MCAT Biology Lecture: Digestive System (1/2)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the anatomy and function of the human digestive system, covering the journey of food from ingestion to absorption. It explains the roles of various organs, the process of mechanical and chemical digestion, and the importance of accessory organs and the enteric nervous system. The script also touches on the hormonal regulation of feeding behavior and the significance of the stomach and duodenum in digestion, providing a comprehensive overview for students of biology and medicine.
Takeaways
- 🍲 The digestive system's role is to break down complex foods into simpler molecules like monosaccharides, fatty acids, and amino acids for absorption and use by the body.
- 🔬 The process involves both intracellular digestion, which is part of metabolism, and extracellular digestion that occurs in the lumen of the alimentary canal.
- 📐 The alimentary canal is divided into specialized sections for different functional roles, primarily digestion and absorption, and is regulated by the enteric nervous system.
- 🦷 Ingestion begins in the oral cavity where mechanical digestion (chewing) and chemical digestion (enzymes in saliva) start to break down food.
- 🔄 Mechanical digestion involves physically breaking down food particles, while chemical digestion involves enzymatic cleavage of chemical bonds.
- 🚫 The pharynx is a shared pathway for food and air, with the epiglottis preventing food from entering the larynx during swallowing.
- 🌀 The esophagus uses peristalsis, rhythmic contractions of its muscles, to propel food towards the stomach.
- 🍽️ The stomach is a central organ for both mechanical and chemical digestion, producing enzymes and acids to break down food into chyme.
- 🧪 In the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, enzymes and hormones are released to continue the chemical digestion process and prepare nutrients for absorption.
- 📉 Hormones such as gastrin, secretin, and cholecystokinin (CCK) play crucial roles in regulating digestion, including the release of bile and pancreatic juices.
- 🚰 Accessory organs like the salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder provide enzymes and lubrication necessary for the digestion of food.
Q & A
What is the primary role of the digestive system?
-The primary role of the digestive system is to break down complex foods into simpler molecules such as monosaccharides, fatty acids, and amino acids, which can be absorbed and used by the body for energy, growth, development, and maintenance.
What are the two types of digestion mentioned in the script?
-The two types of digestion are intracellular digestion, which involves the oxidation of glucose and fatty acids for energy as part of metabolism, and extracellular digestion, which occurs in the lumen of the alimentary canal and involves the extraction of nutrients from food.
What is the process of mechanical digestion?
-Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large food particles into smaller ones. It does not involve breaking chemical bonds and includes processes like chewing (mastication) in the mouth, which increases the surface area for enzymatic digestion.
What is the role of chemical digestion in the digestive system?
-Chemical digestion involves the enzymatic cleavage of chemical bonds in macromolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, breaking them down into smaller units like peptides, monosaccharides, and fatty acids that can be absorbed by the body.
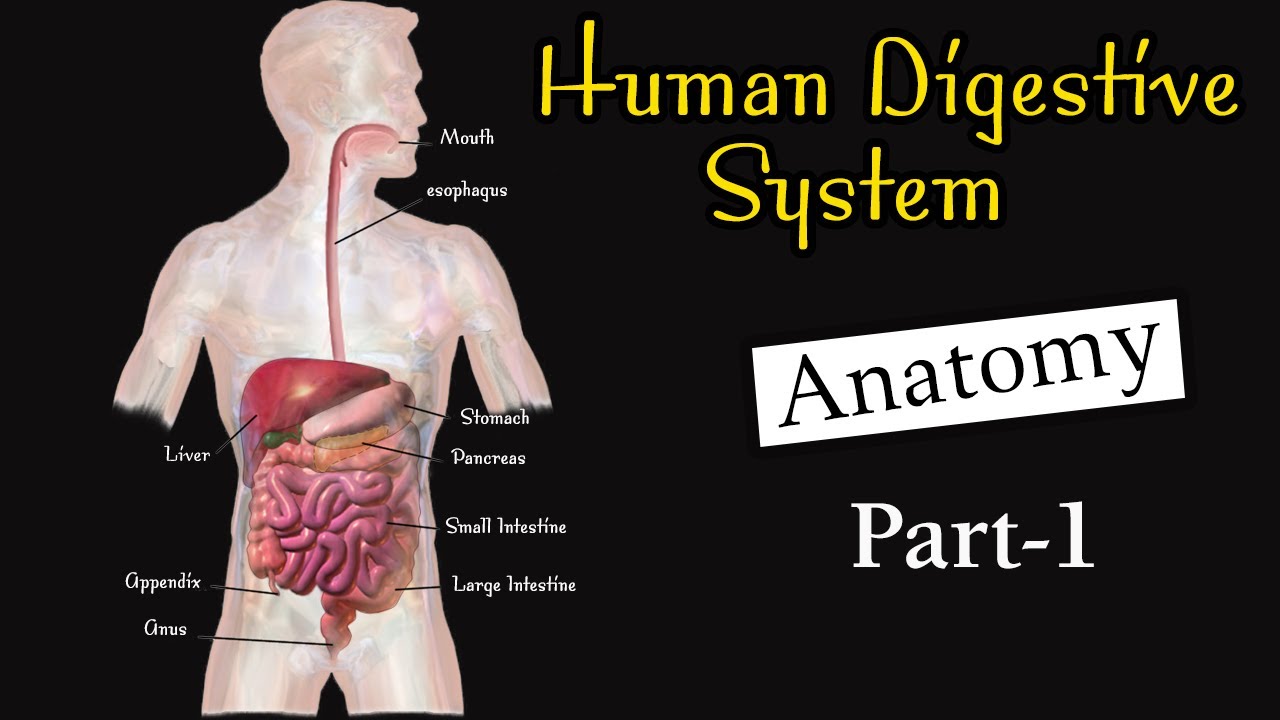
What are the main organs of the digestive system mentioned in the script?
-The main organs mentioned include the oral cavity (mouth), pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and accessory organs such as the salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
What is the function of the enteric nervous system in the gastrointestinal system?
-The enteric nervous system, which contains about 100 million neurons, governs the function of the gastrointestinal system. It triggers peristalsis, the rhythmic contraction of the gut tube, to move material through the system and can function independently of the brain and spinal cord but is regulated by the autonomic nervous system.
How does the stomach contribute to the digestion process?
-The stomach contributes to digestion through mechanical means by churning food and chemical means by secreting substances like hydrochloric acid, pepsinogen (which becomes pepsin), mucus, intrinsic factor, and gastrin. These substances aid in protein digestion, protect the stomach lining, and regulate gastric acid secretion and motility.
What is the role of the duodenum in the digestive process?
-The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine and plays a key role in chemical digestion. It secretes enzymes like disaccharidases and peptidases that break down carbohydrates and proteins, respectively. It also releases hormones like secretin and cholecystokinin (CCK) that regulate the release of pancreatic juices and bile for further digestion.
What is the significance of the lower esophageal sphincter in the digestive process?
-The lower esophageal sphincter is a muscular ring that relaxes and opens to allow the passage of food from the esophagus into the stomach. It prevents stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus, which would cause heartburn or other issues.
What are the main hormones involved in regulating feeding behavior and the feeling of fullness as mentioned in the script?
-The main hormones involved in feeding behavior and fullness include antidiuretic hormone and aldosterone, which promote thirst; glucagon and ghrelin, which promote hunger; and leptin and cholecystokinin, which promote the feeling of fullness.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)