Ivan Pavlov's Classical Conditioning
Summary
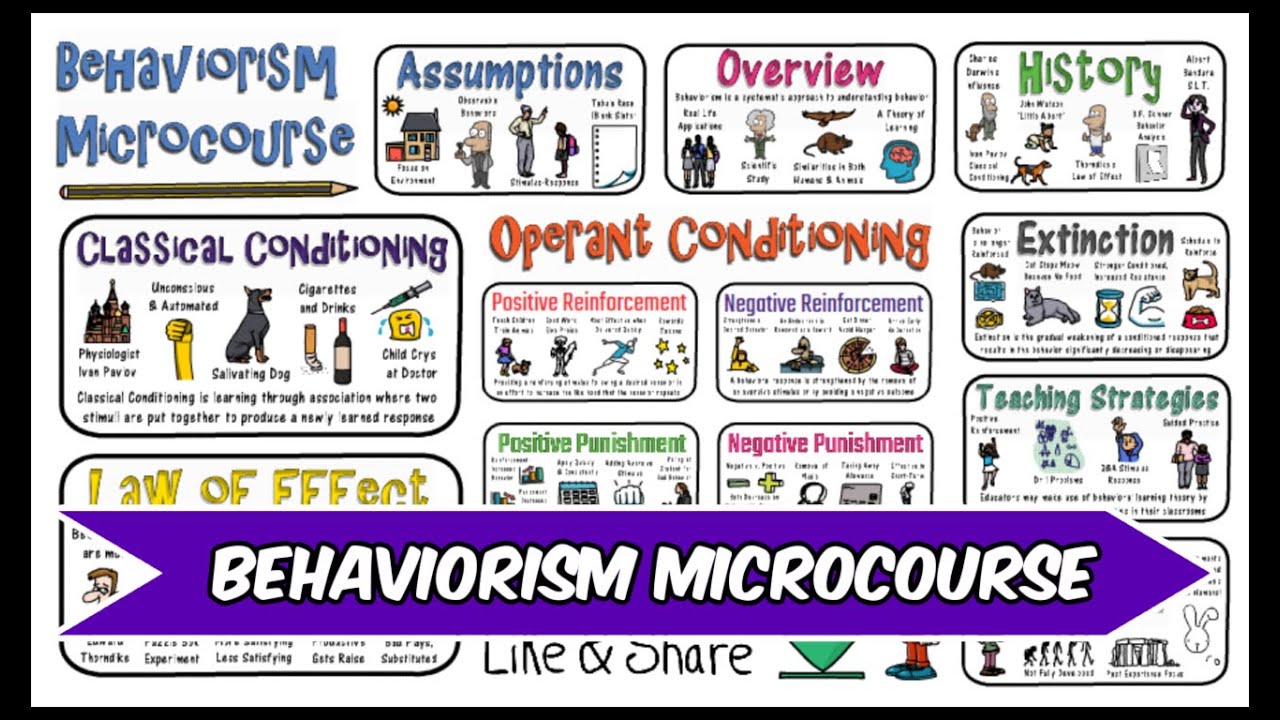
TLDRIn this lecture, the instructor introduces key theories of learning under behaviorism and classical conditioning, emphasizing the works of Pavlov and Watson. The class covers how learning occurs through interactions with the environment, the role of stimuli and responses, and how behavior is shaped by reinforcement and punishment. Classical conditioning is explained in detail, highlighting its applications in the classroom, such as reinforcing positive behaviors, creating routines, and managing classroom dynamics. The lecture concludes with an overview of upcoming topics on other behaviorist theories and a quiz announcement.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The class focuses on the concept of learning theories, particularly under behaviorism.
- 📜 The lecture covers Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning, highlighting its importance in behaviorism.
- 🐶 Classical conditioning involves linking two stimuli to produce a learned response, as demonstrated by Pavlov’s experiment with dogs.
- 🔔 Pavlov's dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell with the presentation of food, resulting in salivation—a conditioned response.
- 👨🏫 Behaviorism emphasizes conditioning and reinforcement in shaping students' responses to stimuli in a classroom environment.
- 🌍 Watson's theory, influenced by Pavlov, argues that individual differences in behavior stem from learned experiences rather than inherent traits.
- 🏫 In the classroom, classical conditioning can reinforce positive behavior, such as associating participation with praise.
- 👏 Teachers can use techniques like clapping or cues to signal students for desired behavior, fostering classroom management.
- 📚 The principles of classical conditioning—acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, and generalization—are explained with examples relevant to teaching.
- 🎓 Future lessons will cover other behavioral learning theories, such as Skinner's operant conditioning and Bandura’s social learning theory.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the lesson discussed in the transcript?
-The main focus of the lesson is on the 'theories of learning' under behaviorism, with an emphasis on classical conditioning by Ivan Pavlov and its implications in education.
What are the two major categories of learning theories mentioned in the transcript?
-The two major categories of learning theories mentioned are behaviorism and cognitivism.
How does behaviorism differ from cognitivism according to the transcript?
-Behaviorism focuses on learning through interaction with the environment and conditioning, while cognitivism emphasizes internal mental processes and how learners organize and relate new information to existing knowledge.
What is classical conditioning as described in the transcript?
-Classical conditioning is a learning process where two stimuli are linked together to produce a new learned response. It involves associating a neutral stimulus with a naturally occurring stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
Who pioneered the concept of classical conditioning, and what experiment is most famous?
-Ivan Pavlov pioneered classical conditioning, and his most famous experiment involved making dogs salivate in response to the sound of a bell after repeated association with food.
What are the four components of classical conditioning outlined in the transcript?
-The four components of classical conditioning are: (1) Unconditioned stimulus, which naturally triggers a response, (2) Unconditioned response, a natural response to the unconditioned stimulus, (3) Conditioned stimulus, a previously neutral stimulus that triggers a conditioned response after pairing with the unconditioned stimulus, and (4) Conditioned response, the learned response to the conditioned stimulus.
How can classical conditioning be applied in the classroom as per the lesson?
-In the classroom, classical conditioning can reinforce positive behaviors by associating certain stimuli (like praise or rewards) with desired behaviors, such as participation in class or completing homework. It can also help establish routines, manage behavior, and capture students' attention.
What is the importance of reinforcement in classical conditioning for learning?
-Reinforcement strengthens the association between the conditioned stimulus and response, helping students learn new behaviors more effectively. Positive reinforcement, like praise or rewards, encourages students to repeat desired behaviors.
What is extinction in classical conditioning, as described in the transcript?
-Extinction occurs when the conditioned response decreases or disappears because the conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with the unconditioned stimulus.
What is stimulus generalization in classical conditioning?
-Stimulus generalization is the tendency for a conditioned stimulus to evoke similar responses after the response has been conditioned. For example, students may react similarly to different but related stimuli, like different sounds used to signal the same behavior.
What is the significance of Pavlov's experiment in understanding human learning, according to the transcript?
-Pavlov's experiment is significant because it demonstrated that learning occurs through association, influencing the field of behaviorism and helping explain how humans and animals learn through environmental stimuli. This understanding has practical implications for educational practices, such as behavior management and reinforcement in classrooms.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
Behaviorism: Skinner, Pavlov, Thorndike, etc.

Behaviorism: Antecedent Influences - Ch9 - History of Modern Psychology - Schultz & Schultz

CLASSICAL VS OPERANT CONDITIONING

Learning Theories Explained

Behavioral Perspective in Learning and Behavior

Classical Conditioning vs. Operant Conditioning -Psychology-
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
