Uniform Circular Motion: Crash Course Physics #7
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the physics of uniform circular motion through the example of carnival rides and NASA's human centrifuge tests. It highlights the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces, and why centrifugal force is considered fictitious. The script covers key concepts like tangential velocity, centripetal acceleration, period, and frequency, using real-life examples and simple experiments to illustrate these principles. The goal is to show how objects move in circles and to calculate if such rides are safe for humans, emphasizing the fascinating and sometimes misunderstood nature of circular motion.
Takeaways
- 🎢 Uniform circular motion involves moving along a circular path consistently.
- ⚖️ Centripetal acceleration is directed inward, while the concept of centrifugal force is a fictitious force.
- 🚀 NASA tested astronauts' tolerance for acceleration using a human centrifuge, finding most could handle 98 meters per second squared for 10 minutes.
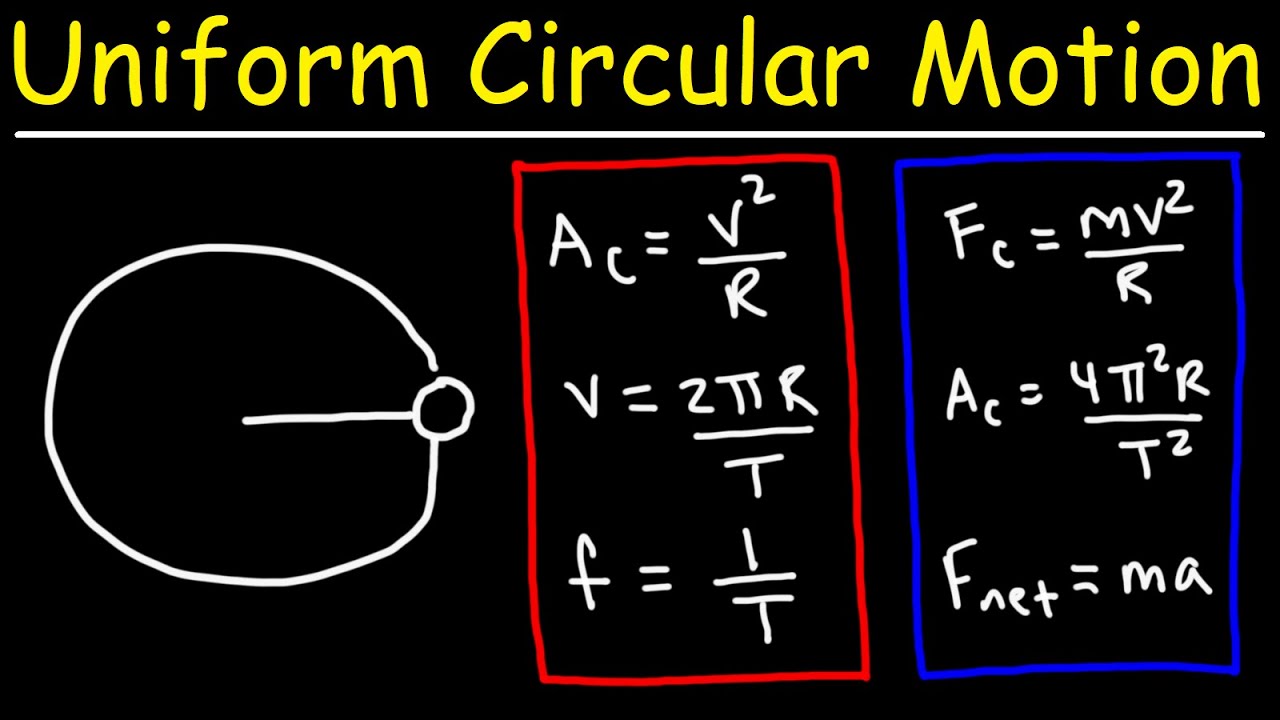
- 🎡 The velocity in circular motion is tangent to the circle, not along the path.
- 🔄 To demonstrate tangential velocity, you can twirl a key on a string and release it to see it fly off tangentially.
- 🌀 Centripetal force keeps an object moving in a circle, pulling it towards the center.
- 👀 From an external perspective, centripetal force is clear, while from an internal perspective, it feels like a centrifugal force.
- ⏳ The period (T) is the time it takes for one complete revolution, and frequency (f) is the number of revolutions per second.
- 📏 The circumference of the circle relates to the distance traveled in one revolution.
- 🔢 The speed in uniform circular motion can be calculated by dividing the circumference by the period.
- 📈 Centripetal acceleration magnitude is given by the speed squared divided by the radius, increasing with speed or decreasing radius.
- ✔️ Calculating safety: for a ride with a speed of 15.7 meters per second and a radius of 5 meters, the centripetal acceleration is 49.3 meters per second squared, considered safe for short periods.
Q & A
What is the experience of being on a twirly carnival ride like?
-The experience is described as intense and nauseating due to the sensation of spinning in a circle, which is a form of uniform circular motion.
What is uniform circular motion?
-Uniform circular motion is the movement of an object along a circular path at a constant speed, resulting in a consistent acceleration inward, known as centripetal acceleration.
Why is centripetal acceleration often misunderstood?
-Centripetal acceleration is often misunderstood because people sometimes confuse it with centrifugal acceleration, which is a perceived outward force but is not a real physical force.
What was the purpose of the human centrifuge used by NASA in 1960?
-The human centrifuge was used to test how much acceleration potential astronauts could withstand before they would black out, which is crucial for space flight.
What is the acceleration limit that most people can withstand for 10 minutes according to NASA's tests?
-Most people can withstand an acceleration of around 98 meters per second squared for 10 minutes, which is about ten times the acceleration caused by gravity.
How is velocity in uniform circular motion different from velocity in straight-line motion?
-In uniform circular motion, the velocity is always tangent to the circle, meaning its direction is perpendicular to the radius at any given point, unlike straight-line motion where the direction is constant.
What is the relationship between the centripetal force and the velocity of an object in circular motion?
-The centripetal force is responsible for changing the direction of the object's velocity, keeping it moving in a circular path. It is always directed toward the center of the circle.
Why do people sometimes feel a centrifugal force when they are in a spinning ride?
-The sensation of a centrifugal force is due to a change in perspective or frame of reference. From the perspective of someone inside a spinning ride, it feels like they are being pushed outward, even though it's the centripetal force pulling them inward.
What is the period of motion in uniform circular motion?
-The period of motion, represented by the variable T, is the time it takes for an object to complete one full revolution around the circle and return to its starting point.
How is the frequency of motion related to the period of motion?
-The frequency of motion, represented by f, is the number of revolutions per second. It is the reciprocal of the period, calculated as 1 divided by the period (f = 1/T).
What is the formula for calculating the speed of an object in uniform circular motion?
-The speed of an object in uniform circular motion is calculated by dividing the distance traveled in one revolution (circumference of the circle, which is 2πr) by the time taken for one revolution (the period, T).
How is centripetal acceleration related to the speed and radius of the circular path?
-The magnitude of centripetal acceleration is equal to the square of the speed divided by the radius of the circle (a_c = v^2 / r). This means that increasing the speed or decreasing the radius results in greater acceleration.
How can you determine if a carnival ride is safe based on the acceleration experienced by riders?
-By calculating the centripetal acceleration experienced by riders using the formula a_c = v^2 / r and comparing it to the known safe acceleration limits, such as those tested by NASA, you can determine if the ride is safe.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)