Cell - The unit of Life | NEET | Plasma Membrane - Fluid Mosaic Model - Part - 1 | Neela Bakore
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the Fluid Mosaic Model of the plasma membrane, proposed by Singer and Nicholson, which builds upon the foundational work of Danielli and Davson. The model highlights the membrane's composition of proteins and phospholipids, classifying proteins into extrinsic and intrinsic based on their attachment to the phospholipid bilayer. It introduces the concept of phospholipid movement through transition and flip-flop, emphasizing the amphipathic nature of these molecules. The video aims to explore whether this model fully explains the properties of the plasma membrane, presenting a trilaminar structure of alternating protein and phospholipid layers.
Takeaways
- 🌟 The Fluid Mosaic Model of the plasma membrane was proposed by Singer and Nicholson, offering a different interpretation from the earlier Danielli-Davson model.
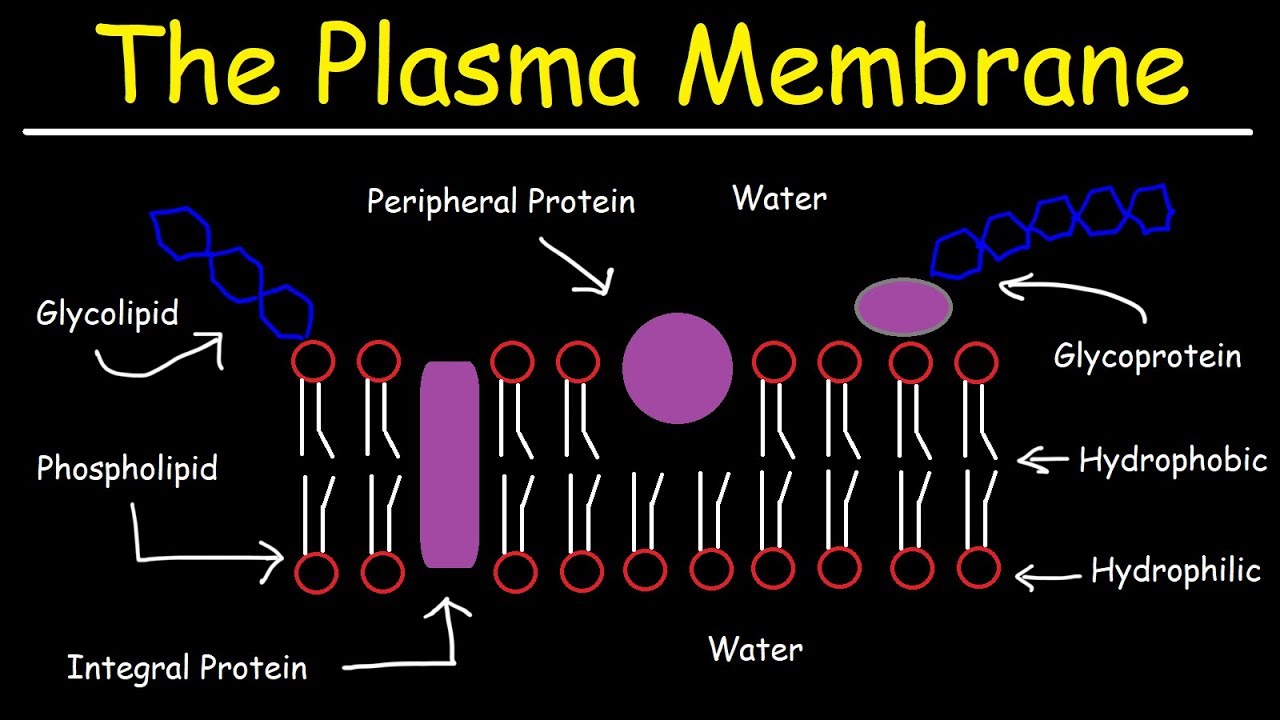
- 🧬 The model suggests that the plasma membrane is composed of proteins and phospholipids, similar to the Danielli-Davson model.
- 🔍 Proteins in the plasma membrane are categorized as alpha-globular, which are spherical and can be either extrinsic or intrinsic.
- 🔄 Extrinsic proteins are loosely attached to the phospholipid heads on the outer side of the membrane and can be easily detached.
- 🌐 Intrinsic proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, either partially or completely, and are more tightly associated with the membrane structure.
- 💧 Phospholipid molecules are amphipathic, having a hydrophilic (polar) head and two hydrophobic (nonpolar) tails.
- 🚶♂️ Phospholipids exhibit two types of movements: lateral diffusion (transition movement) within the same layer and flip-flop movement between layers.
- 🔄 The term 'flip-flop' refers to the movement of phospholipid molecules from one layer of the bilayer to another, a concept not present in the Danielli-Davson model.
- 🔗 The weak force of attraction between phospholipid layers is known as the van der Waals force, which is crucial for maintaining the structure of the bilayer.
- 📚 The arrangement of the plasma membrane is described as a trilaminar structure with alternating layers of protein and phospholipid bilayer.
- 📈 The Fluid Mosaic Model is significant as it explains the fluidity and flexibility of the plasma membrane, accounting for its various properties.
Q & A
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model of the plasma membrane?
-The Fluid Mosaic Model is a concept in cell biology that describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of lipids and proteins, allowing for fluidity and movement of components within the membrane.
Who proposed the Fluid Mosaic Model?
-The Fluid Mosaic Model was proposed by Singer and Nicholson, who built upon the foundational information provided by Danielli and Davson.
What is the difference between the interpretation of Singer and Nicholson and that of Danielli and Davson regarding the plasma membrane?
-While Danielli and Davson described the plasma membrane as having a static structure with proteins embedded in a lipid bilayer, Singer and Nicholson interpreted it as a dynamic, fluid structure with proteins free to move within the lipid bilayer.
What types of proteins are mentioned in the Fluid Mosaic Model?
-The model mentions two types of proteins: extrinsic (loosely attached to the phospholipid heads on the outer side) and intrinsic (partially or completely embedded within the phospholipid bilayer).
How are extrinsic proteins different from intrinsic proteins in the plasma membrane?
-Extrinsic proteins are loosely attached to the phospholipid heads and can be found on the outer side of the membrane, whereas intrinsic proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer and are more integrated into the membrane structure.
What is the amphipathic nature of phospholipid molecules?
-Phospholipid molecules are amphipathic, meaning they have a hydrophilic (polar) head and two hydrophobic (nonpolar) tails, allowing them to form bilayers with the hydrophobic tails facing each other and the hydrophilic heads facing outwards.
What are the two types of movements exhibited by phospholipid molecules in the plasma membrane?
-Phospholipid molecules exhibit two types of movements: lateral movement (or translational movement) within the same layer and flip-flop movement between the two layers of the bilayer.
What is the significance of the term 'flip-flop' movement in the context of the plasma membrane?
-Flip-flop movement refers to the rare phenomenon where phospholipid molecules move from one leaflet of the bilayer to the other, which is significant because it is less common and requires energy.
What is the role of the Vander Waals forces in the plasma membrane structure?
-Vander Waals forces are the weak forces of attraction between the hydrophobic tails of phospholipid molecules, helping to hold the lipid bilayer together.
How is the arrangement of the phospholipid bilayer described in the Fluid Mosaic Model?
-The arrangement is described as having a bilayer structure where the tails of the phospholipids face each other and the heads are oriented towards the aqueous environments, creating a barrier between the cell and its surroundings.
What is the significance of the trilaminar appearance of the plasma membrane in the Fluid Mosaic Model?
-The trilaminar appearance refers to the dark-light-dark pattern seen in electron micrographs, which corresponds to the protein-lipid-protein layers of the membrane, emphasizing the model's fluid nature and the distribution of proteins within the lipid bilayer.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)