[Math 20] Lec 1.5 Lines and Circles
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an in-depth exploration of the equations of lines and circles. It covers essential concepts like the slope of a line, point-slope form, slope-intercept form, and the general equation of a line. The video also discusses perpendicular and parallel lines, finding equations of lines passing through specific points, and the properties of tangent lines to circles. The explanation includes formulas, step-by-step examples, and a focus on how to find the slope and intercept of lines, as well as the equation of a circle and its tangent.
Takeaways
- 📝 The video explains the equations of lines and circles, starting with a review of a unique line and its slope.
- 📏 The slope of a line is determined by the formula: slope (m) = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), representing the steepness of the line.
- 🔄 To find the equation of a line, use the point-slope form: y - y1 = m(x - x1), which is crucial for describing lines.
- 🔗 The slope-intercept form of a line is y = mx + b, where b is the y-intercept of the line.
- 🔍 Parallel lines have the same slope, while perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other.
- 🔄 The video demonstrates how to find the equation of a line that passes through two points or is perpendicular to another line.
- ⚪ The equation of a circle is given as (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where (h, k) is the center and r is the radius.
- 📏 The distance formula between two points is used to relate points on a circle to its center.
- 🧮 The general form of a circle’s equation can be expanded to find specific values for the center and radius.
- 📐 Tangent lines to a circle intersect it at exactly one point and are perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency.
Q & A
What is the slope of a line and how is it determined?
-The slope of a line represents its steepness and is determined using the formula: slope (m) = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on the line.
How do you find the equation of a line using a point and the slope?
-The equation of a line can be found using the point-slope form: y - y1 = m(x - x1), where (x1, y1) is a point on the line and m is the slope.
What is the slope-intercept form of a line equation?
-The slope-intercept form of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept, the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
How do you find the equation of a line that passes through two points?
-To find the equation of a line passing through two points, first calculate the slope using m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), then use the point-slope form y - y1 = m(x - x1) with one of the points.
What does it mean for two lines to be parallel?
-Two lines are parallel if they have the same slope, meaning the slopes of the two lines are equal (m1 = m2).
What is the relationship between the slopes of two perpendicular lines?
-Two lines are perpendicular if the product of their slopes is -1. This means if one line has a slope of m, the other line has a slope of -1/m.
How can you find the equation of a line perpendicular to another line and passing through a given point?
-First, find the slope of the given line and take the negative reciprocal to get the slope of the perpendicular line. Then, use the point-slope form with the given point to find the equation.
What is the definition of a circle in a plane?
-A circle is defined as a set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point called the center. The distance from the center to any point on the circle is the radius.
How do you write the equation of a circle given its center and radius?
-The equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r².
What is a tangent line to a circle, and how is it characterized?
-A tangent line to a circle is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point. At the point of tangency, the line is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
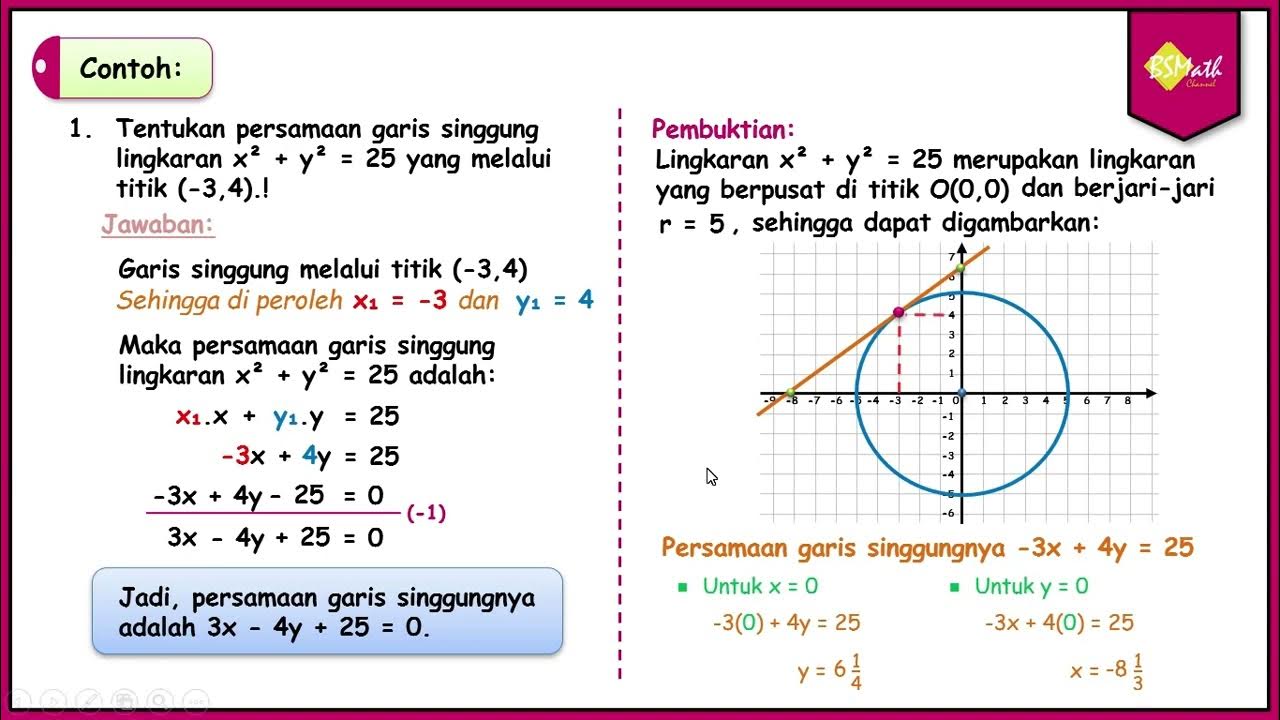
Persamaan Garis Singgung Lingkaran di Suatu Titik Pada Lingkaran - SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Persamaan lingkaran

Lingkaran Bagian 1 - Konsep Dasar dan Persamaan Lingkaran Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI
FENOMENA PERPINDAHAN PANAS KABEL LISTRIK SILINDER

TANGENT AND SECANT SEGMENT || GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q2

Oliveboard live mains mock test July 29-30 ssc chsl #ssccgl #sscchsl #ssccpo #ssccgl2024 #sscgd
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)