Centro de gravedad en aviones | Explicado en detalle
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the critical concept of the center of gravity in aviation, explaining its importance for aircraft stability and flight safety. It illustrates how the center of gravity can be determined by balancing the plane on its wings or using specialized techniques for larger aircraft. The script highlights the ideal center of gravity position, typically at 30% of the wing's chord, and demonstrates the effects of imbalance through a model airplane. It emphasizes the need for proper balance to prevent crashes and inefficient flight, showing practical steps to achieve it, and concludes with the significance of the center of gravity in other transportation modes like cars and helicopters.
Takeaways
- 😀 The center of gravity is crucial for aircraft balance and safe flight, as improper balance can lead to catastrophic accidents.
- 📚 The center of gravity is the average point where the weight of an aircraft is distributed, and it can be found by suspending the plane from its wings.
- 🛫 For larger passenger planes, specialized techniques are used to measure the center of gravity, ensuring the aircraft responds well during flight maneuvers.
- ⚖️ The center of gravity should be in an approximate position where all forces, especially lift generated by the wings, are in balance for stable flight.
- 📏 The ideal center of gravity for most aircraft is around 30% of the chord length from the leading edge to the trailing edge of the wing.
- 🔄 Adjusting the center of gravity can be done by moving internal components, fuel, or even asking passengers to move in commercial planes to achieve the desired balance.
- 🛠 Balancing an aircraft is essential both longitudinally and laterally, with longitudinal balance being more critical and prone to errors by beginners.
- 🚀 Demonstrating aircraft balance involves practical application, such as adding weight to a model plane and observing its flight characteristics.
- 🪙 A simple rule of thumb can be used to find the 30% point on the wing chord for balancing, which is essential for stable flight.
- 💨 A nose-heavy aircraft is easier to manage and can perform better in windy conditions compared to a tail-heavy aircraft, which should not be flown.
- 🛑 In practice, a tail-heavy configuration can quickly lead to a stall and a difficult recovery, highlighting the importance of proper balance.
Q & A
What is the center of gravity in the context of aviation?
-The center of gravity is the point at which an aircraft balances. It is essential for stable flight and can be determined by holding the aircraft by its wings to check its balance.
Why is the correct balance of an aircraft's weight important for flight?
-Correct weight balance is crucial for an aircraft to fly properly. An improper balance can lead to instability, inefficient flight, or even catastrophic accidents.
How is the center of gravity determined for larger passenger planes?
-For larger passenger planes, more specialized techniques are used to measure the center of gravity, beyond simply holding the plane by its wings.
What should be the approximate location of the center of gravity for an aircraft to respond well during flight?
-The center of gravity should be situated in an approximate point where the aircraft pivots during maneuvers in any direction, ensuring that all forces are in balance.
What force is considered more when determining the center of gravity for an aircraft's stable flight?
-The lift force generated by the wings is considered more when determining the center of gravity for a stable flight.
What is the typical location of the center of gravity in relation to the wing's chord?
-Typically, the center of gravity should be situated at about 30% of the wing's chord from the leading edge towards the trailing edge.
How can the balance of an aircraft be adjusted if it is not properly centered?
-The balance can be adjusted by relocating internal components, such as moving the battery or adding or removing weight in the case of model airplanes, or moving fuel and cargo in commercial aircrafts.
What is the significance of the longitudinal balance compared to the lateral balance in aircraft?
-Longitudinal balance is more important and delicate than lateral balance, as it is more commonly mishandled by beginners and can lead to inefficient and unstable flight.
How does the script demonstrate the importance of balancing an aircraft before each flight?
-The script demonstrates this by showing a practical example of balancing a small model airplane by adding weight in the form of coins and observing the flight behavior with different balance configurations.
Why is it generally better to have a 'nose-heavy' aircraft rather than a 'tail-heavy' one?
-A 'nose-heavy' aircraft is easier to manage during flight and can perform better in windy conditions compared to a 'tail-heavy' aircraft, which tends to be less stable and more prone to entering a stall.
How is the center of gravity important in other modes of transportation like cars and multi-rotor helicopters?
-In cars, keeping the center of gravity as low as possible minimizes the chances of overturning, which is critical in high-performance cars like Formula 1 racers. Similarly, in multi-rotor helicopters, maintaining the correct center of gravity is crucial for stable flight.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Principios de Peso y Balance (Parte 2) - Balance y CG

Lecture 01
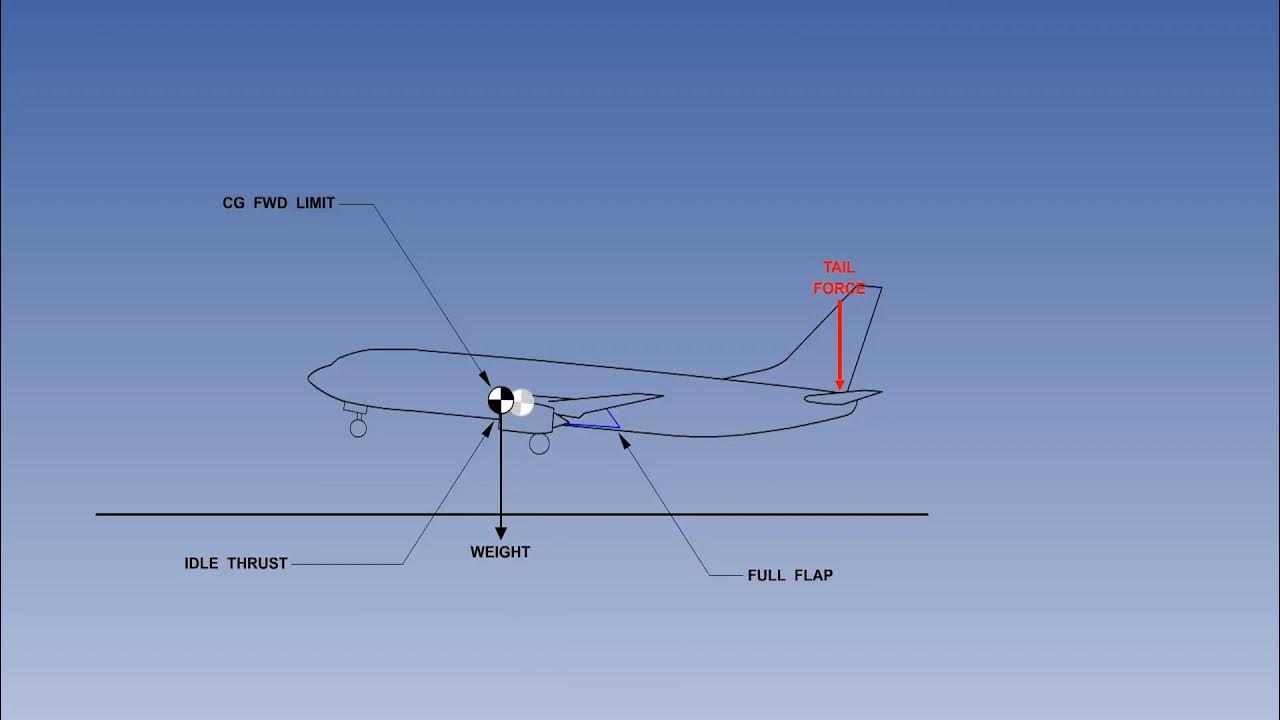
(Part 3) Longitudinal Stability Of Aircraft | Aircraft Axles Stability | Lecture 38

How Center of Gravity Affects Flight | Tail Down Force | Aircraft Stability

Principios de Peso y Balance (Parte 1) - Pesos
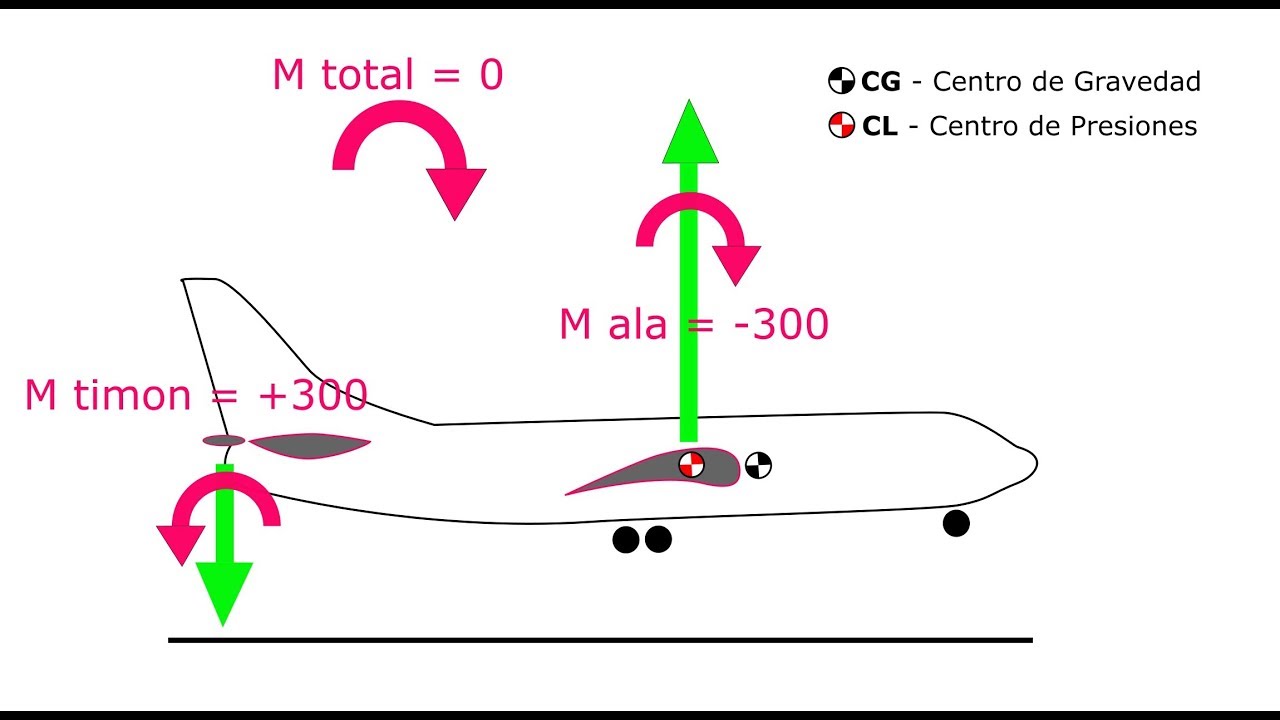
Como poner el centro de gravedad de un avion RC. Estabilidad estatica longitudinal. Punto neutro.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)