Wireless LAN Protocol: Understanding Wi-Fi and IEEE 802.11 in Computer Networks
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the fundamentals of the WLAN protocol, also known as IEEE 802.11, which underpins Wi-Fi technology. It covers the basics, various Wi-Fi versions, the IEEE 802.11 protocol stack, and Wi-Fi architecture, including BSS and ESS. The script also explains the frame format of Wi-Fi, detailing the function of each field within the frame control, addressing the complexities of wireless communication such as the hidden and exposed terminal problems, and the RTS/CTS signaling mechanism. The video aims to clarify how Wi-Fi operates, from accessing the internet through wireless connections to the intricacies of its protocol stack and frame structure.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script introduces the WLAN protocol, also known as IEEE 802.11, which is the foundation of Wi-Fi communication.
- 🌐 The video explains the various versions of Wi-Fi, highlighting the evolution from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz frequencies and the increase in channel bandwidth from 20 MHz to 160 MHz.
- 🚀 The script discusses the Media Access Control (MAC) protocol used in Wi-Fi, which includes CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) to manage data transmission and avoid collisions.
- 🔒 The script mentions the use of RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send) signaling to address the hidden and exposed terminal problems in wireless networks.
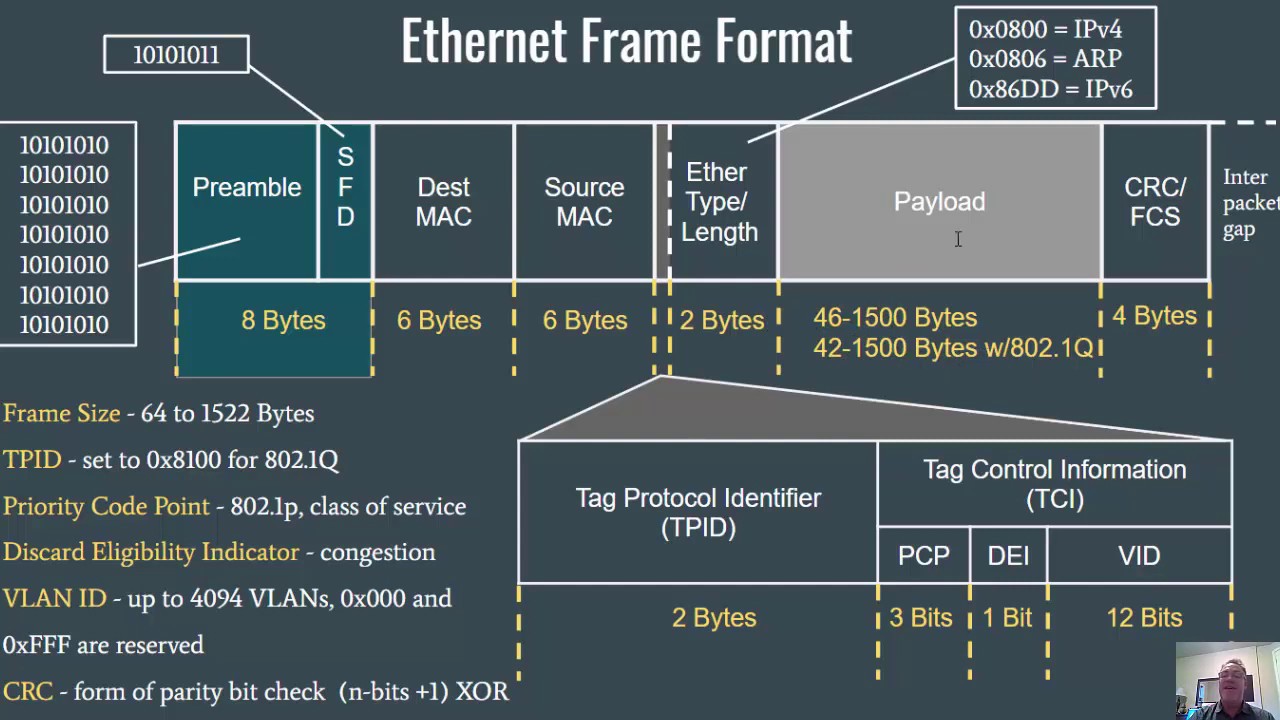
- 📈 The video outlines the frame format of Wi-Fi, detailing the structure of frame control fields, address fields, sequence numbers, and checksum for error detection.
- 🏢 The script explains two types of Wi-Fi architectures: BSS (Basic Service Set) which includes ad hoc networks and infrastructure networks, and ESS (Extended Service Set) which connects multiple BSS.
- 📶 The video describes how Wi-Fi operates on two primary frequencies, 2.4 GHz with three non-overlapping channels and 5 GHz with twenty-three non-overlapping channels.
- 🌟 The script provides an example of how a user can access the internet via Wi-Fi, detailing the process from the application layer down to the physical layer.
- 🔄 The video discusses the role of the distribution system in ESS, explaining how communication occurs between different BSS within the same ESS.
- 🛡️ The script touches on the WEP (Wired Equipment Privacy) bit in the frame control field, which indicates whether a frame is encrypted for security.
- 🔄 The video also explains the use of power management and more data bits in the frame control field, which are related to power-saving modes and the availability of additional data frames.
Q & A
What does WLAN stand for and what is its alternative name?
-WLAN stands for Wireless Local Area Network, and it is also referred to as IEEE 802.11 protocol.
What is the primary media access control method used in Wi-Fi?
-The primary media access control method used in Wi-Fi is CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance).
What are the two issues in wireless communication addressed by CSMA/CA?
-The two issues in wireless communication addressed by CSMA/CA are the hidden terminal problem and the exposed terminal problem.
What is the purpose of RTS and CTS signaling in Wi-Fi?
-RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send) signaling are used to resolve the hidden and exposed terminal problems in Wi-Fi by establishing a clear channel before transmission.
What are the two main frequencies used by Wi-Fi and how many channels do they each have?
-The two main frequencies used by Wi-Fi are 2.4 GHz, which has three channels, and 5 GHz, which has 23 non-overlapping channels.
What is the width of the channels in Wi-Fi at 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz?
-The channels at both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz have a width of 20 megahertz.
How has the maximum data rate evolved from the earliest versions of Wi-Fi to the latest versions?
-The maximum data rate has evolved from 2 Mbps in the earliest versions to up to 2.40 Gbps in the latest versions, due to multiple channels availability and increased channel bandwidth up to 160 megahertz.
What is the difference between an ad hoc network and an infrastructure network in Wi-Fi?
-An ad hoc network allows stations to communicate with each other without a central access point, while an infrastructure network uses an access point for communication between stations.
What is an ESS in the context of Wi-Fi architecture?
-An ESS, or Extended Service Set, is a Wi-Fi architecture where two or more BSS (Basic Service Sets) are connected via a distribution system, allowing communication across different access points.
What are the two types of service sets in Wi-Fi architecture?
-The two types of service sets in Wi-Fi architecture are BSS (Basic Service Set) and ESS (Extended Service Set).
What is the purpose of the frame control field in a Wi-Fi frame?
-The frame control field in a Wi-Fi frame specifies the protocol version, frame type, subtype, and other control information such as power management, WEP encryption, and sequence ordering.
What does the duration field in a Wi-Fi frame indicate?
-The duration field in a Wi-Fi frame indicates the time period for which the frame and its acknowledgment will occupy the channel.
How many address fields are there in a Wi-Fi frame and under what conditions are they used?
-There are four address fields in a Wi-Fi frame. Their usage depends on the 2DS (To DS) and From DS bits, which determine whether the frame is being sent to or from an access point or directly between stations.
What is the purpose of the sequence field in a Wi-Fi frame?
-The sequence field in a Wi-Fi frame is used to avoid duplication of frames and to ensure the reception of frames in the correct order.
What is the role of the checksum in a Wi-Fi frame?
-The checksum, which is a 4-byte field, is used for error detection in a Wi-Fi frame.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)