Motherboards Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers an insightful overview of the motherboard, the central component of a computer, often termed 'mobo'. It explains the CPU socket, memory slots for RAM, expansion slots for additional capabilities like video and sound cards, and storage connectors like SATA and M.2. The evolution from traditional northbridge and southbridge chips to the modern PCH architecture is highlighted. The script also covers various I/O interfaces, integrated video and sound, and the different motherboard form factors, emphasizing ATX as the prevalent standard. A list of recommended motherboards is promised in the video description.
Takeaways
- 🔌 The motherboard is the central circuit board in a computer where all components connect.
- 💻 CPU socket is the placement for the central processing unit (CPU).
- 🔌 Memory slots are for inserting RAM, the primary memory DIMM modules.
- 📀 Expansion slots allow for the installation of additional components like video cards, sound cards, and network cards.
- 🔗 SATA connectors are used to attach storage devices such as SSDs or hard drives.
- 💾 M.2 slots are newer connectors for solid-state drives on modern motherboards.
- 🔄 The Platform Controller Hub (PCH) has replaced the older northbridge and southbridge chips for chipset architecture.
- 🔄 The northbridge was responsible for communication between the CPU, PCI express bus, and memory.
- 🔄 The southbridge managed standard PCI slots, SATA connectors, USB ports, etc.
- 🔌 Motherboards have multiple I/O interfaces, commonly located on the rear I/O panel.
- 🔌 USB ports are common for connecting various peripherals and supplying power.
- 🖥 Integrated video is a built-in video adapter on some motherboards, suitable for light applications.
- 🌐 Network interface cards provide Ethernet connectivity for network access.
- 🔊 Integrated sound is the built-in sound processing feature on some motherboards.
- 📏 Motherboards come in different sizes known as form factors, with ATX being the most common for PCs today.
- 📏 Micro ATX is a smaller form factor designed for smaller cases with fewer features and lower power consumption.
Q & A
What is a motherboard and why is it important in a computer system?
-A motherboard is the main component of a computer, often referred to as the main board or 'mobo' for short. It is a large circuit board that all other computer components connect to, serving as the central hub for communication between the CPU, memory, storage devices, and expansion cards.
What is the role of the CPU socket on a motherboard?
-The CPU socket is the location on the motherboard where the central processing unit (CPU) is placed. It is crucial as it provides the connection point for the CPU, which is the brain of the computer, to interact with other components.
What are memory slots and what do they hold?
-Memory slots on a motherboard are where the primary memory DIMM modules, known as RAM (Random Access Memory), are inserted. RAM is volatile memory that the computer uses to store data that is being processed.
Can you explain the purpose of expansion slots on a motherboard?
-Expansion slots, also known as bus slots, are used to install various components that add more capabilities to a computer, such as a video card, sound card, network card, and others. They allow for the extension of the computer's functionality beyond its base configuration.
What are SATA connectors and how are they used on a motherboard?
-SATA (Serial ATA) connectors are used to attach storage devices, such as SSDs (Solid State Drives) or hard drives, to the motherboard. They provide a high-speed data transfer interface for these devices.
What is an M.2 slot and what is its function?
-An M.2 slot is a newer type of slot on modern motherboards designed for attaching an M.2 solid-state drive. It allows for faster data transfer rates and is often used for high-performance storage solutions.
What is the PCH and how does it relate to the older chipset architecture?
-The PCH, or Platform Controller Hub, is the latest chipset architecture by Intel that has replaced the older northbridge and southbridge architecture. It consolidates the functions of these chips, with the northbridge functions now integrated into the CPU and the southbridge functions handled by the PCH.
What were the roles of the northbridge and southbridge chips in older motherboards?
-In older motherboards, the northbridge chip acted as a middleman between the CPU, PCI express bus, and memory, while the southbridge chip was responsible for standard PCI slots, SATA connectors, USB ports, and other I/O functions.
What are the common input/output interfaces found on the rear I/O panel of a motherboard?
-Common input/output interfaces on the rear I/O panel of a motherboard include USB ports, which are used for connecting various peripherals and providing power, as well as video output ports like HDMI or DisplayPort, and network ports for Ethernet connections.
What is the difference between integrated video and an expansion video card?
-Integrated video is a built-in video adapter on the motherboard that is suitable for light applications and everyday use. An expansion video card, on the other hand, is a more powerful graphics card that is added to the system to handle extensive graphic applications like gaming.
What is a form factor and what are the common motherboard form factors?
-A form factor refers to the size and shape of a motherboard. The most common form factor used in PCs today is ATX (Advanced Technology Extended), which is a standard size of 12 x 9.6 inches. Other form factors include Micro ATX, which is smaller and designed for smaller cases, and the older AT form factor, which is no longer in development.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Every Computer Component Explained in 3 Minutes

What does what in your computer? Computer parts Explained

Computer - Inside the System Unit | Class 4 Computer | Chapter 1 | CodeBot
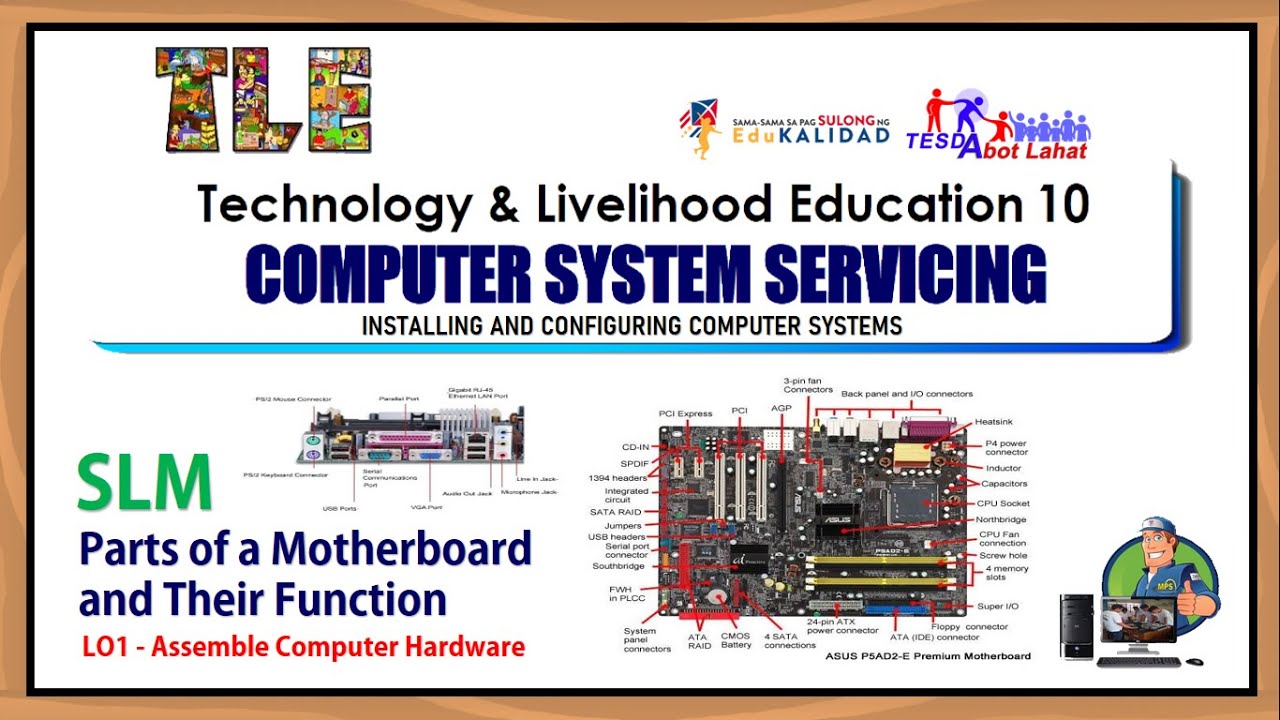
Parts of a Motherboard and Their Function - Part 2 Back Panel Connectors & Ports

What Is Computer Hardware ? | Beginners Guide To Computer Hardware.
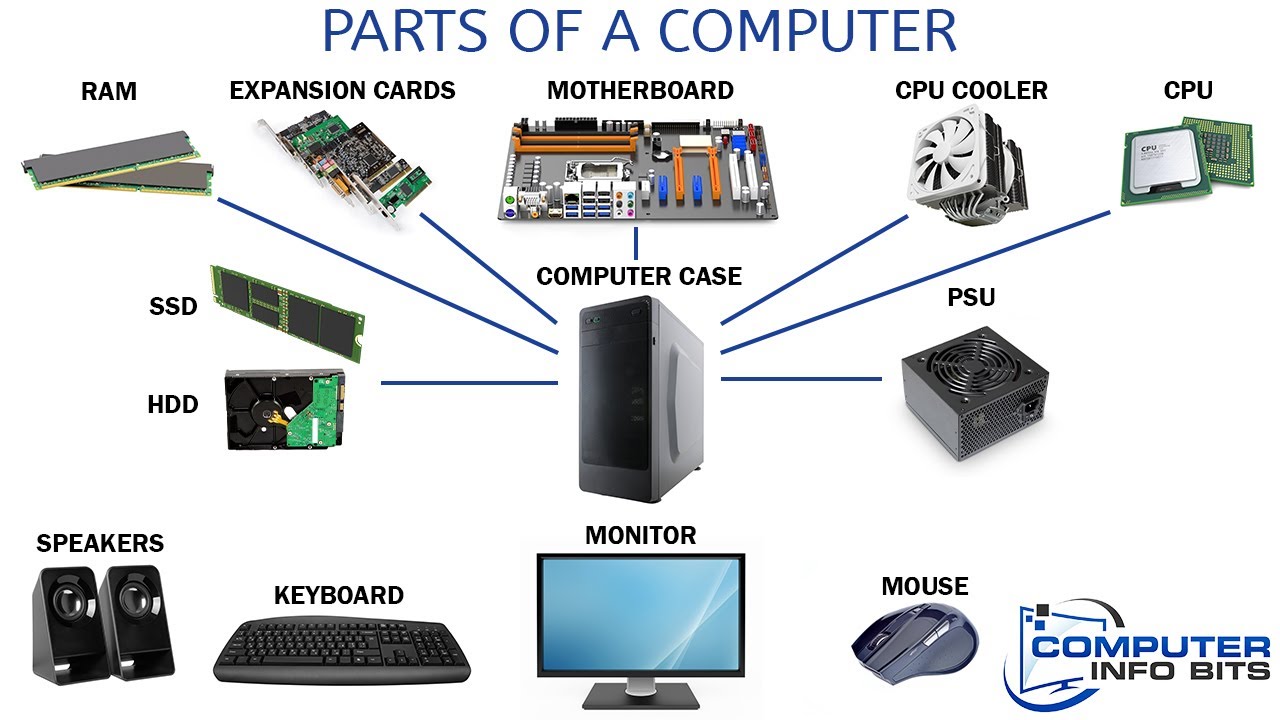
Parts Of A Computer And Their Functions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)