Introduction to Female Reproductive Anatomy - 3D Anatomy Tutorial
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial offers a concise introduction to the female reproductive system, highlighting its key components and their functions. It explains the ovaries' role in egg production and ovulation, the structure and parts of the fallopian tubes, and the uterus's capacity to house and nurture a developing embryo. The script also details the anatomy of the vagina and the peritoneal relationships within the pelvic cavity, including the broad ligament and the pouches it forms.
Takeaways
- 📍 The female reproductive system is located in the pelvic region, with the bladder anteriorly and the rectum and anal canal posteriorly.
- 👩 The ovaries are the primary female sex organs, responsible for producing the egg or ovum, which is released monthly in a process called ovulation.
- 🌐 The ovaries are intraperitoneal and are suspended in the peritoneal cavity by ligaments, releasing the egg into this cavity.
- 🌬️ The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, have fimbriae that help guide the egg from the ovary into the tube, where fertilization commonly occurs.
- 🔍 The uterine tube is divided into four parts: infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, and the intrauterine part, with the ampulla being the most common site for fertilization.
- 🏺 The uterus is a muscular sac where the embryo develops into a fetus and eventually a baby, with distinct parts including the fundus, body, and cervix.
- 🔑 The cervix, the neck of the uterus, protrudes into the vagina and creates recesses known as fornices, which include anterior, posterior, and two lateral fornices.
- 💪 The uterus has three layers: the outer perimetrium, the middle myometrium (muscle layer), and the inner endometrium, which thickens and disintegrates during the menstrual cycle.
- 🚶♀️ The vagina is a fibromuscular tube that extends from the external vaginal orifice to the cervix, with three layers similar to the uterus.
- 🌌 The broad ligament is a sheet of peritoneum that drapes over the pelvic viscera, forming pouches such as the vesico-uterine pouch and the recto-uterine pouch or pouch of Douglas.
- 🔄 The endometrium is under hormonal influence, varying in thickness throughout the menstrual cycle and disintegrating at the onset of menstruation.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
-The ovaries are the primary female sex organs responsible for producing the female sex cells, known as ova or eggs, and releasing them monthly through a process called ovulation.
What are the fallopian tubes also known as?
-The fallopian tubes are also referred to as the uterine tubes, connecting the ovaries to the uterus.
In which part of the uterus does the embryo develop into a fetus?
-The embryo develops into a fetus within the muscular sac of the uterus.
What is the structure that connects the uterus to the vagina?
-The cervix is the structure that connects the uterus to the vagina, protruding into the vagina and creating recesses known as fornices.
What are the four parts of the uterine tube?
-The four parts of the uterine tube are the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, and the intrauterine part where it opens into the uterus.
Where does fertilization most commonly occur in the female reproductive system?
-Fertilization most commonly occurs in the ampulla, the middle and longest part of the uterine tube.
What is the term for the process where the endometrium thickens and disintegrates during the menstrual cycle?
-The process is hormonally influenced and involves the endometrium thickening during the menstrual cycle and disintegrating at the onset of menstruation.
What is the anatomical relationship of the vagina to the bladder and rectum?
-The vagina is a fibromuscular tube that lies anterior to the rectum and anal canal and behind the bladder and urethra.
What are the three layers of the uterus?
-The three layers of the uterus are the perimetrium (outer connective tissue layer), the myometrium (thick middle layer of smooth muscle), and the endometrium (inner mucosal layer).
What is the pouch formed behind the superior end of the vagina called?
-The pouch formed behind the superior end of the vagina is called the recto-uterine pouch, or the pouch of Douglas.
What is the broad ligament and what is its function?
-The broad ligament is a flat sheet of peritoneum that drapes over the pelvic viscera, attaching to the uterus and ovaries, and providing structural support and housing blood vessels.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
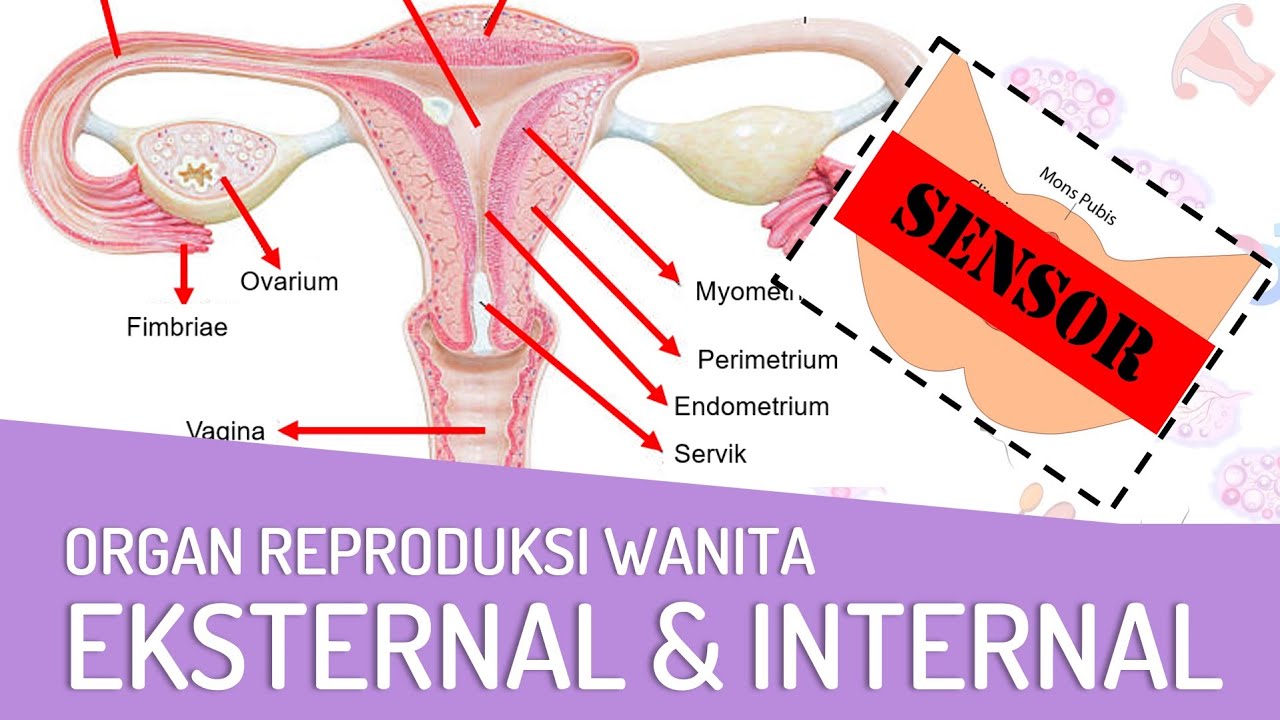
Organ Reproduksi Wanita [Eksternal & Internal] dan Fungsinya

Khan Academy - Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System

PARTS AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (tagalog)

Human #male reproductive system class 10 | sexual reproduction | Biology : CBSE : NCERT X Science

Welcome to the reproductive system | Reproductive system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

Female reproductive system in Hindi | external genitalia Area | Internal genitalia area | Functions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)