(Part 4) Longitudinal Stability Of Aircraft | Lecture
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the concepts of dynamic stability, illustrating various types such as subsidence, divergence, neutral stability, damped oscillation, undamped oscillation, and divergent oscillation. It explains how these dynamics affect an airplane's ability to return to equilibrium after a disturbance. The importance of positive static and dynamic stability for safe flight is highlighted, along with the challenges of pilot-induced oscillations. The discussion also covers longitudinal stability, including long period oscillations known as 'fugoid' and short period oscillations, emphasizing their impact on aircraft control and structural integrity.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script discusses dynamic stability, focusing on longitudinal dynamic stability in the context of aviation.
- 🔍 It introduces the concept of subsidence as a type of dynamic stability, which is not operationally possible for an airplane, using a displacement-time graph to illustrate the behavior.
- 📍 The script explains positive static stability with an airplane returning to equilibrium after a disturbance, indicating stability.
- 🔄 Positive dynamic stability is shown where the system returns to equilibrium over time with oscillations that diminish.
- 🍯 The concept of damping is introduced, explaining how a viscous substance like syrup can cause a ball to return to equilibrium without oscillations.
- 📉 Negative static stability is illustrated where the system moves further away from equilibrium after a disturbance, indicating instability.
- 🔁 Negative dynamic stability is described where the system continues to move away from equilibrium over time, amplifying the instability.
- 🚫 Neutral dynamic stability is presented where the system remains displaced from equilibrium without returning or diverging further.
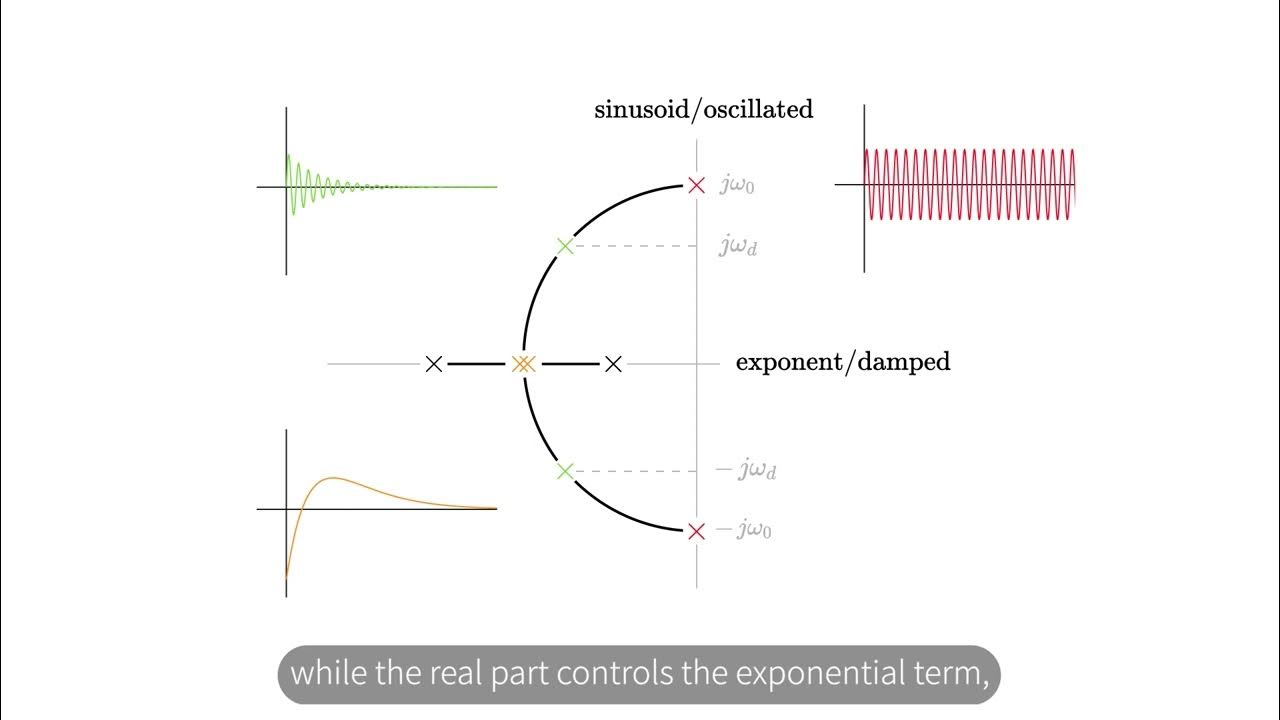
- 🔄 Damped oscillation is a type of positive dynamic stability where the system oscillates back to equilibrium with reducing amplitude.
- 🔁 Undamped oscillation shows positive static stability but neutral dynamic stability as oscillations continue without reduction.
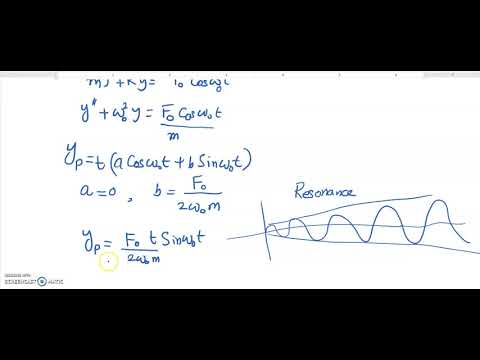
- 📈 Divergent oscillation is a scenario where oscillations increase over time, indicating negative dynamic stability, often resulting from pilot-induced oscillation.
- ✈️ The importance of demonstrating required static and dynamic stability in aircraft is emphasized, as lack of stability can make an aircraft difficult to control.
- 🔄 Longitudinal dynamic stability involves two types of oscillation: the long period oscillation known as the 'fugoid', and the short period oscillation.
- ⏱️ The fugoid has a period of oscillation between one and two minutes, involving gradual interchange of potential and kinetic energy.
- 🚀 Short period oscillation involves rapid pitch oscillations with significant changes in angle of attack and load factor, which can be damaging to the aircraft structure.
- ⚠️ Pilot response time is crucial, as attempting to dampen oscillations can inadvertently worsen the instability if not done correctly.
Q & A
What is dynamic stability in the context of the script?
-Dynamic stability refers to the ability of a system, such as an airplane, to return to its equilibrium state after being disturbed. It is a measure of how the system behaves over time in response to disturbances.
What is the difference between positive and negative static stability?
-Positive static stability is when a system moves back towards its equilibrium position after being disturbed, indicating stability. Negative static stability is when the system moves further away from its equilibrium position, indicating instability.
How does the script describe the behavior of an airplane with positive dynamic stability?
-An airplane with positive dynamic stability will gradually return to its equilibrium position over time after a disturbance, with the motion eventually dying out as it reaches the equilibrium state.
What is subsidence in the context of the script?
-Subsidence, as mentioned in the script, is a type of dynamic stability that is not operationally possible for an airplane. It refers to the system's tendency to move back towards equilibrium after being disturbed.
What is divergence as a type of dynamic stability?
-Divergence is a type of dynamic stability where, after a disturbance, the system's initial reaction is to move further away from equilibrium. Over time, the system continues to move away, illustrating negative dynamic stability.
What role does damping play in dynamic stability?
-Damping is a force or process that reduces the amplitude of oscillations in a system. In the context of dynamic stability, damping helps the system to return to equilibrium without excessive oscillations.
What is neutral dynamic stability?
-Neutral dynamic stability is when a system, after being displaced from equilibrium, neither moves back towards nor further away from equilibrium. The system remains equally displaced over time.
How does the script illustrate the concept of damped oscillation?
-Damped oscillation is illustrated in the script as a system that, after being disturbed, moves back towards equilibrium with several oscillations that gradually decrease in amplitude, indicating positive dynamic stability.
What is undamped oscillation and how does it differ from damped oscillation?
-Undamped oscillation is when a system oscillates back and forth across the equilibrium position without a decrease in amplitude. It differs from damped oscillation in that the oscillations do not decrease over time and may continue indefinitely.
What is divergent oscillation and how does it relate to stability?
-Divergent oscillation is a type of dynamic stability where the system oscillates with increasing amplitude after being disturbed, indicating negative dynamic stability. This can occur if energy is continuously added to the system, such as through pilot-induced oscillation.
What are the two basic types of oscillation in longitudinal dynamic stability mentioned in the script?
-The two basic types of oscillation in longitudinal dynamic stability are long period oscillation, known as the fugoid, and short period oscillation. The fugoid involves a gradual interchange of potential and kinetic energy, while short period oscillation involves rapid pitch oscillations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)