How STEEL is MADE in Great Britain!
Summary
TLDRJoin the journey through a steel production plant, where 3.6 million tons of steel are made annually. Witness the transformation of raw materials into molten iron, then steel, in the blast furnaces. Explore the control room, learn about the 24/7 operation, and the massive undertaking of furnace relining. Discover the intricacies of steelmaking, from desulfurization to alloying, and the impressive continuous caster. Experience the heat, scale, and passion of workers who take pride in their craft, passed down through generations. Sponsored by ShipStation, this episode offers insights into efficient e-commerce shipping solutions.
Takeaways
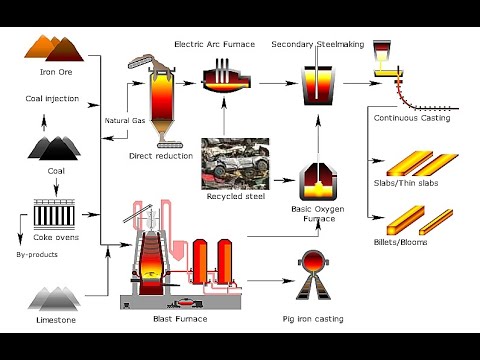
- 🏭 The facility produces around 3.6 million tons of steel annually, utilizing its proximity to the sea for shipping in raw materials like iron ore and coal.
- 🔨 Iron ore is turned into iron through a process in the blast furnace where carbon from coke reacts with the oxygen in the iron ore, removing it and creating molten iron.
- 🚂 Molten iron, carried in 350-ton Torpedoes, is transported for further refining into steel after being tapped from the blast furnace.
- 🕒 The operation at the blast furnaces is continuous, running 24 hours a day, with relining only occurring every several years for maintenance purposes.
- 👷♂️ Workers wear gas monitors for safety when near the furnaces due to the potential presence of harmful gases.
- 🌡️ The blast furnace is subjected to extreme heat, with the tuyeres (pipes) used to inject air and oxygen mixtures at 2,000 degrees Celsius.
- 🛠️ Copper is used for the tuyeres due to its high thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient cooling despite the intense heat.
- ♻️ The desulfurization process removes sulfur from the molten iron using a lance with powdered reagents and nitrogen gas.
- 🗑️ Slag, a byproduct of the iron-making process, is separated from the iron and removed, as it is less dense and floats on top of the molten iron.
- 🛑 The steel production process involves several stages of heating, rolling, and shaping the steel to the desired specifications before it is coiled for storage or further processing.
- 🛒 The video is sponsored by ShipStation, a web-based e-commerce shipping platform that streamlines shipping processes and offers preferential shipping rates.
Q & A
What is the annual steel production capacity of the plant mentioned in the script?
-The plant produces around 3.6 million tons of steel each year.
What are the main raw materials used in the steel production process described in the script?
-The main raw materials used are iron ore and coal, which are shipped to the plant due to its location by the sea.
How is the iron ore processed in the blast furnace?
-In the blast furnace, the carbon from the coke reacts with the oxygen in the iron ore, removing the oxygen and turning the ore into iron.
What is the purpose of the control room for the blast furnaces?
-The control room is where the operation of the blast furnaces is overseen and managed, with a specialist operator for each furnace and a process section overseeing the overall operation.
How often do the blast furnaces need to be re-lined, and what does this process involve?
-The blast furnaces require re-lining every several years; for example, one was re-lined in 2018 after 15 years of operation. This is a significant and expensive process involving removing the old lining and replacing it with a new one.
What is the role of the gas monitor worn by the visitors in the plant?
-The gas monitor is worn to ensure safety by monitoring the presence of potentially harmful gases in the vicinity of the industrial processes.
What is the function of the 'Tria' in the blast furnace?
-The 'Tria', made of copper, is located inside the blast furnace at its hottest point. It is where the hot air and oxygen mix is forced through to facilitate the chemical reactions necessary for steel production.
Why is copper used for the Trias despite having a lower melting point than steel?
-Copper is used because of its high conductivity, which allows the water cooling to remove heat from the copper more effectively than it would from steel or iron.
What happens to the molten iron after it is tapped from the blast furnace?
-After being tapped, the molten iron flows through channels into a hopper, from which it is then transferred into train cars or 'Torpedoes' that carry 350 tons of molten iron at a time for further refining into steel.
What is the process of desulfurization in the steel production, and how is it achieved?
-Desulfurization is the process of removing sulfur from the molten iron. It is achieved by pumping a mixture of powdered reagents and nitrogen gas into the ladle containing the molten iron, which reacts to remove the sulfur.
How is the molten steel transformed into a solid slab in the continuous caster?
-The molten steel is poured into a continuous caster, where it flows through water-cooled copper molds to solidify into a large slab. The slab is then slowly pulled out over rollers and cut into specific lengths for further processing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)