Temperatura - Clase 4 Termodinámica
Summary
TLDRIn this thermodynamics lecture, Gabriel Fernando García Sánchez introduces the concept of temperature, explaining its role as a scalar quantity that indicates how hot or cold a system is. He discusses different types of thermodynamic systems (closed and open) and the foundational Zero Law of Thermodynamics, which explains thermal equilibrium. The lecture also covers various temperature scales like Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin, and Rankine, with a focus on the importance of absolute temperature scales in thermodynamic calculations. The key takeaway is the critical role temperature plays in understanding energy flow and heat transfer.
Takeaways
- 😀 Thermodynamics is the science of energy and its transformations in systems.
- 😀 A thermodynamic system can be a fixed mass (closed system) or a region/volume (open system).
- 😀 Properties of thermodynamic systems, like temperature, help define and study energy interactions.
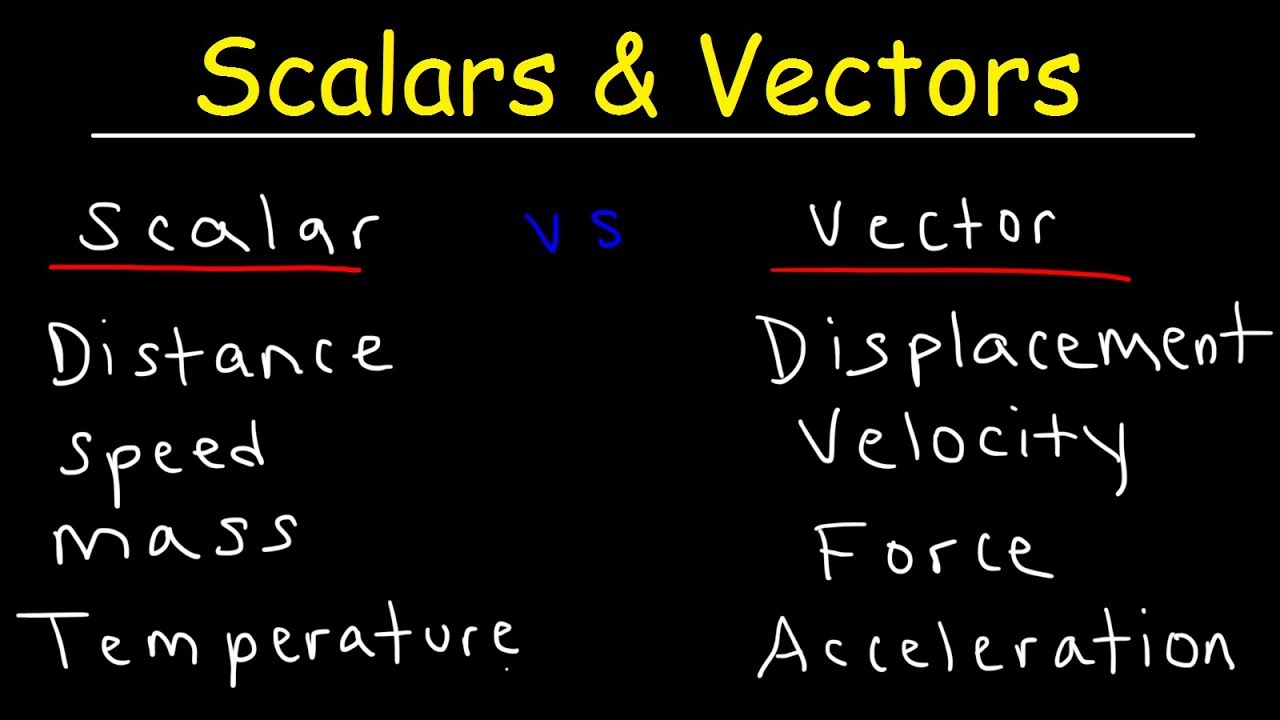
- 😀 Temperature is a scalar quantity that indicates how hot or cold a system is, with no direction or sense.
- 😀 Temperature drives the flow of heat, as seen when a hot coffee cup loses heat to the surrounding environment until thermal equilibrium is reached.
- 😀 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics defines thermal equilibrium: if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are in equilibrium with each other.
- 😀 The Zeroth Law is important because it provides the theoretical foundation for thermometers.
- 😀 Different temperature scales (Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin, Rankine) are based on reference points like freezing and boiling points of water.
- 😀 Celsius scale defines freezing at 0°C and boiling at 100°C under standard atmospheric pressure, with 100 units in between.
- 😀 Kelvin and Rankine scales account for absolute zero, the theoretical lowest temperature possible, where particle movement stops.
- 😀 The formula to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is given, and it's noted that a temperature change in Celsius is equivalent to a change in Kelvin.
- 😀 For thermodynamic calculations, it is better to use absolute temperature scales (Kelvin or Rankine) to avoid errors.
Q & A
What is thermodynamics and what does it study?
-Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that studies energy and its transformations in systems. It focuses on understanding how energy flows and changes form within different systems.
What is a thermodynamic system?
-A thermodynamic system is the part of the universe that is being studied. It could be a fixed mass of matter, known as a closed system, or a specific region of space, referred to as an open system.
What is temperature and how is it defined?
-Temperature is a scalar quantity that indicates how hot or cold a system is. It is defined as a measure of the thermal energy within a system and is crucial for determining heat flow.
Why is temperature considered a scalar quantity?
-Temperature is considered a scalar quantity because it does not have a direction or sense. Unlike vector quantities, temperature only has magnitude, not a directional component.
What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
-The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics states that if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they must also be in thermal equilibrium with each other. This law forms the basis for temperature measurement with thermometers.
How does the Zeroth Law relate to the use of thermometers?
-The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics provides the theoretical foundation for thermometers by ensuring that if a thermometer is in thermal equilibrium with a body, the thermometer and body will have the same temperature.
What are the Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature scales, and how are they defined?
-The Celsius scale is defined by the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C under standard atmospheric pressure. The Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F.
What is absolute zero, and why is it important?
-Absolute zero is the theoretical lowest possible temperature, where particles have no thermal motion. It is important because it sets the lower limit for temperature scales like Kelvin and Rankine.
What are the Kelvin and Rankine scales, and how do they differ from Celsius and Fahrenheit?
-The Kelvin and Rankine scales are absolute temperature scales that start from absolute zero. Kelvin is a modified version of the Celsius scale, while Rankine is a modified version of the Fahrenheit scale. Both scales do not have negative values.
Why are Kelvin and Rankine preferred in thermodynamics over Celsius and Fahrenheit?
-Kelvin and Rankine are preferred in thermodynamics because they are absolute scales, meaning they account for absolute zero and avoid negative temperature values. Many thermodynamic equations and formulas require temperatures to be expressed in these absolute scales for accurate calculations.
What does the concept of temperature difference (ΔT) mean in thermodynamics?
-Temperature difference (ΔT) refers to the change in temperature of a system during a process, calculated by subtracting the initial temperature from the final temperature. It is important because it drives heat flow and energy transfer in thermodynamic processes.
How are temperature differences (ΔT) the same across different temperature scales like Celsius, Kelvin, Fahrenheit, and Rankine?
-Temperature differences (ΔT) are the same across different scales because they represent a change in thermal energy, which remains consistent regardless of the scale used. For example, a 5°C change is equivalent to a 5K change, and similarly, a 5°F change is equivalent to a 5°R change.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)