Polynomials - Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying and Dividing Algebraic Expressions
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script offers a comprehensive guide on polynomial operations, including addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It demonstrates how to combine like terms and use methods like FOIL for binomial multiplication. The script also covers more complex scenarios like multiplying binomials by trinomials and dividing polynomials using factoring, long division, and synthetic division. The presenter encourages viewers to practice these techniques and directs them to additional resources for further learning in various subjects.
Takeaways
- 🔢 To add polynomial expressions, combine like terms by adding their coefficients.
- ➖ When subtracting polynomials, distribute the negative sign to each term in the second polynomial and then combine like terms.
- 🔄 When multiplying binomials, use the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last) to multiply and then combine like terms.
- 📚 For multiplying a binomial by a trinomial, expect to initially have six terms before combining like terms.
- 🔗 When multiplying polynomials, always double-check your work to ensure accuracy.
- 📉 To divide polynomials, consider factoring, long division, or synthetic division methods.
- ✂️ Factoring involves finding two numbers that multiply to the constant term and add to the linear coefficient.
- 🔄 Long division of polynomials is similar to long division of numbers, with the division symbol placed outside the dividend.
- 🔄 Synthetic division is a shortcut for dividing polynomials when the divisor is a linear term, using the root of the divisor.
- 📈 The video provides a comprehensive guide to polynomial operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Q & A
What is the first step when adding polynomial expressions?
-The first step when adding polynomial expressions is to combine like terms. Like terms are terms that have the same variable raised to the same power.
How do you combine like terms in the example given in the video?
-In the example, 4x^2 and 3x^2 are like terms, which combine to 7x^2. 5x and -8x combine to -3x. The constants 7 and 12 combine to 19.
What is the process for subtracting polynomial expressions as described in the video?
-To subtract polynomial expressions, distribute the negative sign to every term in the second polynomial, change the signs of those terms, and then combine like terms.
How does the video demonstrate the multiplication of two binomials?
-The video demonstrates the multiplication of two binomials using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last), which involves multiplying each term in the first binomial by each term in the second binomial and then combining like terms.
What is the result of multiplying (3x + 5) by (2x - 3) as shown in the video?
-The result of multiplying (3x + 5) by (2x - 3) is 6x^2 + x - 15 after applying the FOIL method and combining like terms.
How does the video simplify the expression (2x - 5)^2?
-The video simplifies (2x - 5)^2 by applying the FOIL method to two binomials (2x - 5) multiplied by each other, resulting in 4x^2 - 20x + 25.
What is the initial step when multiplying a binomial by a trinomial according to the video?
-The initial step when multiplying a binomial by a trinomial is to distribute each term in the binomial to each term in the trinomial, resulting in six terms before combining like terms.
How does the video approach the division of polynomials?
-The video approaches the division of polynomials by suggesting three methods: factoring, long division, and synthetic division.
What is the result of dividing x^2 + 7x + 12 by x + 3 using factoring as shown in the video?
-Using factoring, x^2 + 7x + 12 can be factored into (x + 3)(x + 4), so when divided by x + 3, the result is x + 4.
How does the video use synthetic division to divide 2x^2 - 7x + 6 by x - 2?
-The video uses synthetic division by writing the coefficients of the numerator (2, -7, 6) and using the root x = 2 to perform the division, resulting in a quotient of 2x - 3 and a remainder of 0.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
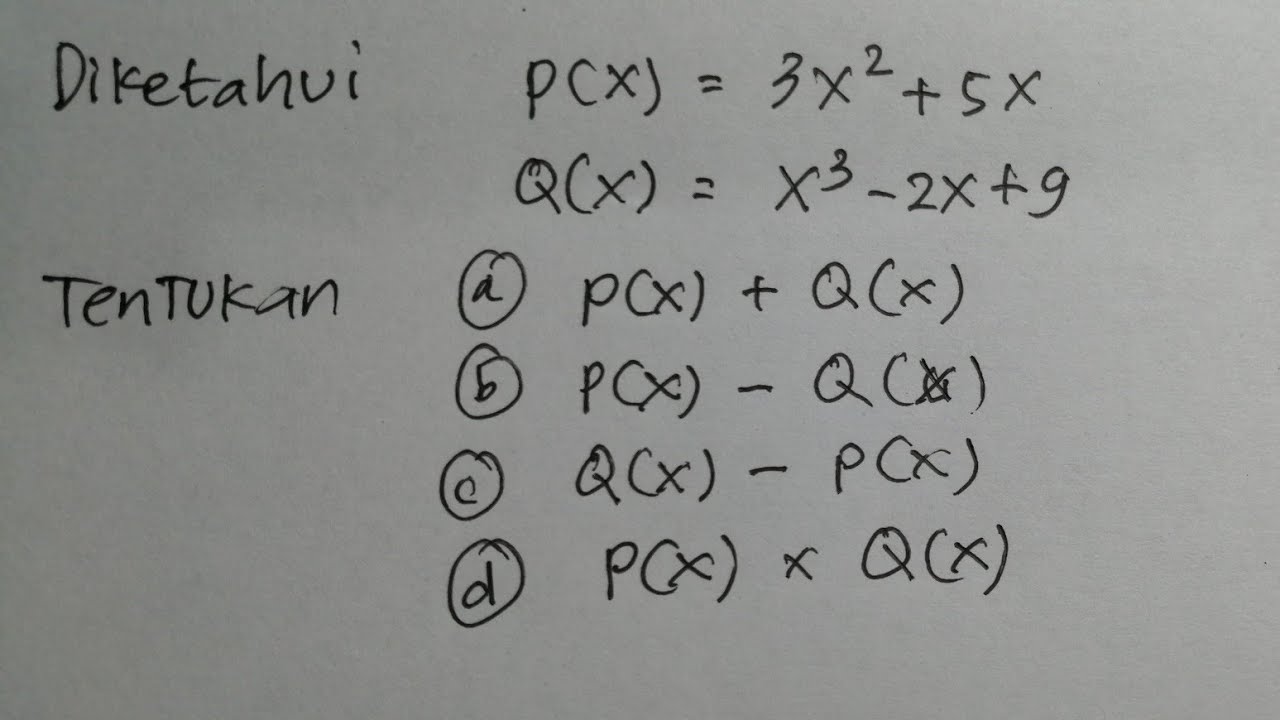
Penjumlahan, Pengurangan, dan Perkalian Suku Banyak Polinomial | Matematika SMA

POLINÔMIOS #02 | ADIÇÃO E SUBTRAÇÃO COM POLINÔMIOS | \Prof. Gis/

BUKU MATEMATIKA PKS GEMATAMA KELAS XI FASE F KURIKULUM MERDEKA MATERI OPERASI ALJABAR PADA FUNGSI

Fractions & Decimals - Chapter 2 - Introduction - Class 7

Perkalian Polinomial - Matematika Tingkat Lanjut Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

ATURAN DASAR OPERASI MATEMATIKA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
