Hershey and Chase Experiment | Class 12 | NEET Biology
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses genetic material transfer experiments involving bacteria and viruses. It explores the transformation principle, where genetic material is transferred from one bacterium to another, and the role of proteins in this process. The script also delves into the concept of infectious cycles and the impact of genetic material transfer on bacterial growth and infection. It concludes with an emphasis on the importance of understanding these processes for scientific advancement.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The script discusses various genetic material experiments, emphasizing growth experiments and historical breakthroughs, particularly from 1978.
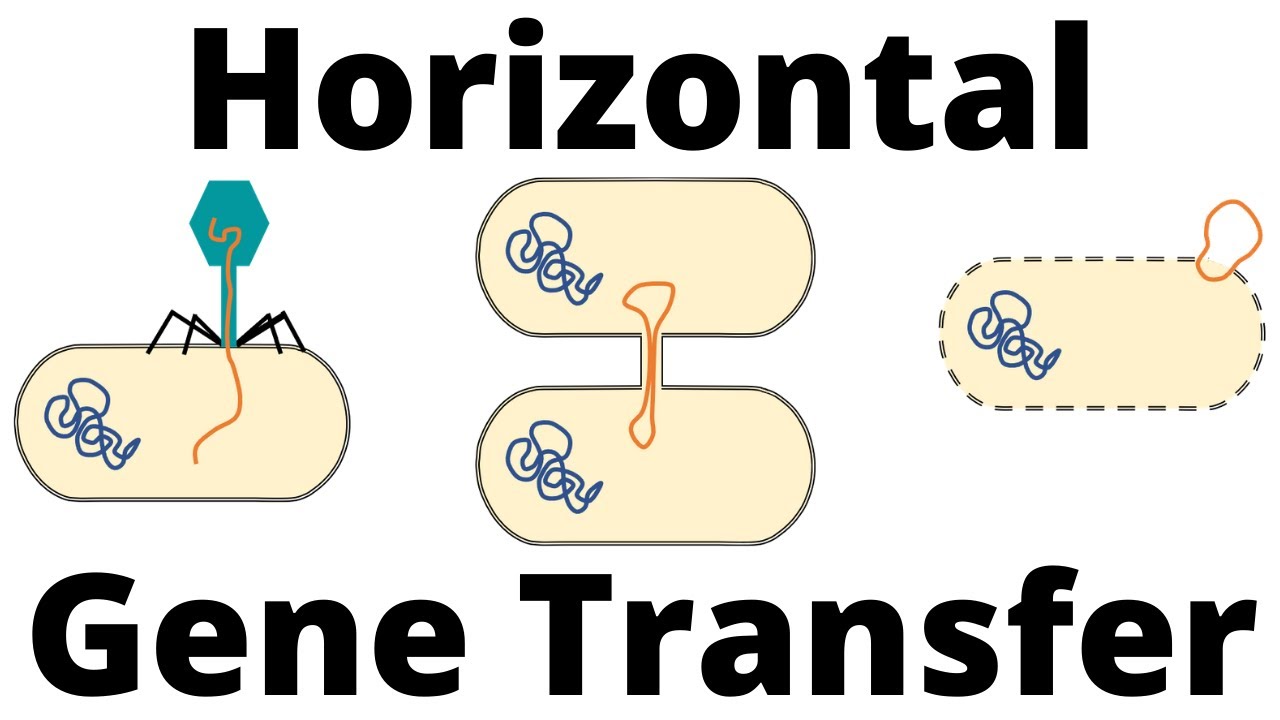
- 🧬 Focus is on understanding how genetic material, specifically DNA, is transferred between bacteria, with references to experiments involving bacterial phages (viruses that infect bacteria).
- 🦠 Bacteriophages play a critical role in the transfer of genetic material, as they inject their DNA into bacteria, causing infection and replication.
- 🧪 Several biochemical experiments, such as extraction of DNA and protein from bacteria, were carried out to understand genetic material transfer and its nature.
- 🔍 The script highlights the Hershey-Chase experiment, which proved that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material transferred by bacteriophages.
- ⚗️ In this experiment, radioactive markers were used to label DNA and protein, revealing that only DNA from the bacteriophage entered the bacteria and caused replication.
- 📉 The process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another is known as transduction, which helps clarify the genetic role of DNA.
- 🧑🔬 The script references how various scientists conducted similar experiments, some of which faced resistance but ultimately led to the acceptance of DNA as the genetic material.
- 🔗 The term 'transduction principle' was introduced, indicating how the infection process relies on the transfer of DNA between bacteria by bacteriophages.
- 📚 Conclusively, the experiments confirmed that DNA, and not protein, serves as the carrier of genetic information, transforming our understanding of bacterial genetics.
Q & A
What was the main focus of the experiment discussed in the script?
-The main focus of the experiment was to investigate the nature of genetic material and how it is transferred, particularly focusing on the experiments related to the transformation and transduction principles in genetic studies.
Which year is mentioned as significant in the history of the genetic experiment?
-The year 1978 is mentioned as significant, highlighting a previous chapter’s discussion related to the experiment and its findings.
What is the 'Transforming Principle' referred to in the script?
-The 'Transforming Principle' refers to the discovery that genetic material can be transferred between organisms, influencing traits such as causing disease. This principle was foundational in identifying DNA as the carrier of genetic information.
Why were some scientists initially skeptical about the experiment?
-Many scientists were skeptical because, despite the evidence, the exact nature of the material responsible for transformation (DNA) was not fully understood at the time.
What role do bacteriophages play in the experiment?
-Bacteriophages, which are viruses that infect bacteria, played a key role in the experiment by demonstrating how genetic material is transferred from the virus to the bacteria, thereby allowing researchers to understand the mechanics of genetic material transfer.
What is transduction in the context of genetic experiments?
-Transduction is the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another. It’s a mechanism that helps to explain how genes can be exchanged between bacterial cells.
What did Hershey and Chase demonstrate through their experiment?
-Hershey and Chase demonstrated that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material responsible for inheritance. Their experiment showed that when bacteriophages infect bacteria, it is the DNA that enters the bacterial cell, not the protein.
What was the significance of using radioactive labeling in the experiment?
-Radioactive labeling was used to distinguish between DNA and proteins in the bacteriophages. This helped determine which component (DNA or protein) was responsible for genetic transfer, ultimately showing that DNA carried the genetic instructions.
How did the experiment contribute to our understanding of genetic material?
-The experiment provided conclusive evidence that DNA is the genetic material responsible for inheritance, solidifying the role of DNA in genetic transmission across generations and organisms.
What was the conclusion of the experiment regarding DNA and proteins?
-The conclusion of the experiment was that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material that is transferred during viral infection of bacteria. This conclusion was reached after finding that the radioactive DNA, but not the protein, was found inside the bacterial cells.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)