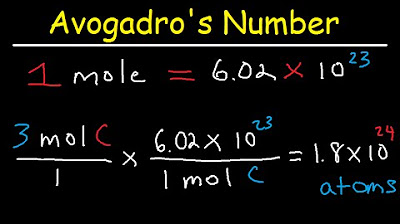Converting Between Moles, Atoms, and Molecules
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script offers a clear guide on converting between moles and the number of atoms or molecules. It introduces the concept of moles as a unit similar to a dozen, but with 6.02x10^23 entities per mole. The script explains two methods: a straightforward calculation and the use of conversion factors. It emphasizes understanding the process and the significance of scientific notation, providing step-by-step instructions for both converting moles to atoms and vice versa, ensuring a solid grasp of the fundamental chemistry concepts.
Takeaways
- 🔄 Moles can be converted to atoms or molecules, and vice versa, using basic multiplication or division.
- 🔢 Atoms and molecules are often referred to as particles, which can represent any individual thing, like a jellybean or coin.
- 🧮 A mole is similar to a dozen but contains 6.02 x 10^23 things, known as Avogadro's number.
- 📐 Converting moles to atoms involves multiplying the number of moles by 6.02 x 10^23.
- ➗ Converting atoms to moles involves dividing the number of atoms by 6.02 x 10^23.
- ⚖️ Conversion factors can simplify these calculations, though they can be confusing at first.
- 📝 Always remember to account for significant figures when rounding the final answer.
- 💻 Scientific calculators often use 'E' notation for exponents in scientific notation.
- 💡 Understanding the analogy between dozens and moles can make mole calculations easier to grasp.
- 🔍 Scientific notation is a convenient way to handle very large or very small numbers in these calculations.
Q & A
What is a mole, and how is it similar to a dozen?
-A mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry, similar to a dozen, but much larger. While a dozen represents 12 items, a mole represents approximately 6.02 x 10^23 particles, such as atoms or molecules.
How do you convert from moles to atoms?
-To convert from moles to atoms, multiply the number of moles by 6.02 x 10^23, which is the number of atoms in one mole.
Why is scientific notation used when dealing with moles?
-Scientific notation is used because the numbers involved in mole calculations are extremely large. For example, 6.02 x 10^23 is more manageable than writing out 602 followed by 21 zeros.
What are conversion factors, and why are they important in mole calculations?
-Conversion factors are ratios used to convert from one unit to another. In mole calculations, they are important because they allow you to accurately convert between moles, atoms, and other units by canceling out the original unit.
How do you use conversion factors to convert from moles to atoms?
-To use conversion factors for converting moles to atoms, multiply the number of moles by a conversion factor where moles are in the denominator (to cancel out) and atoms are in the numerator. The conversion factor is 6.02 x 10^23 atoms per mole.
What is the relationship between moles and Avogadro's number?
-Avogadro's number, 6.02 x 10^23, represents the number of particles (atoms, molecules) in one mole. This constant is fundamental in converting between moles and individual particles.
Why is it necessary to consider significant figures in mole calculations?
-Significant figures are important because they reflect the precision of the measurements used in calculations. When multiplying or dividing, the result should be rounded to the number of significant figures in the least precise measurement.
How do you convert from atoms to moles?
-To convert from atoms to moles, divide the number of atoms by 6.02 x 10^23, the number of atoms in one mole.
What does the 'E' represent in scientific notation on a calculator?
-In scientific notation on a calculator, 'E' represents 'times ten to the power of.' For example, 6.02E23 means 6.02 x 10^23.
How can understanding the concept of a dozen help in understanding moles?
-Understanding a dozen, which is simply a group of 12, helps in grasping the concept of a mole as a much larger group (6.02 x 10^23). This analogy makes it easier to understand how moles function as a counting unit in chemistry.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)