Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep1: Factoring Polynomials
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Teacher Joshua introduces viewers to factoring polynomials, focusing on identifying the greatest common monomial factor. Through examples and explanations, he walks students through the process of prime factorization and applying it to algebraic expressions. The lesson aims to enhance critical thinking and mathematical skills, emphasizing the importance of practice and learning from mistakes.
Takeaways
- 📘 The lesson focuses on factoring polynomials, specifically identifying the greatest common monomial factor.
- 🔢 The process of finding the greatest common factor (GCF) involves prime factorization for numbers and considering both numerical and literal coefficients for algebraic expressions.
- 🟠 Prime factorization is illustrated through examples, such as finding the GCF of 8 and 12, which is 4.
- 📚 Variables and their exponents are discussed, emphasizing that a variable raised to an exponent means the variable is multiplied by itself that number of times.
- 🔍 The script provides a method to find the GCF of algebraic expressions by identifying common factors in both numerical and literal coefficients.
- 📐 The term 'polynomial' is defined, and the script explains the components of a polynomial, including terms, variables, constants, numerical coefficients, and literal coefficients.
- ✅ The script demonstrates how to factor polynomials by dividing each term by the GCF and then expressing the polynomial in factored form.
- 📉 Examples are given to practice finding the GCF of various expressions, including cases where the GCF is 1, indicating the expressions are relatively prime.
- 📖 The lesson concludes with a recap of the steps to factor polynomials and a reminder that factoring is the reverse process of polynomial multiplication.
- 👨🏫 Teacher Joshua emphasizes the importance of practice and learning from mistakes to improve mathematical skills and become a better thinker.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the Deaf Ed TV video?
-The main topic discussed in the Deaf Ed TV video is factoring polynomials, specifically focusing on finding the greatest common monomial factor.
What is the first step in finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more numbers?
-The first step in finding the GCF of two or more numbers is prime factorization, where each number is written as a product of prime factors.
How is the greatest common factor of algebraic expressions with variables and exponents determined?
-The greatest common factor of algebraic expressions with variables and exponents is determined by identifying the common variables with the least exponent that appear in each term of the expressions.
What is the greatest common factor of the numbers 8 and 12?
-The greatest common factor of the numbers 8 and 12 is 4, which is the product of their common prime factors 2 times 2.
What is a polynomial according to the Compact Oxford English Dictionary?
-A polynomial is an algebraic expression that shows a sum or difference of two or more terms, containing whole number exponents on the variable.
What is the difference between a variable and a constant in algebra?
-In algebra, a variable is a symbol that represents an unknown value, while a constant is a symbol or number with a fixed value in an algebraic term.
How is the greatest common factor of algebraic expressions with numerical and literal coefficients found?
-The greatest common factor of algebraic expressions with numerical and literal coefficients is found by identifying common factors in both the numerical and literal coefficients and then multiplying them together.
What is a prime polynomial?
-A prime polynomial is one whose greatest common monomial factor is one, meaning it cannot be factored further using the greatest common factor method.
What is the process of factoring a polynomial using its greatest common monomial factor?
-The process of factoring a polynomial using its greatest common monomial factor involves finding the GCF of the numerical coefficients, identifying the variables with the least exponent, multiplying these to get the GCF, dividing the polynomial by this GCF to find the other factor, and writing the polynomial in its factored form.
What is the significance of finding the greatest common factor in mathematics?
-Finding the greatest common factor is significant in mathematics as it helps simplify polynomial expressions, making them easier to work with in calculations and problem-solving.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Common Monomial Factoring - Polynomial Factoring - Grade 8 Math

Factoring Polynomials using Greatest Common Monomial Factor
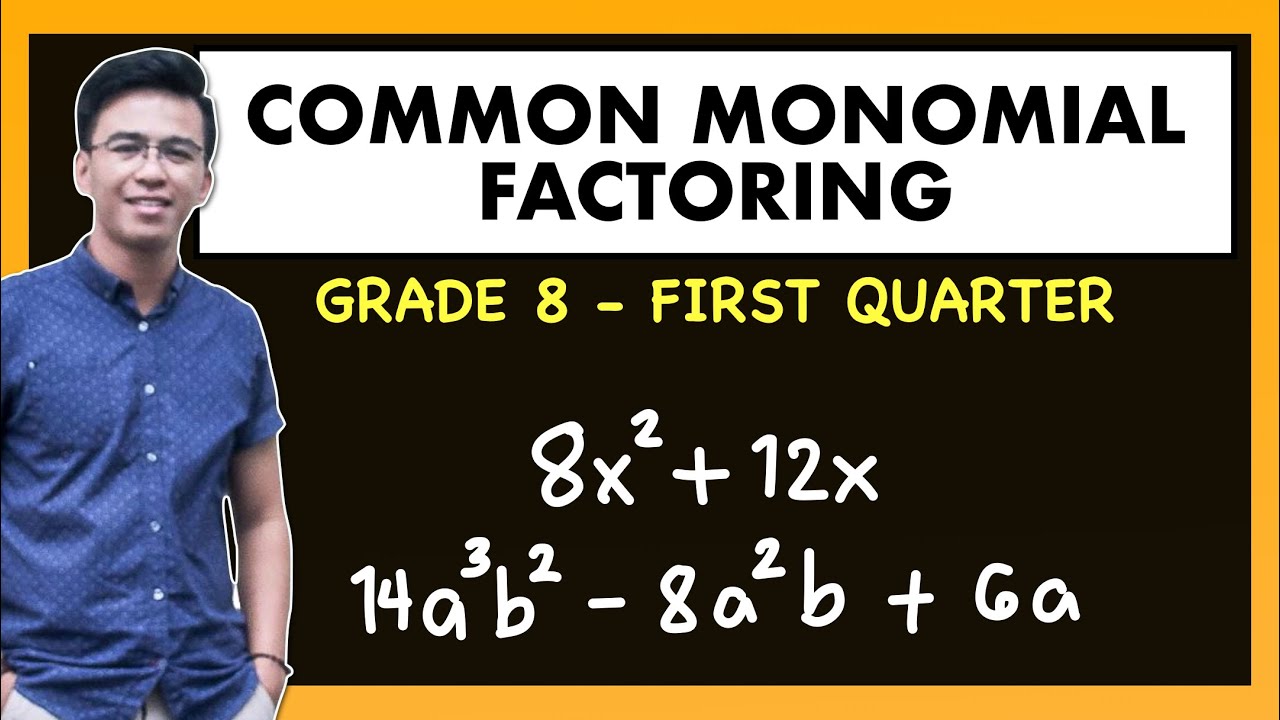
Factoring Part 1 - Common Monomial Factoring | Grade 8 Q1 @MathTeacherGon

Factoring Greatest Common Monomial Factor

Factor Polynomials with GCMF Video
Factoring Cubic Polynomials- Algebra 2 & Precalculus
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
