Signal: Basics, Function, Graph, Properties, and Examples in Signals & Systems

For Oom Piet - Poem Analysis

Eric's Calculus Lecture: Evaluate the Indefinite Integral ∫e^(3x+1)dx
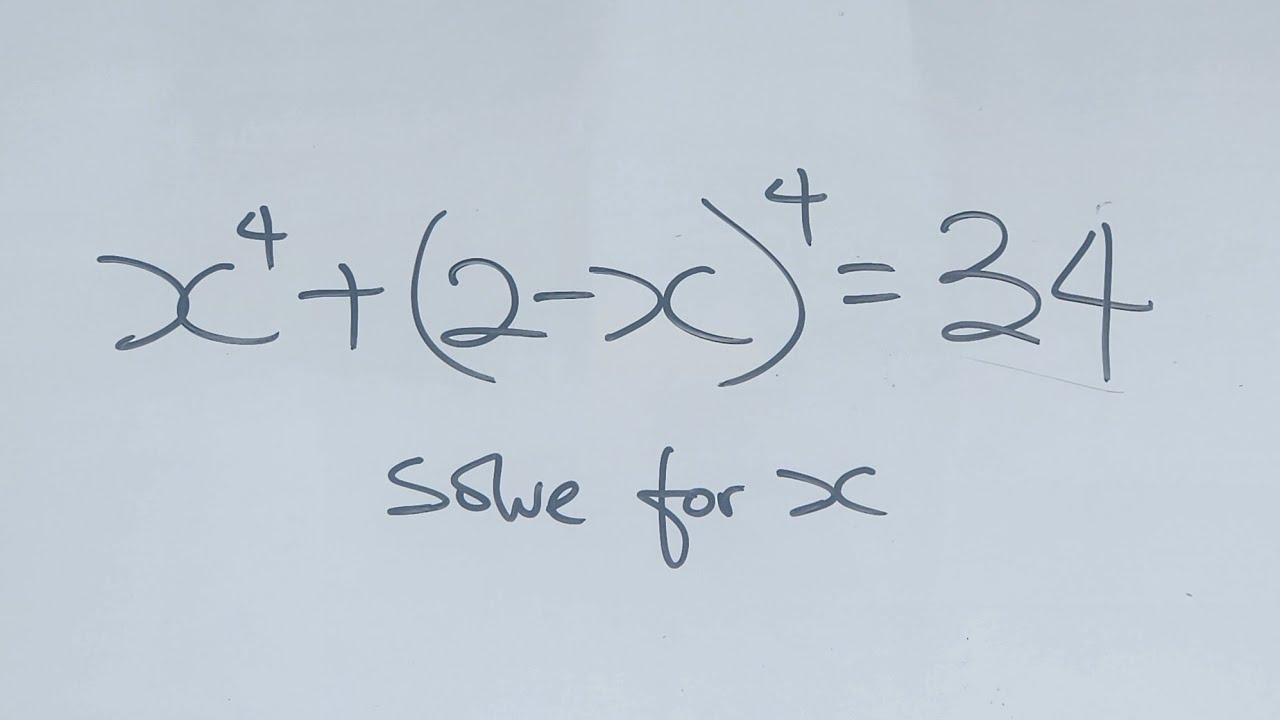
Maths Olympiad Question | A nice algebraic equation | You should know this trick!

How to Diagnose and Replace Universal Joints (ULTIMATE Guide)

Complements of Sets
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
