Lorenz Curve and Gini Coefficient - Measures of Income Inequality
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into measuring income inequality through the Lorenz Curve and the Gini Coefficient. It visually compares income distributions of Norway and South Africa, illustrating how the Lorenz Curve's proximity to the line of perfect equality indicates income equality, while the Gini Coefficient quantifies this disparity on a scale from 0 to 1. The script also suggests using these tools to assess the impact of government policies on income redistribution, providing a valuable insight for students writing essays on economic policies.
Takeaways
- 📊 Income inequality is a significant issue in free labor markets, and it's essential to measure it to determine if government intervention is necessary for income redistribution.
- 📈 Two primary tools are used to measure income inequality: the Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient. The Lorenz curve provides a visual representation, while the Gini coefficient offers a numerical measure.
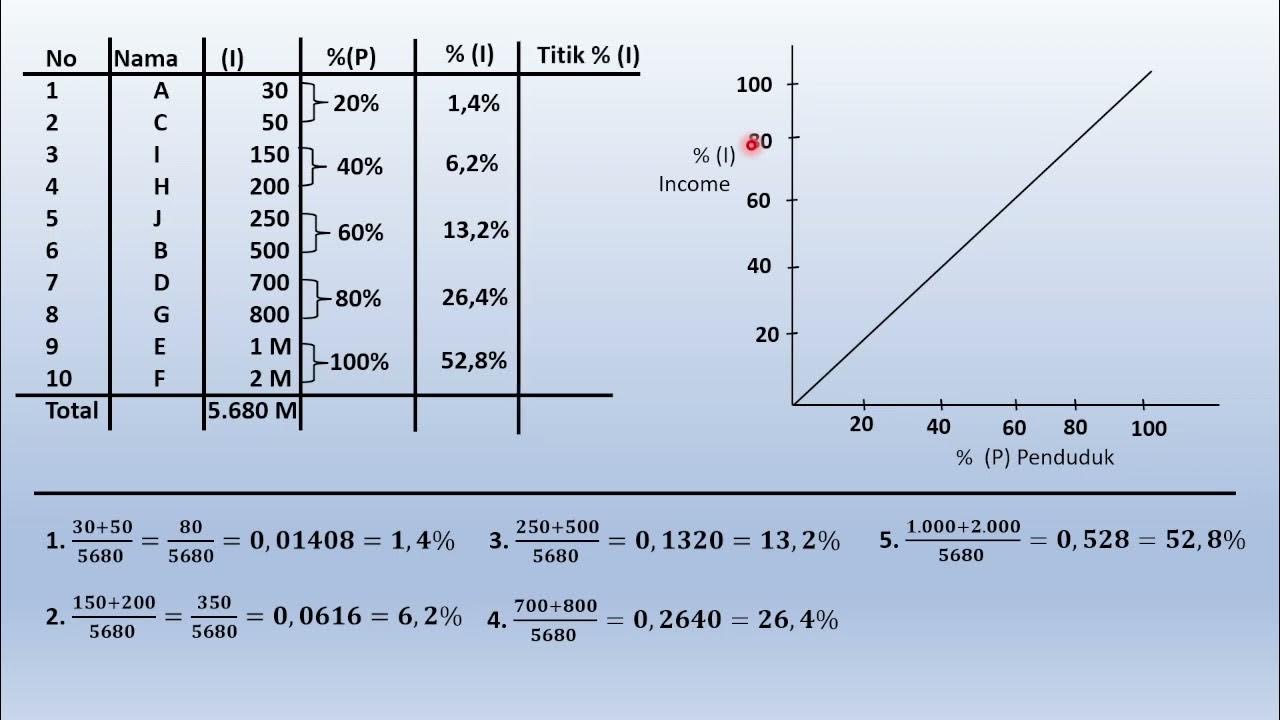
- 📚 The Lorenz curve is constructed by plotting the cumulative percentage of income against the cumulative percentage of the population, with the line of perfect equality representing an equal distribution of income.
- 🔍 Norway and South Africa are used as examples, with Norway having a more equal income distribution and South Africa being one of the most unequal countries in the world.
- 📉 The closer the Lorenz curve is to the line of perfect equality, the more equal the income distribution; the further away, the more unequal it is.
- 📝 The Gini coefficient is calculated by the ratio of the area between the Lorenz curve and the line of perfect equality to the total area under the line of perfect equality.
- 🔢 The Gini coefficient ranges from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality), with values closer to 0 indicating more equal income distribution and values closer to 1 indicating more unequal distribution.
- 🌐 The Gini coefficient can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of government policies aimed at reducing income inequality by showing how such policies might shift the Lorenz curve closer to the line of perfect equality.
- 📈 For essay writing, using Lorenz curves and Gini coefficients can illustrate the impact of policies on income distribution and make a strong case for government intervention.
- 📊 Norway has a Gini coefficient around 0.25, indicating a relatively equal income distribution, while South Africa's Gini coefficient is around 0.65, indicating a highly unequal distribution.
- 👍 Understanding and effectively using these tools in essays can help to 'smash' the topic and make a compelling argument for or against government policies on income redistribution.
Q & A
What is income inequality and why is it important to measure it?
-Income inequality refers to the uneven distribution of income among a population. It is important to measure income inequality to determine whether government intervention is necessary to redistribute income and reduce disparities.
What are the two methods economists use to measure income inequality?
-Economists use the Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient to measure income inequality. The Lorenz curve provides a visual representation, while the Gini coefficient offers a mathematical calculation.
How is the Lorenz curve constructed and what does it represent?
-The Lorenz curve is constructed by plotting the cumulative percentage of income against the cumulative percentage of the population. It represents the actual distribution of income in a country compared to a line of perfect equality, where each percentage of the population earns an equal percentage of the income.
What is the significance of the line of perfect equality in the context of the Lorenz curve?
-The line of perfect equality serves as a benchmark in the Lorenz curve diagram. It represents a scenario where income is distributed equally among the population, with each percentage of the population earning an equal percentage of the total income.
How does the distance of the Lorenz curve from the line of perfect equality relate to income inequality?
-The closer the Lorenz curve is to the line of perfect equality, the more equal the distribution of income is. Conversely, the further away the curve is from this line, the more unequal the distribution of income, indicating a higher level of income inequality.
What is the Gini coefficient and how is it calculated?
-The Gini coefficient is a measure of income inequality that ranges from 0 to 1. It is calculated by dividing the area between the Lorenz curve and the line of perfect equality (section A) by the total area under the line of perfect equality (section A plus section B).
What does a Gini coefficient of 0 indicate?
-A Gini coefficient of 0 indicates perfect equality, where the Lorenz curve coincides with the line of perfect equality, meaning there is no income disparity in the society.
What does a Gini coefficient of 1 indicate?
-A Gini coefficient of 1 indicates perfect inequality, where all income is earned by the last person in society, meaning there is maximum income disparity.
How can the Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient be used to evaluate government policies on income redistribution?
-The Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient can be used to visually and mathematically demonstrate the effectiveness of government policies aimed at income redistribution. Changes in the curve and the coefficient number can show how policies impact income equality.
What are some examples of countries with very different levels of income inequality as mentioned in the script?
-Norway is mentioned as having a very equal distribution of income with a Lorenz curve closer to the line of perfect equality, while South Africa is cited as having one of the most unequal income distributions in the world, with a Lorenz curve far from the line of perfect equality.
How can the understanding of Lorenz curves and Gini coefficients be beneficial in writing essays about income redistribution policies?
-Understanding Lorenz curves and Gini coefficients allows one to visually and mathematically demonstrate the impact of income redistribution policies. It helps in illustrating how such policies can shift the Lorenz curve closer to the line of perfect equality and reduce the Gini coefficient, indicating a more equal distribution of income.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GINI RATIO

Indikator Ketimpangan Distribusi Pendapatan

The Gini Coefficient Explained in One Minute

PENDAPATAN PER KAPITA DAN DISTRIBUSI PENDAPATAN NASIONAL | MATERI EKONOMI KELAS XI KURIKULUM MERDEKA
Kurva Lorenz #2

How The Dutch Economy Shows We Can't Reduce Wealth Inequality With Taxes | Economics Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)