CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Course - 1.4 Use Appropriate Cryptographic Solutions - PART B
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores essential cryptographic techniques for securing digital information. It covers obfuscation, steganography, tokenization, data masking, and hashing, emphasizing their roles in protecting sensitive data. It also discusses key concepts like salting, digital signatures, key stretching, blockchain, digital certificates, and OCSP, highlighting their importance in maintaining the integrity and security of digital transactions and communications in our digital age.
Takeaways
- 🔒 Obfuscation is a strategy that makes data unclear to unauthorized viewers, protecting sensitive information from being easily deciphered.
- 🎨 Steganography is the art of hiding information within other non-secret data, such as embedding a message in a digital image that is undetected to the naked eye.
- 🔄 Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive substitutes called tokens, commonly used in financial services to secure transactions.
- 👁️ Data masking obscures specific data within a database, protecting sensitive information like Social Security numbers from regular users but allowing access to authorized personnel.
- 🔑 Hashing is a one-way process that converts data into a fixed-size string, used for securely storing passwords where the original data cannot be easily derived from the hash.
- 🧂 Salting adds random data to a password before hashing, ensuring uniqueness and thwarting rainbow table attacks.
- 🔑 Key stretching techniques like bcrypt are used to strengthen weak passwords by transforming them into longer, more complex keys to protect against brute force attacks.
- 💼 Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that ensures the integrity and verifiability of data, making tampering extremely difficult.
- 📑 An open public ledger in cryptocurrencies is a decentralized and transparent system that allows anyone to view transaction histories and balances, ensuring security.
- 🛡️ Digital certificates authenticate the identity of a website or user, providing a secure and trustworthy connection, issued by certificate authorities.
- 🔄 Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) list certificates that have been revoked before their expiration dates, usually due to compromise.
- 🔒 The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is used to obtain the revocation status of a digital certificate, enhancing security by verifying certificate validity.
Q & A
What is the purpose of obfuscation in the context of digital security?
-Obfuscation is used to make data unclear or unintelligible to unauthorized viewers, which is a critical strategy for protecting sensitive information from being easily deciphered if accessed improperly.
Can you provide an example of steganography?
-Steganography is the art of hiding information within other non-secret data. An example is embedding a secret message within a digital image, making it undetected to the naked eye but retrievable by those who know it's there.
How does tokenization contribute to securing financial transactions?
-Tokenization replaces sensitive data, such as payment card information, with non-sensitive substitutes known as tokens. This secures transactions while processing payments by ensuring that the actual sensitive data is not exposed.
What is data masking and how does it protect sensitive information in a database?
-Data masking involves obscuring specific data within a database to protect it. For example, in customer databases, sensitive information like Social Security numbers may be masked for regular users but visible to authorized personnel.
How does hashing differ from encryption in terms of data security?
-Hashing converts data into a fixed-size string of characters which is a hash. Unlike encryption, hashing is a one-way process, meaning that even if the hash is accessed, the original password or data cannot be easily derived from it.
What is the role of salting in enhancing password security?
-Salting adds random data to a password before hashing. This ensures that the hash is unique even if the underlying password is the same, thus thwarting attacks like rainbow table attacks.
What are digital signatures and how do they verify the authenticity of digital messages?
-Digital signatures are cryptographic techniques used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital messages or documents. They ensure that the message has not been tampered with and confirms the identity of the sender.
Can you explain the concept of key stretching and its purpose?
-Key stretching techniques, such as bcrypt, are used to strengthen weak passwords against brute force attacks by transforming them into longer, more complex keys, making them harder to crack.
How does blockchain technology ensure the integrity and verifiability of data?
-Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that ensures the integrity and verifiability of data recorded in the blockchain. It makes tampering extremely difficult due to its decentralized and immutable nature.
What is the function of digital certificates in establishing secure connections?
-Digital certificates authenticate the identity of a website or user. Certificate authorities issue these certificates, ensuring a secure and trustworthy connection between users and websites.
What are the differences between self-signed certificates, third-party CA certificates, and root of trust certificates?
-Self-signed certificates are issued by the entity itself, while third-party CA certificates are issued by a trusted certificate authority. Root of trust certificates are part of a system that establishes a baseline for trusted identities in a network.
How do wildcard certificates provide security for a domain and its subdomains?
-Wildcard certificates secure a domain and all its subdomains, allowing for a single certificate to be used across multiple levels of a domain structure, simplifying management and ensuring security.
What is the purpose of the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)?
-The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is used to obtain the revocation status of a digital certificate. It helps to check if a certificate has been revoked before its expiration date, usually due to compromise.
What is a Certificate Revocation List (CRL) and its significance in security?
-A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) lists certificates that have been revoked before their expiration dates, typically due to compromise. It is significant in security as it helps in maintaining a record of untrusted certificates.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

types of cryptography explain in Telugu 1.symmetric 2. Asymmetric #types#cryptography#telugu#

CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Course - 1.4 Use Appropriate Cryptographic Solutions - PART A
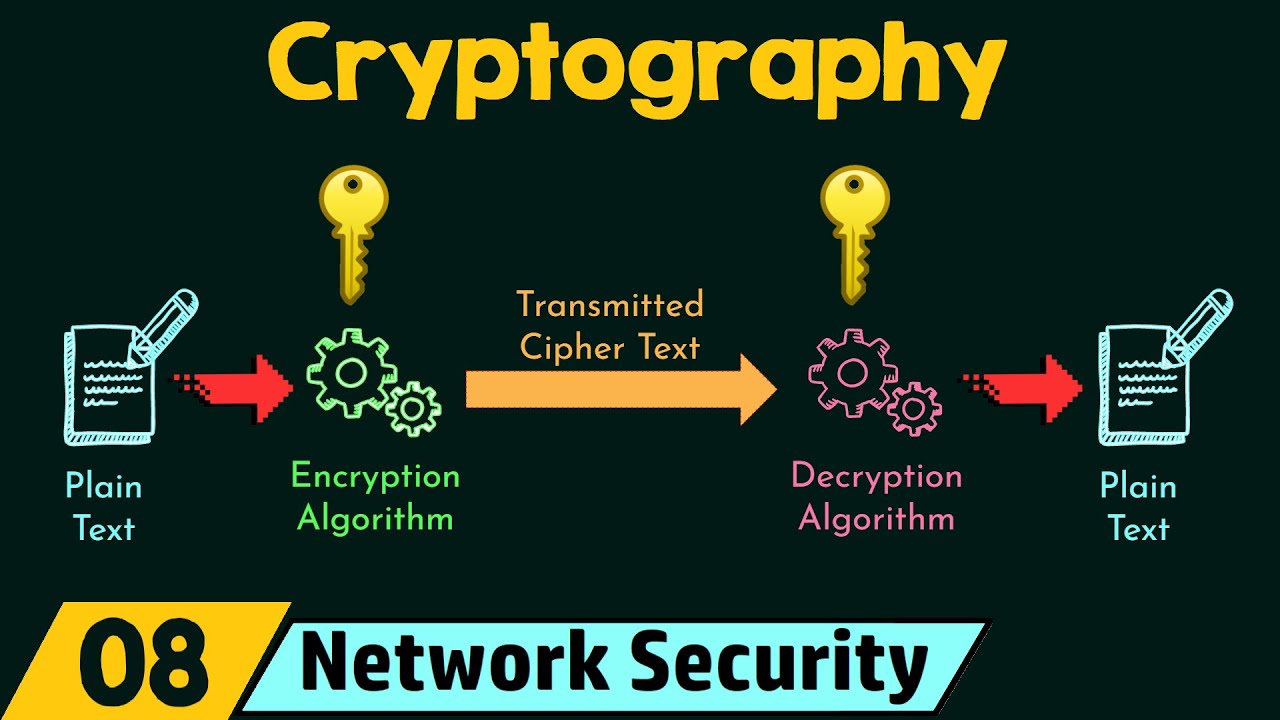
Cryptography

01 CYBER SECURITY ESSENTIALS 2

AES and DES Algorithm Explained | Difference between AES and DES | Network Security | Simplilearn

ARSIP DIGITAL
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)