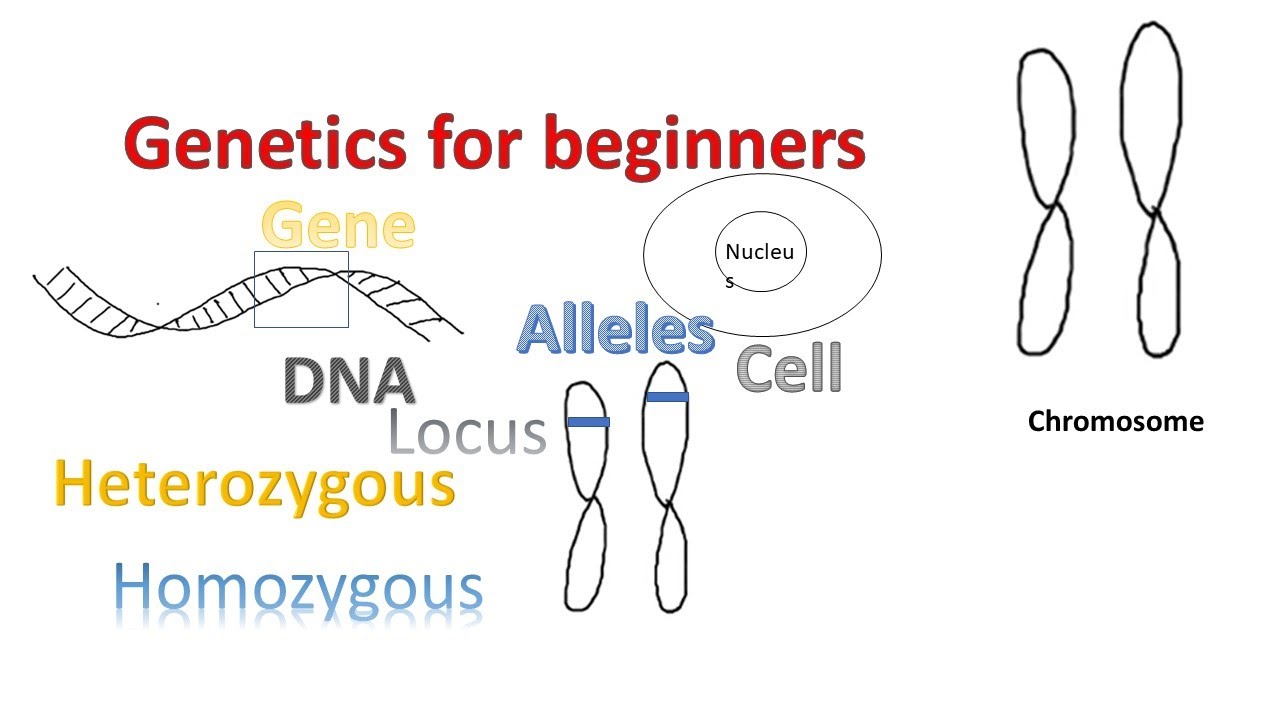
Introduction to Cytogenetics (Filipino) Genes Alleles Chromosomes
Summary
TLDRThe video transcript provides an introduction to key concepts in genetics, focusing on dominant and recessive genes, inheritance patterns, and cytogenetics. It explains how traits such as earlobes, dimples, and eye color are inherited from parents through dominant and recessive alleles. The transcript also delves into the structure of DNA and chromosomes, discussing how DNA is organized within cells and how genes are expressed. The explanation covers important terms like genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, and the process of protein synthesis.
Takeaways
- 🧬 50% of your genes come from your mom and 50% from your dad.
- 👂 Dominant traits, like free earlobes, dimples, or tongue-rolling, are easily expressed and can pass through generations.
- 🧠 Recessive traits need two parents to carry the gene for it to appear in the offspring.
- 🔬 Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and inheritance, with chromosomes containing DNA.
- 📜 DNA contains around 3 billion bases and is condensed into chromosomes using proteins called histones.
- 🧪 During mitosis, DNA replicates to pass identical genetic information to daughter cells.
- 🧬 Humans have 46 chromosomes, organized into 23 pairs, where one set comes from each parent.
- 💡 Genes carry hereditary information that codes for traits like hair and eye color, with variations called alleles.
- 📊 Genotype refers to the gene makeup, while phenotype refers to the physical expression of these genes.
- 🧬 Dominant alleles are represented by capital letters, while recessive alleles are represented by lowercase letters.
Q & A
What percentage of your genes come from your parents?
-50% of your genes come from your mother, and 50% come from your father.
What is an example of an autosomal dominant trait mentioned in the transcript?
-An example of an autosomal dominant trait is having a dimple, which means one of your parents likely has a dimple, and this trait could be passed down to future generations.
What is the difference between a dominant gene and a recessive gene?
-A dominant gene will be expressed if one parent has it, while a recessive gene needs to be inherited from both parents to be expressed.
What is cytogenetics?
-Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes, which are condensed DNA structures that carry all genetic information.
How is DNA organized in a chromosome?
-DNA is coiled around proteins called histones, forming structures called nucleosomes, which eventually condense to form chromosomes.
What are autosomal chromosomes and how many do humans have?
-Humans have 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes, which are non-sex chromosomes that carry genetic information, plus 1 pair of sex chromosomes (X and Y).
What is the role of messenger RNA (mRNA) in protein production?
-mRNA copies a portion of DNA in the nucleus and carries it to the ribosome, where it is translated into a protein.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
-Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype is the physical expression or characteristics that result from the genotype and environmental factors.
What is the function of alleles in genetics?
-Alleles are the different varieties of a gene, and each individual inherits one allele from each parent, which together determine specific traits like eye or hair color.
What is a Punnett square and how is it used in genetics?
-A Punnett square is a tool used to predict the probability of offspring inheriting specific traits based on the alleles of the parents.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)