Pathophysiology: Shock
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into shock, a critical medical state where organs are starved of oxygen-rich blood. It outlines various causes like injuries, infections, and allergic reactions, and lists symptoms such as shortness of breath and dizziness. The script categorizes shock into types including cardiogenic, hypovolemic, neurogenic, anaphylactic, septic, and obstructive, detailing their unique triggers and effects. It emphasizes the high mortality rate of cardiogenic shock and the rapid onset of anaphylactic shock, concluding with treatment options and the importance of prompt medical intervention.
Takeaways
- 💡 Shock is a critical condition where organs and tissues lack sufficient oxygenated blood.
- 🚑 Causes of shock are diverse, including injury, infections, allergic reactions, heart issues, and other medical emergencies.
- 🔍 Signs of shock include shortness of breath, dizziness, confusion, rapid pulse, weakness, coldness, nausea, and thirst.
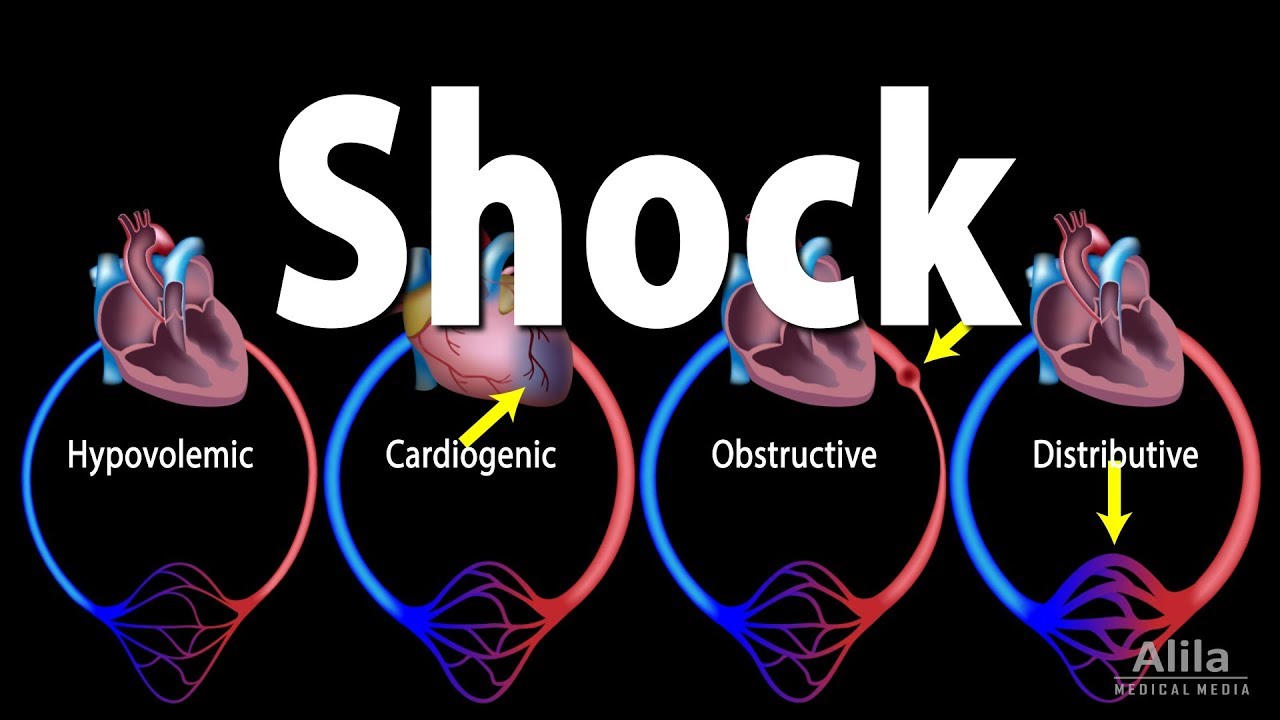
- 💔 Cardiogenic shock is due to the heart's inability to pump enough blood, with a high mortality rate over 70%.
- 🩸 Hypovolemic shock follows significant blood or fluid loss, leading to decreased blood pressure and potential organ damage.
- 🌡️ Neurogenic shock is caused by widespread vasodilation due to parasympathetic nervous system overactivity and sympathetic inhibition.
- 🦠 Anaphylactic shock is a rapid immune response to allergens, causing vasodilation and increased vascular permeability.
- 🚑 Treatment for anaphylactic shock includes epinephrine, antihistamines, steroids, and fluids to counteract symptoms.
- 🤒 Septic shock stems from blood infections leading to systemic inflammatory response and can be triggered by various infections.
- 🚫 Obstructive shock occurs due to blood flow blockages like pulmonary embolism, causing circulation issues and organ failure.
- 👋 The video aims to educate viewers on the different types and aspects of shock, emphasizing its seriousness and urgency.
Q & A
What is shock in medical terms?
-Shock is a serious medical condition where the body's organs and tissues do not receive an adequate supply of oxygenated blood.
What are some common causes of shock?
-Shock can be caused by traumatic injury, severe infections, allergic reactions, heart attack or failure, and other medical conditions.
What are the signs and symptoms of shock?
-Signs and symptoms of shock include shortness of breath, dizziness or confusion, rapid pulse, weakness, feeling cold, nausea, and thirst.
What is cardiogenic shock?
-Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, often due to heart attack, severe heart failure, or other cardiac issues, and has a high mortality rate.
Why does hypovolemic shock occur?
-Hypovolemic shock occurs when there is a significant loss of blood or fluid volume in the body, such as from bleeding, dehydration, or severe burns, leading to decreased blood pressure and potential organ damage.
How does the body compensate during hypovolemic shock?
-During hypovolemic shock, compensatory mechanisms are activated, including the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, antidiuretic hormone secretion, and movement of interstitial fluid into the vascular system.
What causes neurogenic shock?
-Neurogenic shock results from trauma to the nervous system, depressive or anesthetic medications, severe pain, or emotional distress, leading to widespread vasodilation and inhibited sympathetic nervous system activity.
What is anaphylactic shock and how does it occur?
-Anaphylactic shock is an immune system reaction to an allergen, causing the release of inflammatory cytokines and resulting in widespread vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
What treatments are used for anaphylactic shock?
-Treatment for anaphylactic shock includes administration of epinephrine (adrenalin), antihistamines, steroids, vasopressors, beta adrenergic agonist bronchodilator inhalers, and fluids.
How is septic shock different from other types of shock?
-Septic shock results from an infection in the blood, leading to systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and is characterized by fever, increased heart and respiratory rates, and a high white blood cell count.
What causes obstructive shock?
-Obstructive shock occurs when there is a blockage in blood flow, such as a pulmonary embolism or tension pneumothorax, preventing proper blood circulation and leading to organ damage and failure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)