How does an electric motor work?
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the working principle of a direct current (DC) electric motor. It starts by demonstrating how a wire wrapped around a metal ball creates an electromagnet with poles that change with the current's polarity. The motor's operation is illustrated with an electromagnet mounted on a spindle between two permanent magnets, which keeps spinning as the polarity is switched. The addition of a commutator and brushes allows continuous rotation by changing the electromagnet's polarity. More loops in the armature increase torque, and stronger electromagnets enhance spinning force. The stationary part, called the stator, usually consists of permanent magnets, and the motor's function is to drive various applications.
Takeaways
- 🔌 An electric motor operates on the principle of electromagnetism, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- 🌀 Wrapping a wire around a metal ball creates an electromagnet when an electric circuit is completed, aligning magnetic particles.
- 🧲 Electromagnets have north and south poles and can attract or repel other magnets based on their polarity.
- 🔄 Reversing the polarity of the voltage changes the direction of the electric current, which in turn changes the poles of the electromagnet.
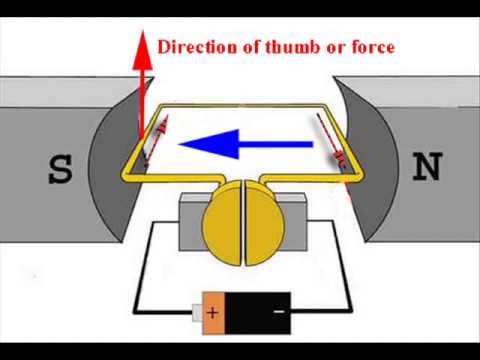
- 🔄 Mounting the electromagnet on a spindle and between two permanent magnets allows it to align with the side magnets, creating a rotating force.
- 🔌 Swapping the wires changes the polarity of the electromagnet, enabling continuous rotation due to the attraction and repulsion of magnetic poles.
- 🛠️ A curved permanent magnet positioned beside the electromagnet strengthens the magnetic field, enhancing the motor's performance.
- 🔁 The commutator, a ring with gaps, is connected to brushes that maintain contact as it spins, allowing for continuous current flow and polarity switching.
- 🔄 The brushes switch contact to the opposite side of the commutator ring, causing the electromagnet (armature) to keep spinning.
- 🔗 Adding more loops or windings to the armature increases the strength of the electromagnet and the motor's torque.
- 🏗️ The stationary part of the motor, known as the stator, usually consists of permanent magnets that provide a stable magnetic field for the rotating armature.
- 🔧 Electric motors are versatile and can be used in various applications to provide motion and power to different systems.
Q & A
How does a direct current (DC) electric motor work?
-A DC electric motor works by creating an electromagnet using a wire wrapped around a metal ball. This electromagnet, when placed between two permanent magnets and connected to a power source, aligns with the permanent magnets and changes polarity as the circuit is completed, causing it to spin.
What happens when the polarity of the voltage is reversed in an electric motor?
-Reversing the polarity of the voltage changes the direction of the electric current flow, which in turn changes the poles of the electromagnet, allowing for continuous rotation when the polarity is switched back and forth.
What is the purpose of the spindle in an electric motor?
-The spindle is the rotating central axis on which the electromagnet is mounted, allowing it to align with the permanent magnets and rotate freely.
How does a commutator in an electric motor function?
-The commutator, with gaps on the opposite sides, turns together with the armature and connects to brushes on the sides. It switches the contact to the other side of the commutator ring, changing the polarity of the electromagnet and allowing the armature to keep spinning.
What is the role of brushes in an electric motor?
-Brushes maintain contact with the commutator as it spins, allowing the current to flow through them, the commutator, the armature loop, and back through the other brush, thus enabling the continuous rotation of the motor.
Why is a curved permanent magnet positioned to the side of the electromagnet in a motor?
-A curved permanent magnet is used to strengthen the magnetic field around the electromagnet, making the electromagnet stronger and enhancing the motor's performance.
What is the significance of the armature in an electric motor?
-The armature is a metal loop that acts as the electromagnet in the motor. It is responsible for generating the magnetic field necessary for the motor's operation.
How does increasing the number of loops in the armature affect the electric motor?
-Increasing the number of loops in the armature, or winding more wires around it, strengthens the electromagnet, resulting in more spinning force and stronger torque.
What is the stator in an electric motor?
-The stator is the stationary part of the motor, usually consisting of permanent magnets that create a magnetic field for the rotating part, or rotor, to interact with.
What is the function of the additional loop in the commutator ring?
-The additional loop in the commutator ring allows the brushes to change their contact points, enabling the motor to continue spinning as the loops take turns acting as electromagnets.
How do electric motors find application in various customer needs?
-Electric motors are versatile and can be used as drive motors in various applications, providing the necessary force and motion to keep different types of machinery and equipment in motion.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
DC Motors: How Do They Work? Construction & Working Principle of a DC Motor | Electrical4U

Cara Kerja Motor Listrik DC

Get Amped Up: The Science of Galvanometer Current Detection

How Do Electric Vehicles Work?

3 point starter | 3 point starter dc motor | three point starter of dc motor | three point starter

Listrik Dinamis Part 1 materi arus listrik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)