Ketogenic Diets: What the Science Says
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host delves into the ketogenic diet, explaining how it works by shifting the body's fuel source from carbohydrates to fats, producing ketones for energy. They clarify misconceptions, emphasizing the diet's traditional high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carb nature. Discussing its benefits for fat burning and satiety, the host challenges the diet's superiority for weight loss without a metabolic advantage. Special attention is given to the diet's potential in managing diseases like epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and cancer, where it may offer therapeutic benefits. The host advises consulting healthcare professionals and warns against the diet's sustainability for long-term weight management.
Takeaways
- 🍽️ The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet that shifts the body's metabolism to use fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
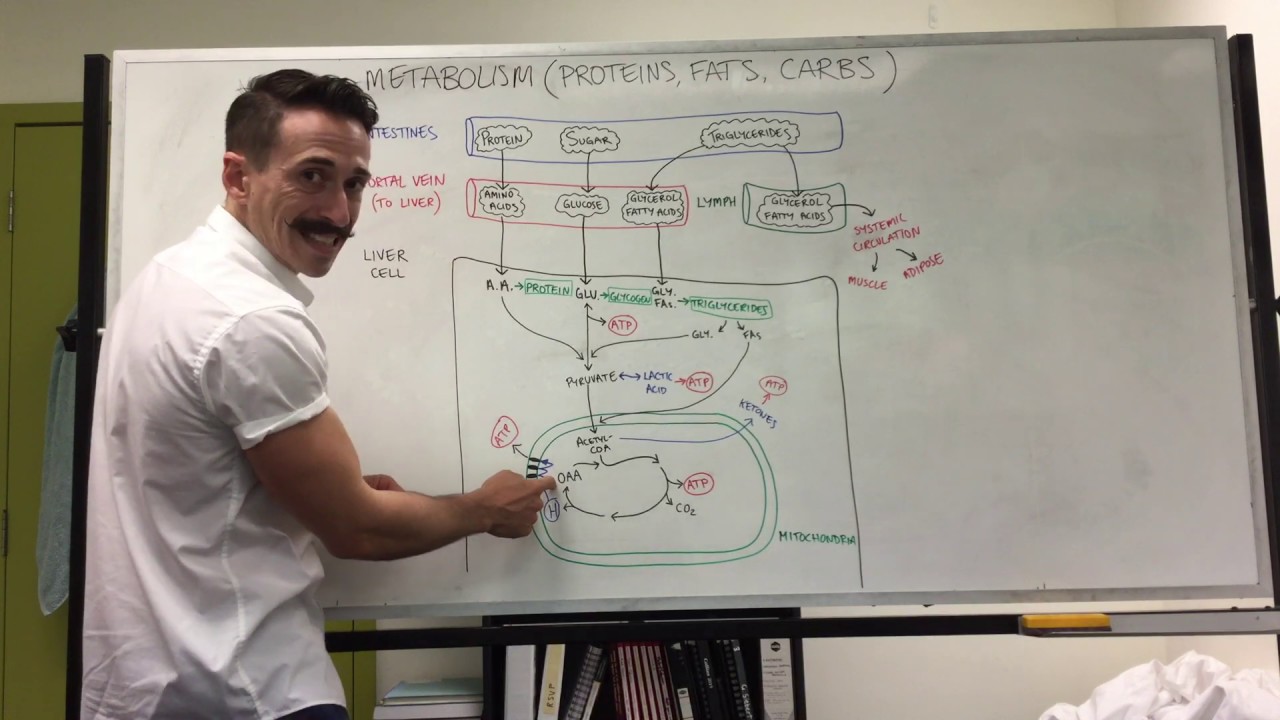
- 🧠 Ketones, produced in the liver, serve as an alternative fuel source for tissues like the brain and muscles when carbohydrate intake is low.
- 🏋️♂️ Traditional bodybuilding diets often include high protein intake, which may not allow for ketogenesis, thus not aligning with the true ketogenic diet.
- 🔍 Research suggests that a ketogenic diet does not necessarily offer a metabolic advantage for fat loss when compared to non-ketogenic, high-protein diets with equal caloric intake.
- 🏃♂️ For endurance and performance athletes, exogenous ketones may provide an alternative fuel source, potentially improving performance without the need to reduce carbohydrate intake.
- 🧬 In specific disease states like epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and certain types of cancer, a ketogenic diet has been shown to offer therapeutic benefits.
- 🧬 The Warburg hypothesis suggests that cancer cells rely on glucose for energy, and a ketogenic diet can slow tumor growth by reducing glucose availability and increasing ketones.
- 💉 It's important to approach ketogenic diets with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for those with specific health conditions.
- 🍰 The sustainability of a ketogenic diet for long-term weight management is questioned, as it may not be a sustainable eating pattern for everyone.
- 📈 The health benefits of a ketogenic diet may be attributed more to calorie restriction rather than the diet's macronutrient composition.
Q & A
What is a ketogenic diet?
-A ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet that shifts the body's metabolism away from glucose and towards fat for energy, resulting in the production of ketones.
What happens when you fast for an extended period?
-When you fast for about 18 hours, your body starts producing a lot of ketones, as it switches from using carbohydrates as its primary fuel source to using fat, which leads to ketogenesis.
Why does the body produce ketones during a ketogenic diet?
-The body produces ketones as an alternative fuel source when carbohydrate intake is very low. This spares blood glucose for tissues that require it, such as the brain and red blood cells.
What are the traditional macronutrient ratios for a ketogenic diet?
-Traditionally, a ketogenic diet consists of over 70% fat, 20 to 25 percent protein, and less than 5% carbohydrates.
How does the body make glucose without carbohydrate intake?
-The body can produce glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, using substrates like amino acids, glycerol, and glycerides, even with zero glucose intake.
What are the potential benefits of a ketogenic diet?
-Potential benefits of a ketogenic diet include burning more fat for fuel, increased satiety, stable blood glucose levels, and muscle-sparing effects due to the use of ketones as an alternative fuel source.
Do ketogenic diets offer a metabolic advantage for fat loss compared to non-ketogenic diets?
-Research suggests that when diets are equated for calories and protein, there is no significant difference in fat loss between ketogenic and non-ketogenic diets.
In what specific disease states might a ketogenic diet be particularly beneficial?
-A ketogenic diet may be beneficial for certain diseases like epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and certain types of cancer, where the diet can provide an alternative fuel source and potentially improve symptoms or slow disease progression.
What is the Warburg hypothesis and how does it relate to cancer and ketogenic diets?
-The Warburg hypothesis states that cancer cells primarily use glucose for energy due to dysfunctional mitochondria. A ketogenic diet can reduce glucose availability and increase ketones, which cancer cells cannot use, potentially slowing tumor growth.
What are exogenous ketones and how might they benefit performance and health?
-Exogenous ketones are ketone supplements that provide an alternative fuel substrate without the need to reduce carbohydrate intake. They may benefit endurance athletes by sparing blood glucose and potentially improving performance, and could have therapeutic effects for certain health conditions.
Why might the ketogenic diet not be sustainable for some people?
-The ketogenic diet might not be sustainable for some individuals because it requires a significant change in eating habits, particularly the elimination of many carbohydrate-rich foods. This can be challenging to maintain long-term, potentially leading to weight regain.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)