Taking Vitamin D3? This Might Save Your Life
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the complex relationship between vitamin D3, calcium, and vitamin K2 in the body. It refutes the claim that high D3 levels cause hypercalcemia, emphasizing the crucial role of K2 in directing calcium to bones and preventing arterial calcification. The speaker discusses the biochemical processes involving osteocalcin and Matrix GLA protein, and the importance of choosing the right form of K2 supplements, advocating for a balanced diet and proper supplementation to maintain heart and bone health.
Takeaways
- 💊 Vitamin D3 and calcium supplementation can have conflicting effects on health, with some studies showing increased bone density and others indicating a risk of heart and artery problems.
- 🩸 The script challenges the common belief that high levels of Vitamin D3 (hypervitaminosis D) necessarily lead to high blood calcium levels (hypercalcemia), suggesting that this is a misconception.
- 🧬 Vitamin D3 and K2 are crucial for calcium metabolism, with D3 enhancing calcium absorption and K2 being necessary for the proper functioning of certain proteins involved in calcium regulation.
- 🦴 Osteocalcin and Matrix GLA protein (MGP) are proteins that require Vitamin D3 and K2 to bind calcium effectively, with osteocalcin aiding in bone mineralization and MGP preventing arterial calcification.
- 🔬 The process of carboxylation, facilitated by K2, is vital for the high affinity binding of calcium by osteocalcin and MGP, which is essential for bone health and arterial protection.
- 🌱 Different forms of Vitamin K2 (menaquinones) exist, such as MK4 and MK7, with MK7 having a longer half-life and being more effective for long-term regulation of calcium deposition.
- 🥩 Dietary sources of K2 are mainly animal-based, including organ meats, cheese, and eggs, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet for optimal health.
- 💡 The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding the biochemical pathways and mechanisms involved in calcium regulation to safely create supplement regimes.
- 📚 The script criticizes the lack of education on Vitamin D3 and K2 among some health professionals and advocates for more detailed knowledge in this area.
- 💡 The recommendation for Vitamin D3 and K2 supplementation is provided, suggesting one Super K supplement for every 10,000 units of D3, based on the speaker's clinical experience.
- 🚫 The speaker warns against taking advice from those who do not understand the complexities of Vitamin D3 and K2, including the importance of the cis and trans forms of K2.
Q & A
What is the main concern raised about vitamin D3 supplementation in the video script?
-The main concern is that some studies suggest vitamin D3 supplementation can lead to too much calcium in the blood, increasing the risk of hardening of the arteries, like in atherosclerotic heart disease.
What is the role of vitamin D3 in calcium metabolism according to the script?
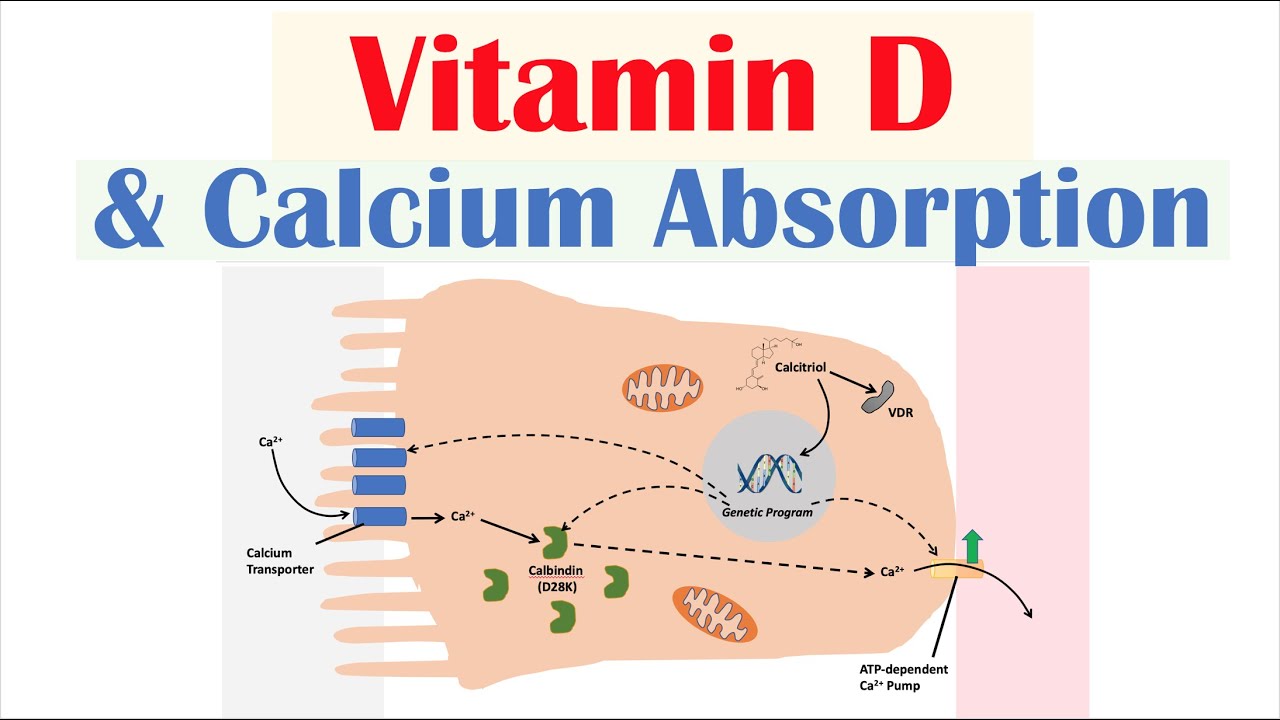
-Vitamin D3, specifically its active form calcitriol, enhances calcium absorption from the gut by increasing the expression of calcium-binding proteins in the intestine, helps maintain calcium levels in the blood, and potentially mobilizes calcium from bones when necessary.
What are osteocalcin and Matrix GLA protein (MGP), and how do they relate to vitamin D3 and K2?
-Osteocalcin and MGP are proteins that depend on vitamin D3 for their production and on K2 for their proper functioning. Osteocalcin is involved in bone mineralization, while MGP prevents calcium deposition in arteries, thus maintaining vascular health.
Why is K2 important for the function of osteocalcin and MGP?
-K2 is a co-factor for the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase, which is responsible for the carboxylation of osteocalcin and MGP. This process confers a high affinity for calcium ions, allowing these proteins to effectively bind calcium and perform their roles in bone health and vascular protection.
What is the significance of the different forms of vitamin K2 (menaquinones) mentioned in the script?
-Different forms of K2, such as MK4 and MK7, have varying half-lives and roles in the body. MK4 is found in specific tissues and regulates gene expression involved in bone metabolism, while MK7 has a longer half-life and is effective in long-term regulation of calcium deposition in bones and preventing arterial calcification.
What is the video's stance on the advice given by a world-famous biohacker regarding the use of K2 supplements?
-The video strongly disagrees with the advice, stating that the biohacker lacks understanding and suggesting that most of the time, the advice given is not well-informed.
What is the recommended ratio of vitamin D3 to K2 supplementation according to the script?
-The script suggests that for every 10,000 units of D3, one should take one Super K supplement, which is a form of K2.
Why does the speaker believe that many doctors and researchers are poorly educated regarding vitamin D3 and K2?
-The speaker believes that many in the medical field are not aware of the importance of K2 activity and the roles of osteocalcin and Matrix GLA protein in calcium regulation, leading to conflicting study results and misguided supplement advice.
What are some dietary sources of K2 mentioned in the script?
-Dietary sources of K2 mentioned include animal tissues such as organ meats, chicken, beef, grass-fed pork, cheese, eggs, and duck.
What is the speaker's view on plant-based diets in relation to K2 intake?
-The speaker suggests that a plant-based diet may not be sufficient for obtaining K2, as it is primarily found in animal tissues, and implies that a carnivorous diet is more aligned with human nutritional needs for this vitamin.
What advice does the speaker give regarding the selection of K2 supplements?
-The speaker advises to choose a K2 supplement that clearly states it contains the trans form of MK7, as this is the natural form found in our diet. The speaker recommends Super K by Life Extension as it specifies that all the MK7 is in the trans form.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The Unique Benefits of Using Vitamin D and K2 Combined

Should You Take Vitamin K and Vitamin D Together

Vitamin K2 Benefits You Never Knew!
Vitamin D and Calcium Absorption - Biochemistry Lesson

Warning! Don't Take Magnesium, Vitamin D3 & K2 until You Know This

10 BEST supplements for Every Budget | Dr. Steven Gundry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)