IIMFC2022016-V006400
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the concept of duration gap analysis, a critical tool for financial institutions to assess their exposure to interest rate risks. It explains the process of calculating the market value of equity and the weighted average duration of assets and liabilities. The example provided illustrates how a 1% change in interest rates can significantly impact the market value of a firm's equity, emphasizing the importance of this analysis for understanding and managing financial risk.
Takeaways
- 📊 Duration Gap Analysis is a method to measure a bank's exposure to interest rate risks, focusing on the sensitivity of the market value of its equity to interest rate movements.
- 🏦 The market value of equity is calculated by multiplying the number of equity shares issued by the firm by the market price per share.
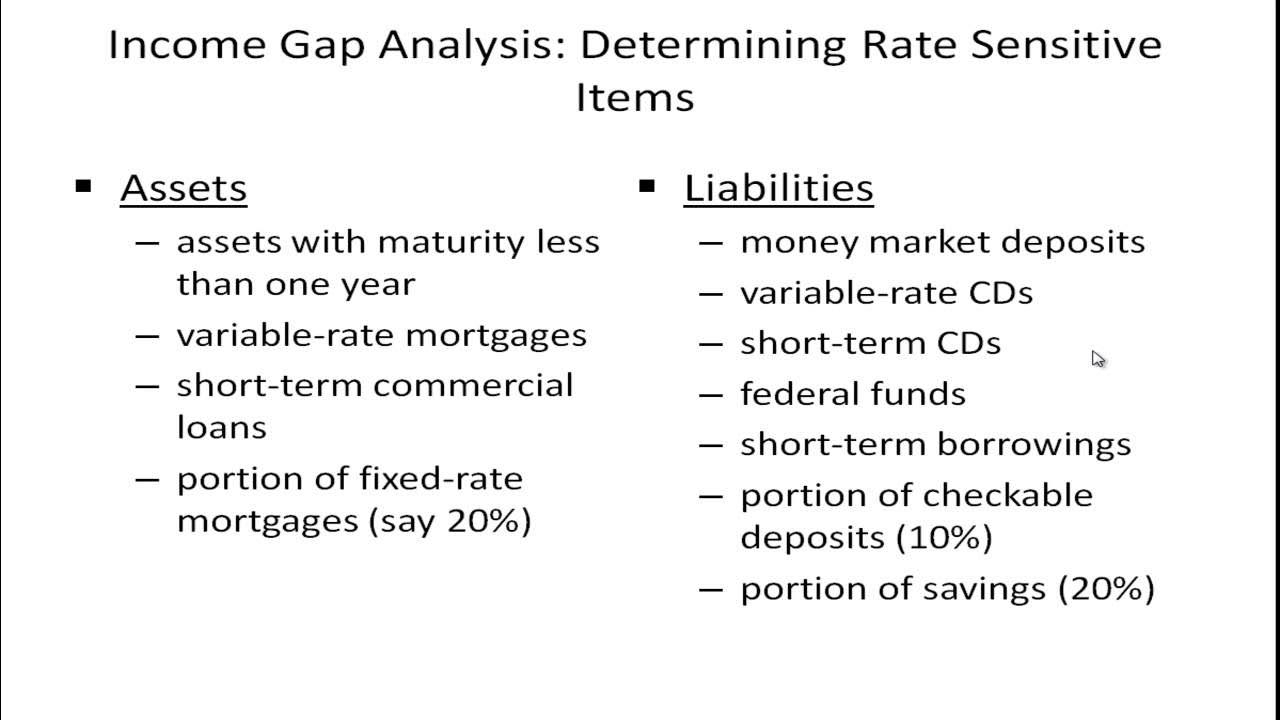
- 📈 The process involves three main steps: bucketing risk-sensitive assets and liabilities, computing the modified duration of these assets and liabilities, and assessing the impact on net interest income and market value of the firm when interest rates change.
- 📋 Duration is a key concept in this analysis, representing the weighted average time to receive the present value of cash flows from an asset or liability.
- 📉 The duration of an asset or liability is calculated by multiplying the present value of cash flows by the time period and dividing by the market value of the asset or liability.
- 💹 The weighted average duration for assets and liabilities is used to calculate the duration Gap, which indicates the bank's overall interest rate risk exposure.
- 📝 The net interest income is derived from the interest earned on assets and the interest paid on liabilities, reflecting the bank's profitability from interest rate spreads.
- 📉 An increase in interest rates will generally decrease the market value of assets with longer durations more significantly than those with shorter durations.
- 📈 A decrease in the duration Gap indicates a reduction in the bank's interest rate risk exposure, as the weighted average duration of assets becomes more aligned with that of liabilities.
- 💡 Duration Gap Analysis is a valuable tool for financial institutions to manage interest rate risk and is often a mandatory reporting requirement by central banks.
- 🌐 The impact of interest rate changes on a bank's market value of equity can be substantial, affecting stakeholders and investors' confidence in the institution.
Q & A
What is duration Gap analysis in the context of a financial institution?
-Duration Gap analysis is a method used to measure the sensitivity of a bank's market value of equity to changes in interest rates. It assesses the bank's exposure to interest rate risks by examining the impact of interest rate movements on the market value of its equity.
What are the steps involved in performing a duration Gap analysis?
-The steps in duration Gap analysis include: 1) Bucketing all risk-sensitive assets and liabilities based on residual maturity or repricing dates into various time bands, 2) Computing the modified duration of the risk-sensitive assets and liabilities, and 3) Using these measures to assess the impact on net interest income and the market value of the firm when interest rates change.
How is the market value of equity calculated?
-The market value of equity is calculated by multiplying the number of equity shares issued by the firm by the market price per share. It reflects the current market price at which the firm's shares are trading.
What is the significance of the 'duration' column in the spreadsheet example?
-The 'duration' column is fundamental to duration Gap analysis. It represents the sensitivity of the market value of the assets and liabilities to changes in interest rates, and it is used to determine the potential impact of interest rate changes on the financial institution.
Can you explain how the duration of a financial instrument is calculated?
-The duration of a financial instrument is calculated by summing the present value of each cash flow, multiplied by the time period it is received, and then dividing this sum by the total present value of all cash flows. This gives a weighted average time to receipt of cash flows, which is the duration.
What is the purpose of calculating the weighted average duration for assets and liabilities?
-The weighted average duration for assets and liabilities helps to determine the overall sensitivity of a financial institution's balance sheet to interest rate changes. It provides a measure of how much the net interest income and market value of equity might change with a shift in interest rates.
How is the net interest income calculated in the context of duration Gap analysis?
-Net interest income is calculated by taking the interest income from assets, such as loans and bonds, and subtracting the interest expenses on liabilities, such as deposits. The rates used are the current market rates, and the calculation takes into account the market values of these financial instruments.
What is the duration Gap, and how is it calculated?
-The duration Gap is the difference between the weighted average duration of risk-sensitive assets and the weighted average duration of risk-sensitive liabilities. It is calculated by subtracting the duration of liabilities (adjusted for their market value as a proportion of total assets) from the duration of assets.
What impact does a change in interest rates have on the market value of equity according to the duration Gap analysis?
-A change in interest rates affects the market value of equity inversely to the duration Gap. If interest rates rise, and the duration Gap is positive (assets have a longer duration than liabilities), the market value of equity will decrease, and vice versa.
Why is duration Gap analysis important for financial institutions and their stakeholders?
-Duration Gap analysis is important because it helps financial institutions manage and communicate the risk associated with interest rate fluctuations. It provides stakeholders with insights into how sensitive the institution's profitability and equity value are to changes in the interest rate environment.
How might central banks use duration Gap analysis in their regulatory framework?
-Central banks may mandate the inclusion of duration Gap analysis in financial reporting requirements to ensure that financial institutions are transparent about their interest rate risk exposure. This allows regulators and investors to assess the institution's risk profile and financial stability.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Managing Interest Rate Risk - Income Gap Analysis

Part 2: Management of Translation Exposure |English| #InternationalFinance| M. Com|MBA
3.1. Credit Scoring | DATA SCIENCE PROJECT

MANAJEMEN RISIKO KEUANGAN || TUGAS SESI 1|| SHARLA TWO DILLA

Why did Silicon Valley Bank Fail?

What is Customer Due Diligence | What is Risk-Based Approach | CDD Documentation - AML/KYC Tutorial
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)