Transição demográfica
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the demographic transition, a shift from high birth and death rates to lower levels, leading to slower population growth. It explains how factors like urbanization, improved sanitation, and medical advancements have historically reduced mortality rates, causing a population boom. The script then discusses the subsequent decline in birth rates due to increased living costs in urban areas and women's entry into the workforce, which has led to a demographic slowdown. The presenter uses the example of Brazil, which is nearing the completion of its demographic transition, and contrasts it with Europe, which started its transition earlier and is now facing population decline due to lower birth rates.
Takeaways
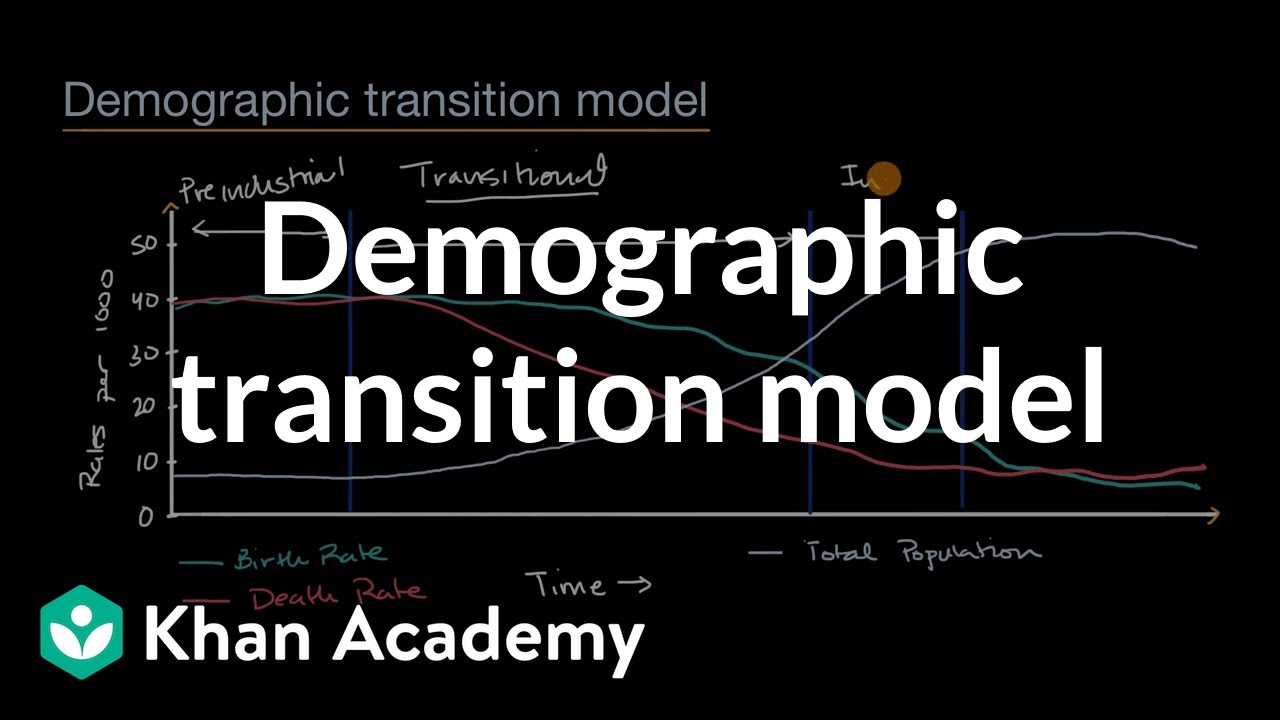
- 🌏 The demographic transition model explains the shift in birth and death rates from high to low levels, affecting population growth patterns.
- 📈 Initially, both birth and death rates are high, resulting in slow population growth due to a balance between births and deaths.
- 🏥 The second phase sees a significant drop in death rates without a change in birth rates, leading to accelerated population growth as fewer people die.
- 🏢 The decline in death rates is attributed to urbanization, improved sanitation, water treatment, vaccination campaigns, and better medical care.
- 👶 In the third phase, birth rates start to fall while death rates remain low, leading to a decrease in population growth as people have fewer children, often due to higher living costs in urban areas.
- 🌱 The fourth and final phase of demographic transition is characterized by both low birth and death rates, resulting in slow or negative population growth.
- 👴 An aging population with more elderly than children can lead to an increase in death rates, even with high-quality healthcare and living conditions.
- 🇪🇺 Some European countries and Japan are experiencing negative population growth due to lower birth rates and an aging population.
- 🇧🇷 Brazil started its demographic transition later than Europe, with significant urbanization and improvements in healthcare occurring in the mid-20th century.
- 📉 In the 1960s and 70s, Brazil experienced a sharp decline in birth rates due to urbanization, increased access to contraceptives, and more women entering the workforce.
- ⏳ The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) projects that Brazil will enter the fifth stage of demographic transition around 2040, potentially leading to population decline.
- 🌍 Different regions of the world are at various stages of demographic transition, explaining the diverse rates of population growth observed today.
Q & A
What is the demographic transition?
-The demographic transition refers to the transformation of a region's demographic reality from a pattern of slow growth due to high birth and death rates to another pattern of slow growth due to significantly reduced birth and death rates.
How does the initial phase of the demographic transition manifest in terms of birth and death rates?
-In the initial phase, both birth and death rates are high, resulting in a slow natural growth. Many people are born and die, leading to a stagnant population growth.
What factors contribute to the significant reduction in mortality rates during the second phase of the demographic transition?
-The reduction in mortality rates is mainly due to the process of urbanization, improved sanitation, water treatment, vaccination campaigns, and better access to medical treatments, which decrease the prevalence of diseases and increase the effectiveness of medical care.
How does the third phase of the demographic transition differ from the second in terms of birth rates?
-In the third phase, there is a noticeable decline in birth rates while death rates are already low. This leads to a high but decreasing natural growth rate, as fewer children are born while the mortality rate remains low.
What are the main reasons for the decline in birth rates during the third phase of the demographic transition?
-The decline in birth rates is associated with urbanization, where higher living costs lead people to plan for smaller families. Additionally, the increased availability of contraceptives and women's greater participation in the workforce contribute to this decline.
What paradox does a country face after completing the demographic transition?
-After completing the demographic transition, a country may face a paradox where, despite improvements in quality of life and medical care, mortality rates may begin to increase due to an aging population with more elderly people than children.
What is the projected year for Brazil to enter the fifth stage of the demographic transition according to IBGE projections?
-According to IBGE projections, Brazil is expected to enter the fifth stage of the demographic transition, where the population begins to decrease, around the year 2040.
How does the demographic transition process in Brazil compare to that of Europe?
-Brazil started its urbanization process in the early decades of the 20th century, about a century later than Europe, which began its urbanization at the turn of the 18th to 19th century. As a result, Europe has already completed its demographic transition, while Brazil is just concluding it.
What are some of the technical advances that contributed to the reduction of mortality rates in Brazil during the 20th century?
-The production of vaccines and medicines were significant technical advances that contributed to the reduction of mortality rates in Brazil, coinciding with the urbanization process and improvements in public health.
Why might a country experience negative growth after completing the demographic transition?
-A country may experience negative growth if mortality rates exceed birth rates, leading to a shrinking population year after year due to an aging demographic with fewer children being born.
How does the demographic transition affect the perception of a country's quality of life?
-While the demographic transition can initially improve the quality of life through better health and living conditions, it can later pose challenges such as an increased mortality rate due to an aging population, potentially affecting the overall perception of quality of life.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Demographic cycle | PSM lecture | Community Medicine lecture | PSM made easy | PSM rapid revision

Demographic transition | Society and Culture | MCAT | Khan Academy

APES Video Notes 3.9 - Demographic Transition

População mundial/animação
Demographic transition model| Human populations| AP Environmental science| Khan Academy

Demografiska transitionen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)