We Just Found a Missing Link For Evolution of Animal Life Hiding in a Toxic Lake
Summary
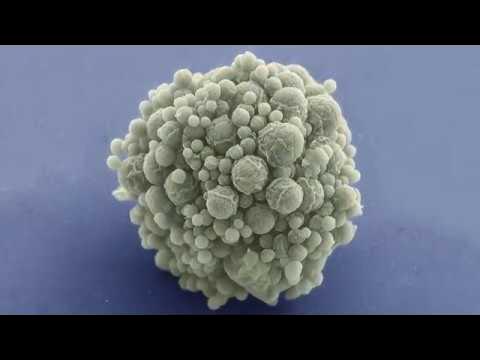
TLDRIn Mono Lake, California, scientists have discovered a unique flagellated protist, suggesting a 'missing link' in the evolution from unicellular to multicellular life. Resembling a blastula, it forms colonies with bacteria, indicating a symbiotic relationship and a potential early model for multicellular life. This discovery, named 'Bara monosiera,' offers insights into the complex interactions between ancient eukaryotes and microbes, hinting at a possible microbiome similar to those found in animals.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Mono Lake in California, known for its extreme salinity, has been discovered as a habitat for a unique organism.
- 🔬 Scientists have recently uncovered a flagellated eukaryotic cell, which represents a potential 'missing link' in the evolution from unicellular to multicellular life.
- 🌿 This organism forms colonies and exhibits a symbiotic relationship with bacteria, similar to the human gut microbiome.
- 🐠 The discovery suggests a possible model for understanding the evolution of complex life on Earth.
- 📚 Historical records show that similar organisms, known as quano flagellates, have been studied for almost 200 years.
- 🏞️ Quano flagellates have a distinctive morphology and use their flagella for both movement and feeding, consuming bacteria, food particles, and even viruses.
- 🤔 The ability of some quano flagellates to form colonies has led biologists to consider them as potential precursors to multicellular life.
- 🧬 Recent genetic analysis places quano flagellates as close relatives to metazoans, supporting the theory of a common ancestor.
- 🌐 The 2019 discovery of colonial behavior in quano flagellates, including responses to light and changes in shape, adds to the evidence of their evolutionary significance.
- 🤝 The symbiotic relationship between quano flagellates and bacteria in Mono Lake is the first discovery of a multicellular colony with a microbiome, offering new insights into ancient life forms.
Q & A
What is Mono Lake known for?
-Mono Lake is known for being extremely salty, making it inhospitable for most life forms.
What was the intriguing discovery made by scientists in Mono Lake?
-The discovery was of a complex eukaryotic cell with flagella, capable of forming colonies and symbiotic relationships with bacteria, which could be a missing link between unicellular and multicellular life.
What is the significance of the flagellated eukaryotic cell found in Mono Lake?
-This cell is significant as it represents a potential transitional form between single-celled and multicellular organisms, providing insights into the evolution of complex life on Earth.
How do the flagella of these cells function?
-The flagella serve dual purposes: they are used for locomotion and also act as a 'vacuum cleaner' to help the cells consume food particles, smaller bacteria, and even viruses.
What are 'quano flagellates' and how do they resemble human sperm?
-Quano flagellates are a group of free-living cells that resemble human sperm in shape, structure, and locomotion. They use their flagella for movement and to ingest food.
Why are some members of the quano flagellates group considered important for understanding multicellular life?
-Certain members of the quano flagellates group can form colonies, which is a behavior that has been seen as a precursor to multicellular life, suggesting they might be a stepping stone to more complex organisms.
How do the colonies formed by quano flagellates relate to the concept of multicellular life?
-The colonies formed by quano flagellates resemble the early stages of multicellular life, potentially showing us the beginnings of all multicellular life and specifically animal life on Earth.
What is the connection between quano flagellates and metazoans?
-Genomic studies have shown that quano flagellates are closely related to metazoans, suggesting they might be a cousin to all animals and could have played a role in the evolution of early animals like sponges.
What new behavior was observed in quano flagellates in the 2019 study?
-In 2019, it was observed that quano flagellates can exhibit colonial behavior, coordinating with each other in response to light and changing their shape and position, which is reminiscent of early animal behavior.
What is the significance of the bacteria found in association with the quano flagellates?
-The bacteria found with quano flagellates represent the first discovery of a multicellular colony with a microbiome, suggesting a symbiotic relationship that could be crucial for the survival of these organisms in the harsh environment of Mono Lake.
What role might the bacteria be playing in the life of the quano flagellates?
-While the exact role is unknown, it's speculated that the bacteria might be providing detoxification or protection against the toxic environment, similar to the role of the human microbiome, or possibly serving as a food source.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

What is Volvox?

Cells, Unicellular Organisms, and Multicellular Organisms

EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Quarter 2 Lesson 1: Introduction to Life Science
Atheist Answers #21: Creating Life From Non-Life is Impossible

CARACTERÍSTICAS GERAIS DOS SERES VIVOS | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

Science in Action: How Science Works | California Academy of Sciences
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
