What Happens to your Heart when you Exercise - The Human Body - A User's Guide
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the role of the heart during exercise, illustrating its function in pumping oxygen-rich blood to the body. It describes the journey of blood from the right atrium to the left ventricle, emphasizing the pulmonary circulation and the heart's muscle-like structure. The script highlights how exercise increases heart rate and stroke volume, doubling the blood flow to working muscles, which consume 80% of blood flow during activity versus 10% at rest.
Takeaways
- 💓 The heart's primary function is to pump blood throughout the body.
- 🔄 Blood that is tired and low on oxygen returns to the heart via the right atrium.
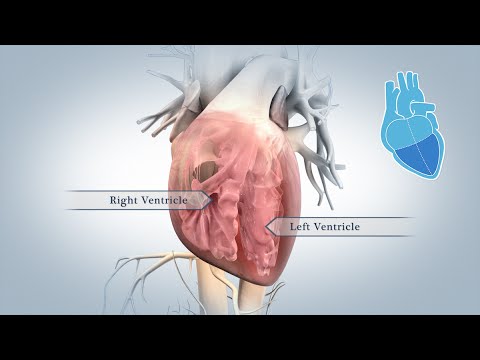
- 🚀 The right ventricle's role is to send this blood to the lungs for reoxygenation, a process known as pulmonary circulation.
- 🌬 The term 'pulmonary' is related to the lungs and is used to describe circulation involving the lungs.
- 🔄 After reoxygenation, the blood returns to the heart, entering the left atrium and then being pumped into the left ventricle.
- 💪 The left ventricle is the strongest part of the heart, responsible for distributing oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
- 🏋️♂️ During exercise, the heart rate increases, pumping blood faster to supply the body's muscles with oxygen.
- 🌊 Stroke volume also increases during exercise, allowing the heart to pump more blood with each beat.
- 🔝 The heart can double its blood output during exercise, primarily to supply working muscles with oxygen.
- 🏃♂️ Muscles consume 80% of the blood flow during exercise, compared to just 10% when at rest.
- 🧠 Understanding the heart's function and its response to exercise can help appreciate the importance of physical activity for cardiovascular health.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the heart?
-The primary function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.
What is the first chamber of the heart that receives blood returning from the body?
-The first chamber of the heart that receives blood returning from the body is the right atrium.
What is the role of the right ventricle in the heart's function?
-The right ventricle's role is to send the blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen, which is part of the pulmonary circulation.
What does the term 'pulmonary circulation' refer to?
-Pulmonary circulation refers to the process of blood flow between the heart and the lungs for the purpose of oxygenation.
When blood returns to the heart after being oxygenated, which chamber does it enter first?
-After being oxygenated, the blood first enters the left atrium of the heart.
What is the strongest part of the heart and what is its function?
-The left ventricle is the strongest part of the heart, and its function is to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout the entire body.
How does the heart's appearance resemble bagpipes and why is this comparison used?
-The heart's appearance is likened to bagpipes to provide a visual analogy, emphasizing its role as a muscular organ that powers the circulation of blood.
What happens to the heart rate and stroke volume during exercise?
-During exercise, the heart rate increases, and the stroke volume deepens, allowing the heart to pump more blood around the body.
How much of the blood flow do muscles consume during exercise compared to when at rest?
-During exercise, muscles consume about 80% of the blood flow, whereas at rest, they receive only about 10%.
What percentage of the increased blood flow during exercise is directed towards working muscles?
-During exercise, about 80% of the increased blood flow is directed towards the working muscles.
What is the significance of the heart's ability to double its blood output during exercise?
-The heart's ability to double its blood output during exercise is significant because it ensures that the working muscles receive an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to meet their increased demands.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)