Biography of Werner Heisenberg
Summary
TLDRWerner Heisenberg, a German physicist born in 1901, profoundly influenced quantum mechanics and introduced the uncertainty principle, challenging classical physics with the notion that exact knowledge of a subatomic particle's position and momentum is impossible. Heisenberg's work, including contributions to atomic physics and the development of quantum mechanics, earned him the Nobel Prize in 1932. His life, marked by scientific achievements and involvement in the Nazi nuclear program, reflects the complex interplay of science, politics, and ethics.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Werner Heisenberg was a German physicist who made significant contributions to quantum mechanics and the uncertainty principle.
- 🎓 Born into an academic family, Heisenberg showed early aptitude for mathematics and physics and studied under notable professors like Arnold Sommerfeld and Max Born.
- 🎼 Heisenberg was an accomplished pianist and shared a love for classical music, which led to meeting his future wife, Elisabeth Schumacher.
- 🔬 In 1927, Heisenberg formulated the uncertainty principle, a revolutionary concept that challenged classical physics by introducing inherent uncertainty in the description of subatomic particles.
- 🏆 Heisenberg, along with Max Born and Pascual Jordan, was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Physics by Albert Einstein, and Heisenberg won the award in 1932 for his work in quantum mechanics.
- 🔬 Heisenberg's work extended beyond quantum mechanics, as he contributed to theories on hydrodynamics, the atomic nucleus, ferromagnetism, cosmic rays, and subatomic particles.
- 💣 During World War II, Heisenberg was a principal scientist in the Nazi nuclear weapons program and played a role in planning the first West German nuclear reactor.
- 🏛️ After the war, Heisenberg became the director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics and later the Max Planck Institute for Physics and Astrophysics.
- 🕊️ Heisenberg passed away in 1976, leaving a lasting legacy in physics, with his work on quantum mechanics and the uncertainty principle continuing to influence modern physics.
- 🌐 His life and career highlight the power of scientific inquiry and the complex relationship between science, politics, and ethics in the 20th century.
Q & A
Who was Werner Heisenberg and what is he famous for?
-Werner Heisenberg was a renowned German physicist who is famous for his immense contributions to the development of quantum mechanics and the formulation of the uncertainty principle.
What was Heisenberg's academic background?
-Heisenberg studied physics and mathematics at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and the Georg-August University of Göttingen, receiving his doctorate in 1923 under Arnold Sommerfeld.
What significant event did Heisenberg attend in June 1922 that influenced his work?
-In June 1922, Heisenberg attended the Bohr Festival in Göttingen where he met Niels Bohr for the first time and listened to a series of lectures on quantum atomic physics, which had a lasting effect on him.
How did Heisenberg's interest in music influence his personal life?
-His interest in music led to Heisenberg meeting his future wife, Elisabeth Schumacher, at a private music recital in January 1937, and they married later that year.
What is the uncertainty principle and why is it significant?
-The uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know the exact position and momentum of a subatomic particle with absolute precision. It challenged classical physics and introduced an inherent uncertainty into the description of subatomic particles, fundamentally altering the understanding of the quantum world.
What was the broader impact of Heisenberg's uncertainty principle on the field of physics?
-Heisenberg's uncertainty principle was part of a broader transformation in physics that led to the development of matrix mechanics and wave mechanics, which were later unified into quantum mechanics.
Who nominated Heisenberg for the Nobel Prize in Physics and when did he win it?
-Albert Einstein nominated Heisenberg, Max Born, and Pascual Jordan for the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1928, and Heisenberg won the award in 1932 for his creation of quantum mechanics.
What other areas of physics did Heisenberg contribute to besides quantum mechanics?
-Heisenberg made contributions to theories of the hydrodynamics of turbulent flows, the atomic nucleus, ferromagnetism, cosmic rays, and subatomic particles.
What was Heisenberg's involvement in the Nazi nuclear weapons program during World War II?
-Heisenberg was a principal scientist in the Nazi nuclear weapons program during World War II, and he was instrumental in planning the first West German nuclear reactor at Karlsruhe and a research reactor in Munich in 1957.
What were Heisenberg's professional roles after World War II?
-Following World War II, Heisenberg was appointed director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics and later became director of the Max Planck Institute for Physics and Astrophysics from 1960 to 1970.
How did Heisenberg's life and career reflect the intersection of science, politics, and ethics?
-Heisenberg's life and career exemplify the power of scientific inquiry and the complex intersection of science, politics, and ethics, particularly in the context of his involvement in the Nazi nuclear weapons program and his leadership roles in post-war scientific institutions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

What is the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle? - Chad Orzel

Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle Explained & Simplified - Position & Momentum - Chemistry Problems
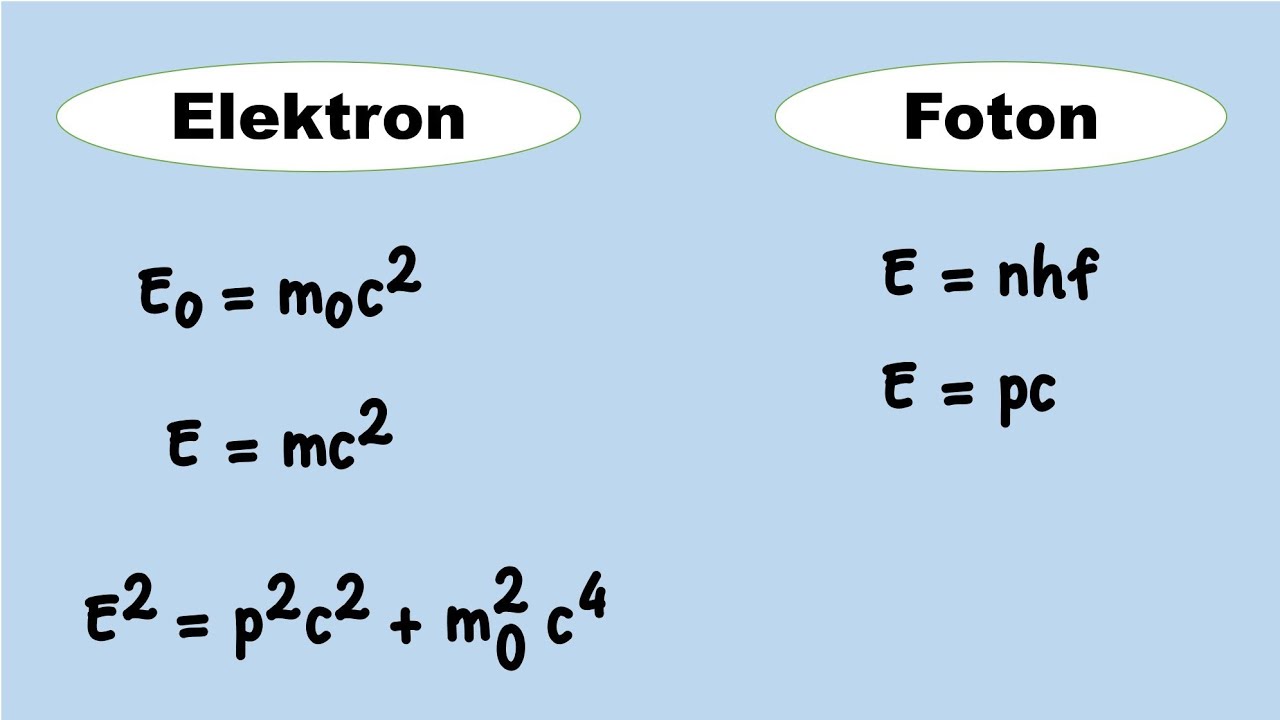
Konsep Dasar Fisika Modern-Kuantum

¿Qué es el Principio de incertidumbre de Heisenberg? - Chad Orzel
Numerical problems on Quantum Mechanics Part 1-VTU physics

O Princípio da Incerteza Explicado
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
